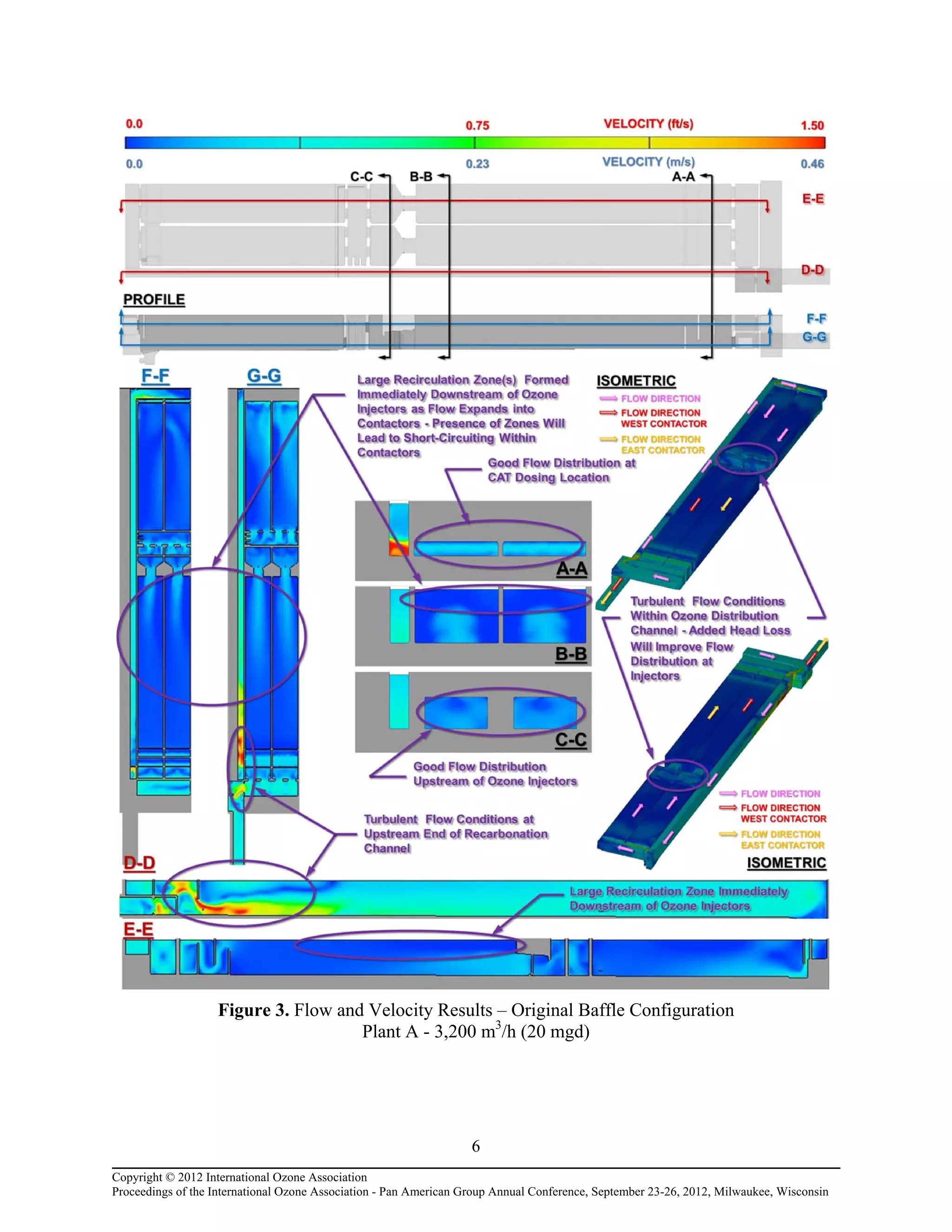
