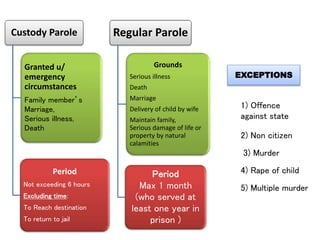
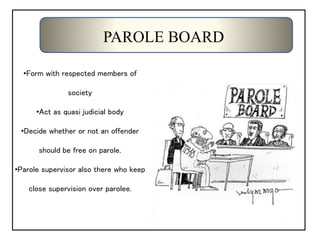
The document discusses parole as a method of prisoner reformation and rehabilitation, allowing temporary release after serving part of a sentence under specific conditions such as good behavior. It outlines the objectives and regulations of parole, including potential grounds for emergency release and the role of the parole board. Additionally, it highlights critical issues facing the parole system and emphasizes the need for improved procedures and oversight to enhance its effectiveness.