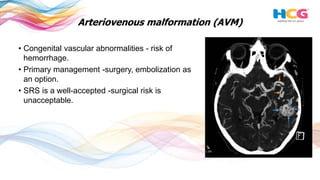
This document discusses the use of radiosurgery to treat pediatric brain tumors. It notes that brain tumors make up 20% of childhood cancers and radiation therapy is an important treatment. Radiosurgery aims to deliver high radiation doses to discrete tumor targets while minimizing dose to surrounding healthy tissue. The document reviews the use of radiosurgery to treat several types of benign and malignant pediatric brain tumors, including arteriovenous malformations, vestibular schwannomas, craniopharyngiomas, ependymomas, medulloblastomas, and gliomas. It finds radiosurgery can achieve high tumor control rates with low risks of complications for recurrent or residual pediatric brain tumors.