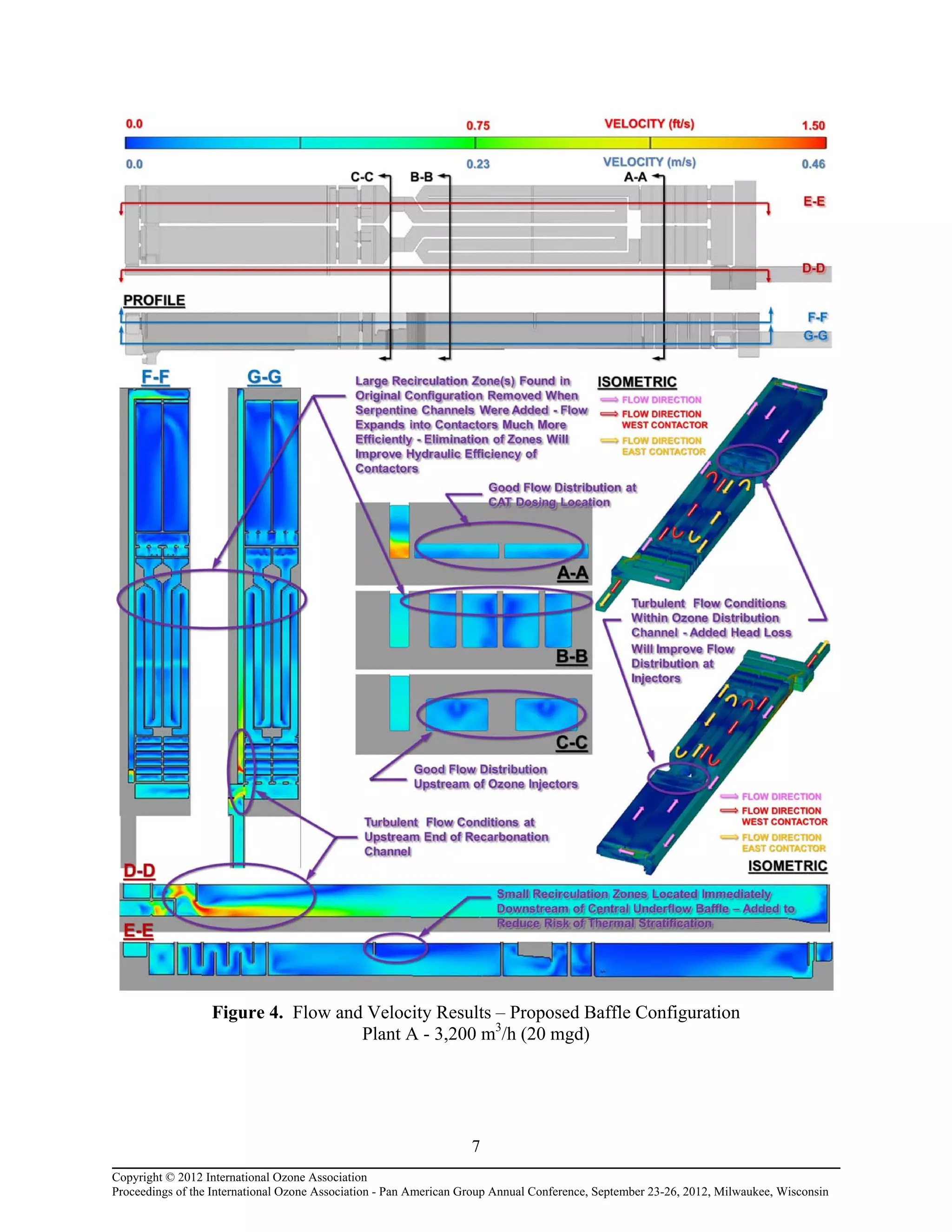
