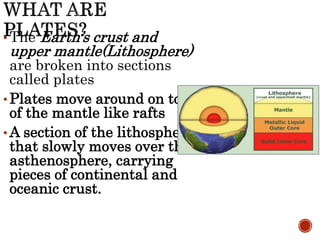
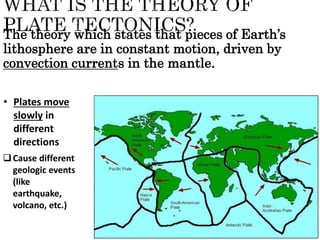
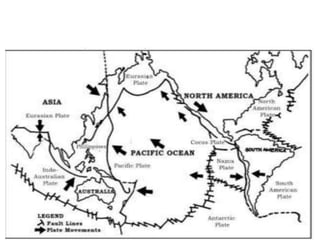
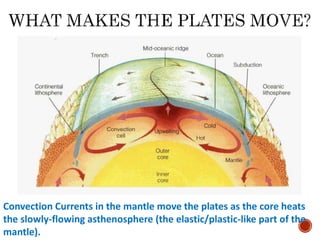
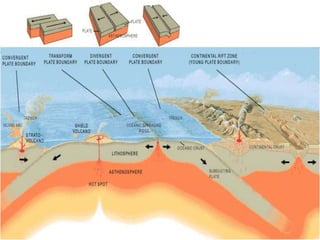
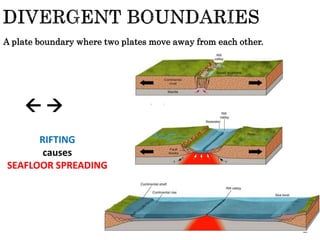
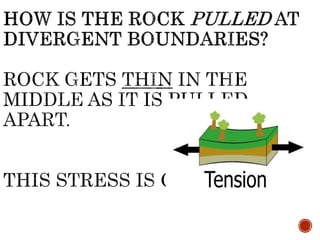
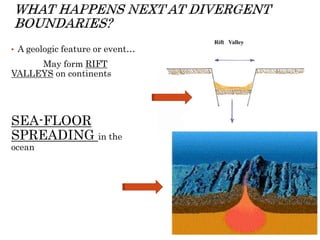
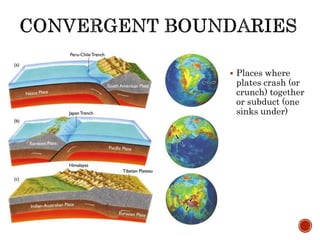
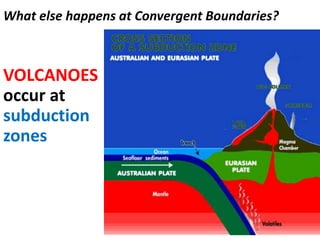
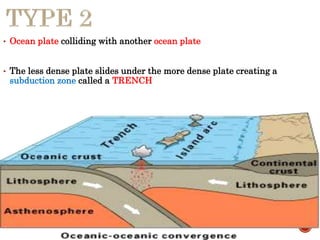
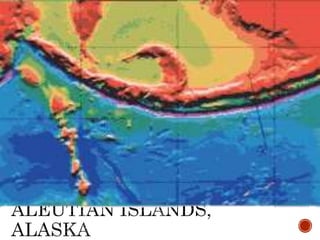
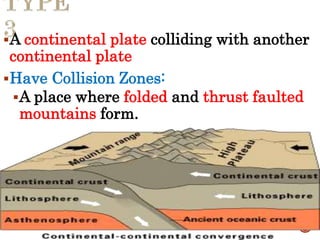
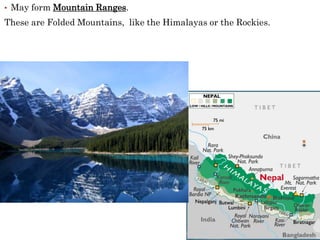
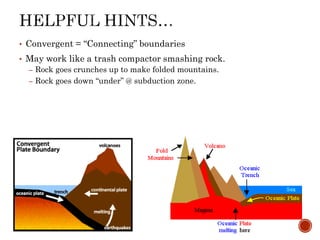
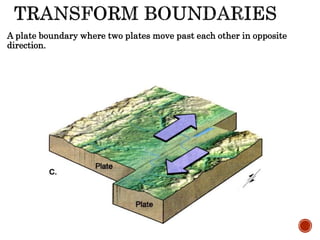
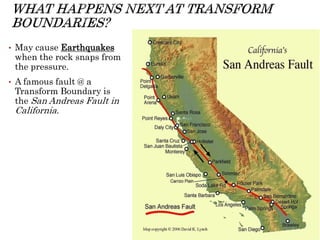
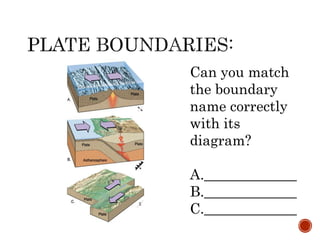
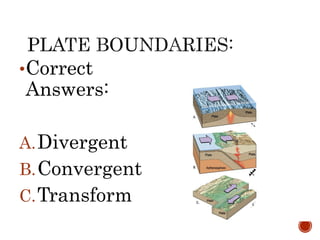
The theory of plate tectonics states that Earth's lithosphere is broken into plates that slowly move atop the asthenosphere. There are three types of plate boundaries: divergent boundaries where plates move apart, convergent boundaries where plates collide, and transform boundaries where plates slide past one another. Plate tectonics explains volcanoes, earthquakes, mountain building, and other geologic phenomena observed on Earth's surface and interior.