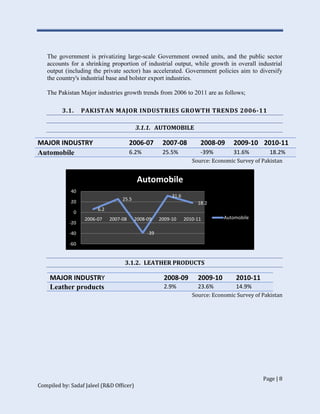
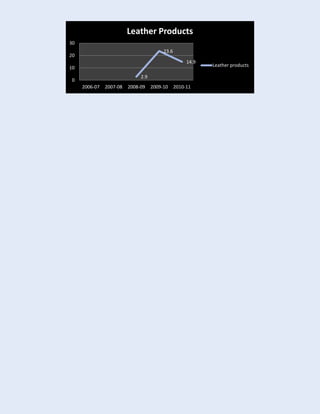
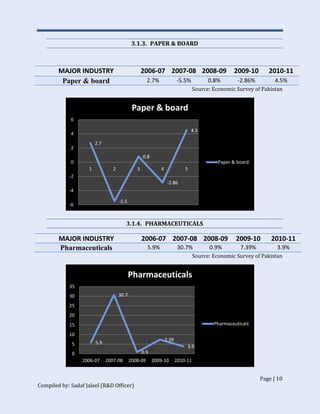
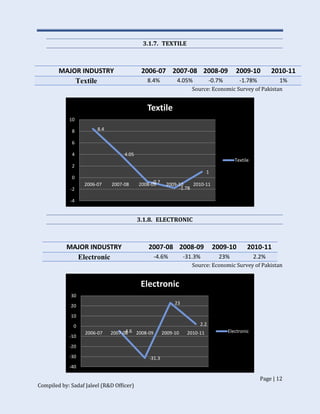
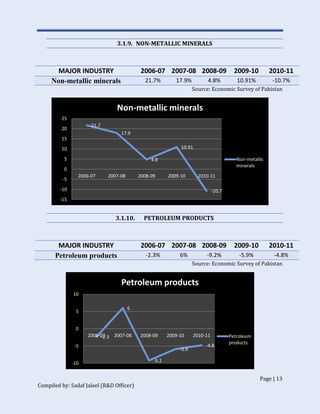
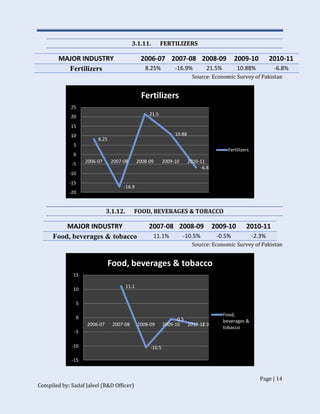
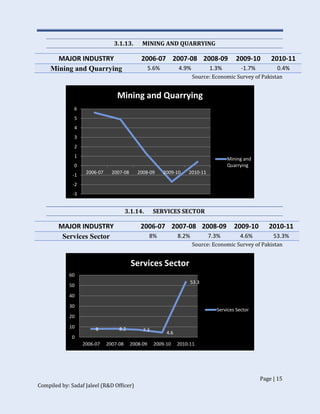
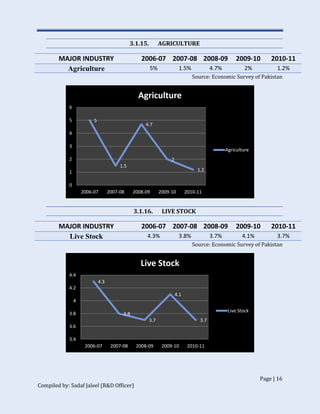
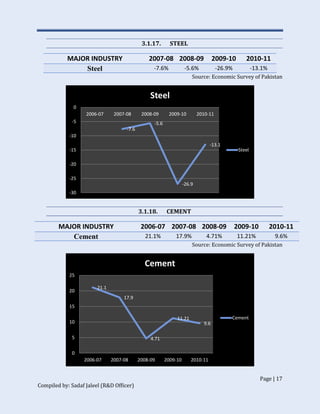
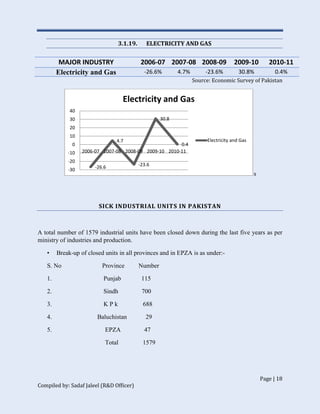
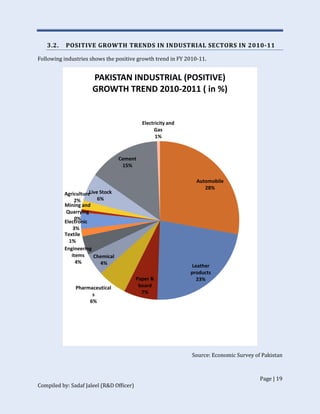
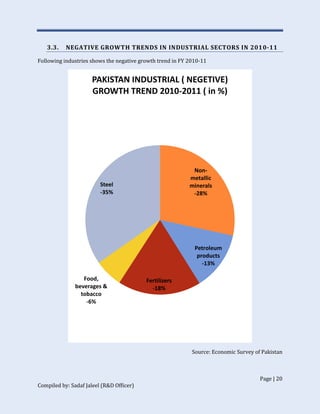
The document discusses Pakistan's industrial sector growth and performance over time. It notes that at independence in 1947, Pakistan had a negligible industrial base and only 34 industries. The industrial sector has since grown and now accounts for 25% of GDP, though its growth has been uneven and it has yet to fulfill its full potential. The document analyzes sectoral contributions to GDP growth between 2006-2011 and lists the major industries in Pakistan, discussing their growth trends over that period. Impediments to industrial development are also examined.