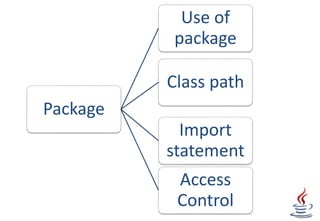
Packages in Java allow grouping of related classes and interfaces to avoid naming collisions. Packages place classes in a directory structure that matches their package declaration. The import statement allows accessing classes from other packages without specifying their full package name. The classpath environment variable specifies where Java looks for packages and classes. Access specifiers like private, public, and protected control whether other classes can access members of a class.