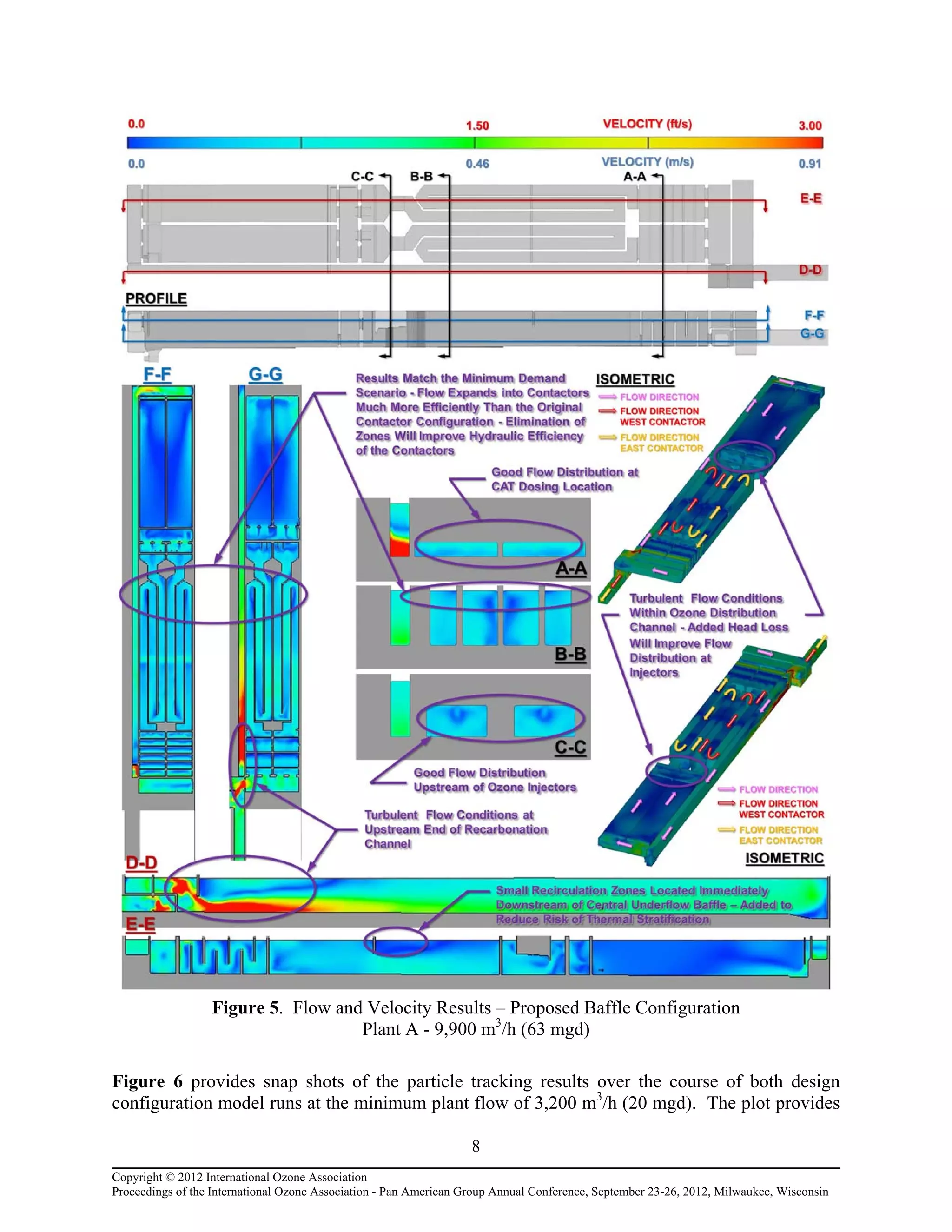
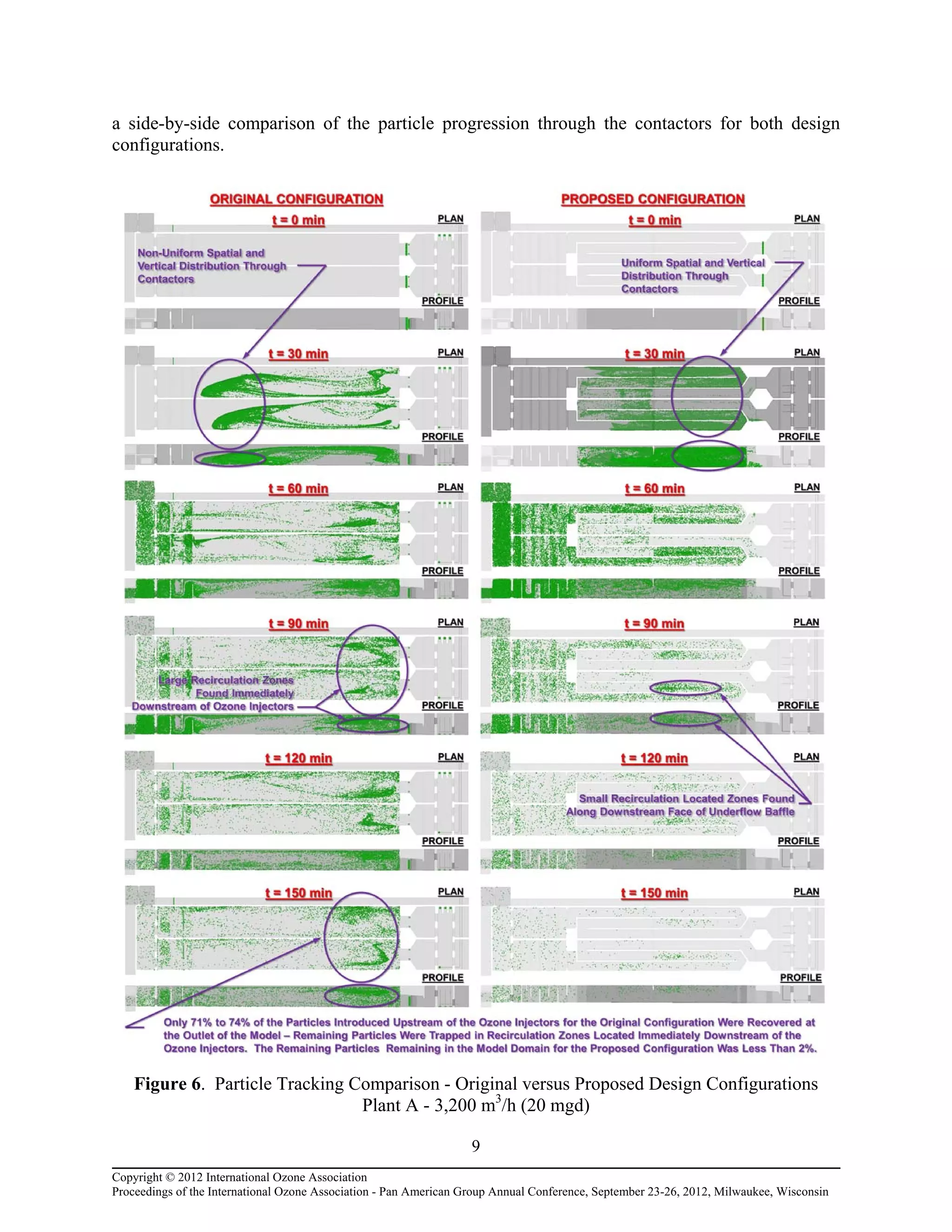
