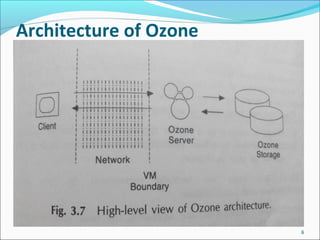
The document discusses Ozone, an object-oriented database management system (OODMS) developed entirely in Java, focusing on its features, architecture, and differences from Java Data Objects (JDO). Ozone allows developers to manage Java objects in a transactional environment, providing capabilities such as object serialization, multi-user access, and garbage collection, all without relying on a traditional back-end database. The architecture of Ozone includes client-side, network layer, server management, and a core system that oversees transactions and storage.