This document discusses pain sensation and the pathways involved in pain transmission. It covers:
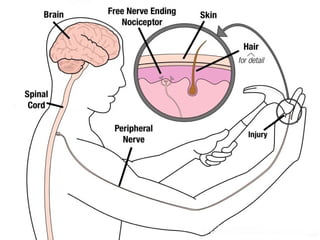
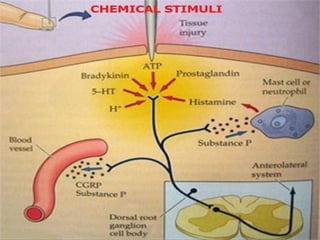
1. Types of pain receptors and the mechanisms by which they are stimulated.
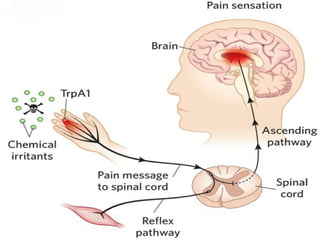
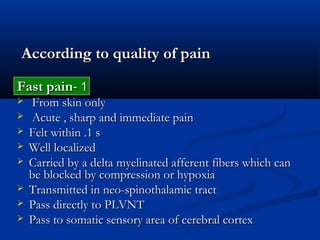
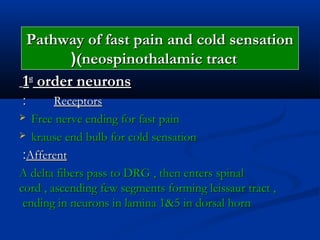
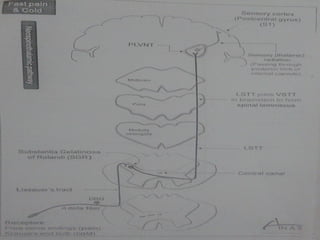
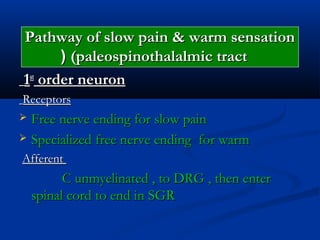
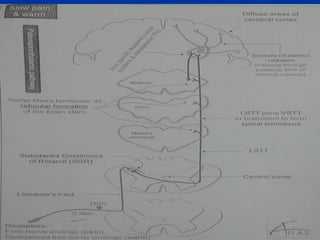
2. The pathways for fast pain/cold sensation (neospinothalamic tract) and slow pain/warm sensation (paleospinothalamic tract), including the neurons involved at each stage from receptor to cortex.
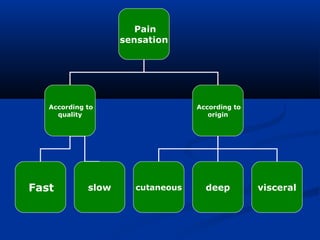
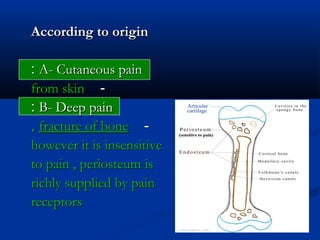
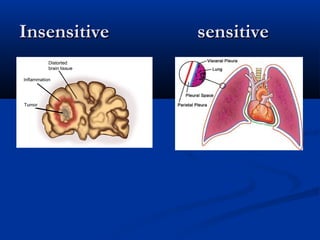
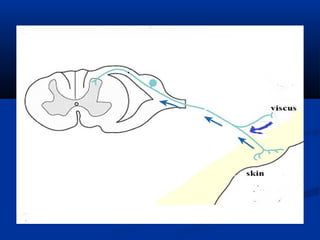
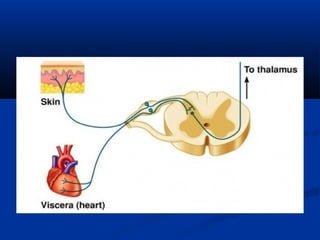
3. Characteristics of cutaneous, deep, and visceral pain according to origin and quality. Reactions to different types of pain and the phenomenon of referred pain are also described.
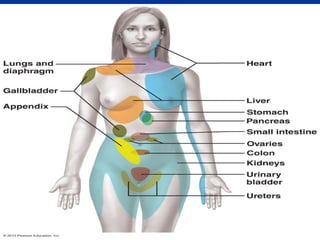
4. Examples of referred pain from various organs are provided.