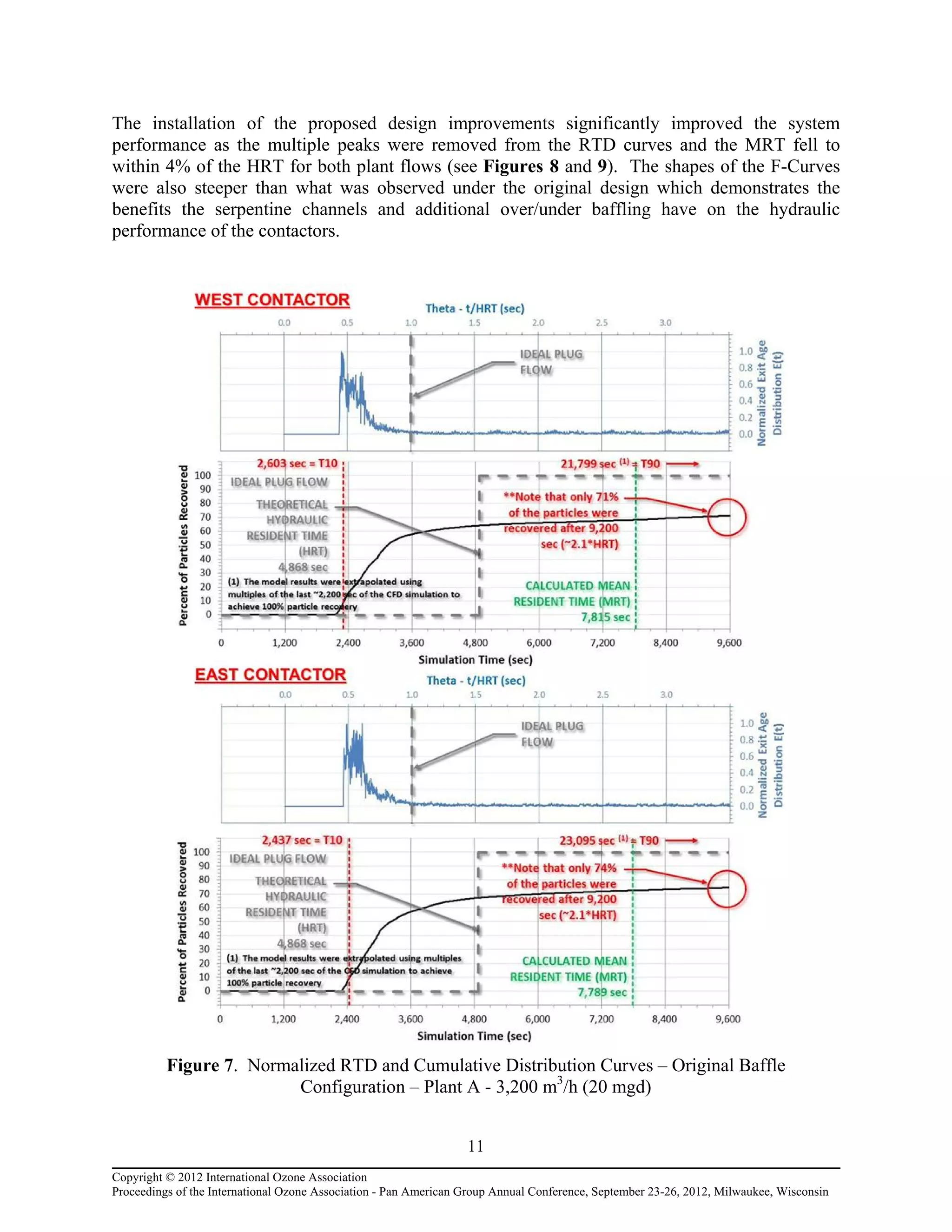
