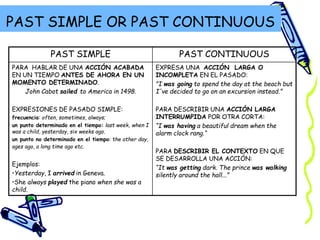
This document provides information about forming and using the past simple and past continuous tenses in English. It explains that the past simple is used to talk about completed actions in the past, while the past continuous expresses ongoing or incomplete actions in the past. It provides examples of regular verb conjugations in the past simple, and how to form the past continuous using "was/were" plus the verb's gerund form. It also discusses using the past tenses in affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences, and how the past simple and past continuous can be combined using conjunctions like "when", "while", and "as".