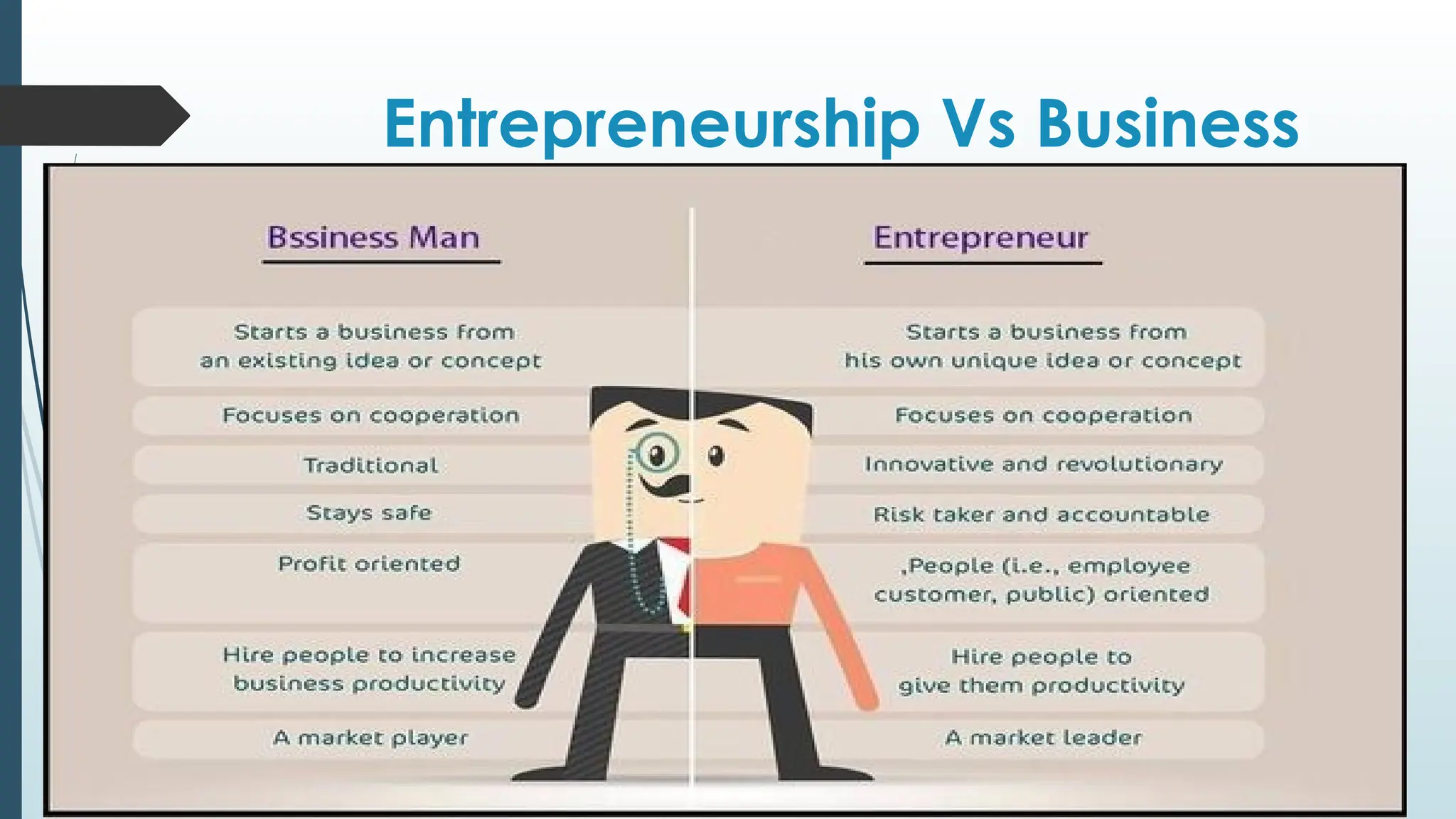
The document provides an overview of entrepreneurship, defining it as the process of creating and managing a new business, and describes the characteristics and motivations of entrepreneurs. It outlines the importance of entrepreneurship in economic development, the various types of entrepreneurship including small business, scalable startups, and social entrepreneurship, and discusses common fears faced by aspiring entrepreneurs. Additionally, it includes a self-assessment quiz for personal entrepreneurial characteristics and emphasizes the significance of qualities like creativity, risk-taking, and planning.