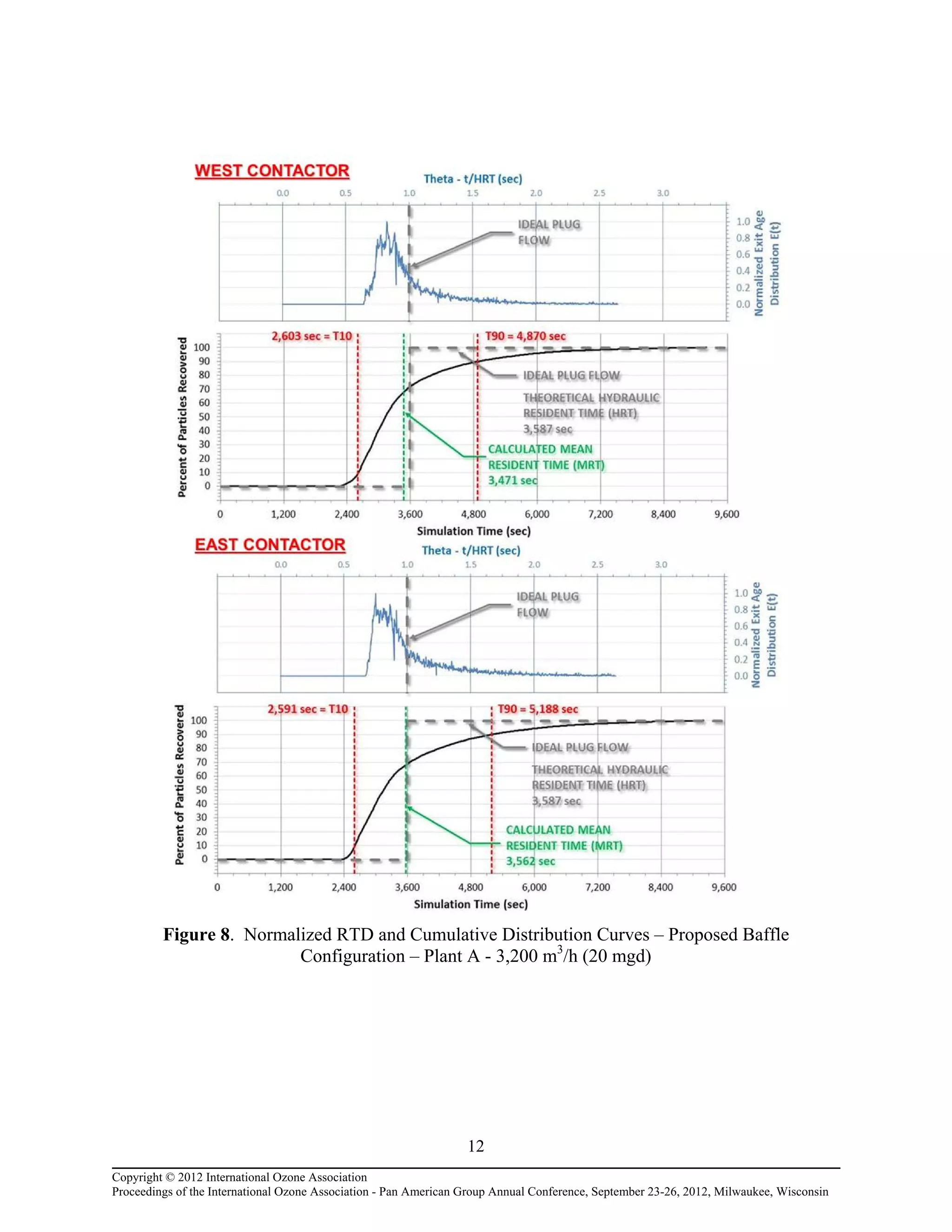
