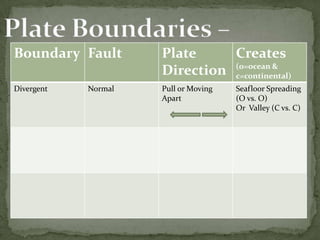
The theory of plate tectonics states that the Earth's crust is divided into plates that move over the mantle. There are three types of boundaries where plates meet: divergent boundaries where plates pull apart and new crust is formed; convergent boundaries where plates push together resulting in subduction zones, volcanoes, or mountain building; and transform boundaries where plates slide past one another causing earthquakes. Convection currents in the mantle are believed to drive the motion of tectonic plates.