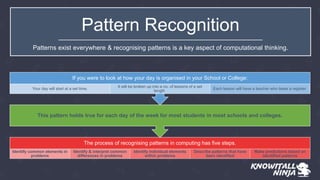
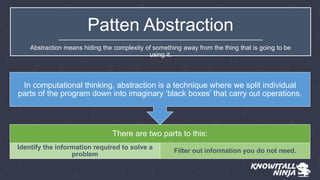
This document discusses pattern recognition, generalization, and abstraction in computational thinking. It explains that pattern recognition involves identifying common and differing elements in problems to describe patterns and make predictions. Abstraction involves identifying necessary information and filtering out unnecessary details when representing a problem. Generalization occurs when common themes are identified between patterns. The document provides examples of patterns in a student's school day and how variables, constants, processes, inputs and outputs can represent parts of a problem.