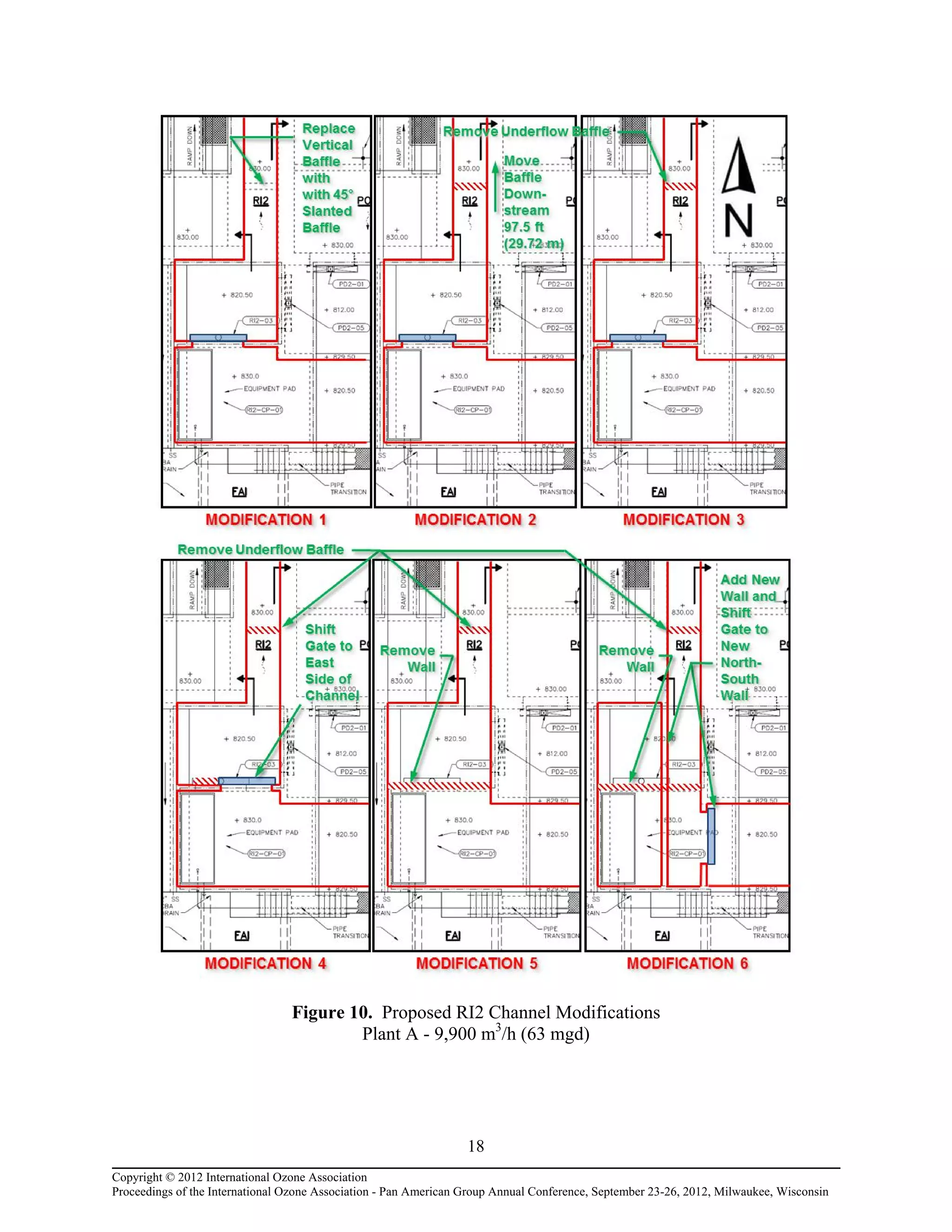
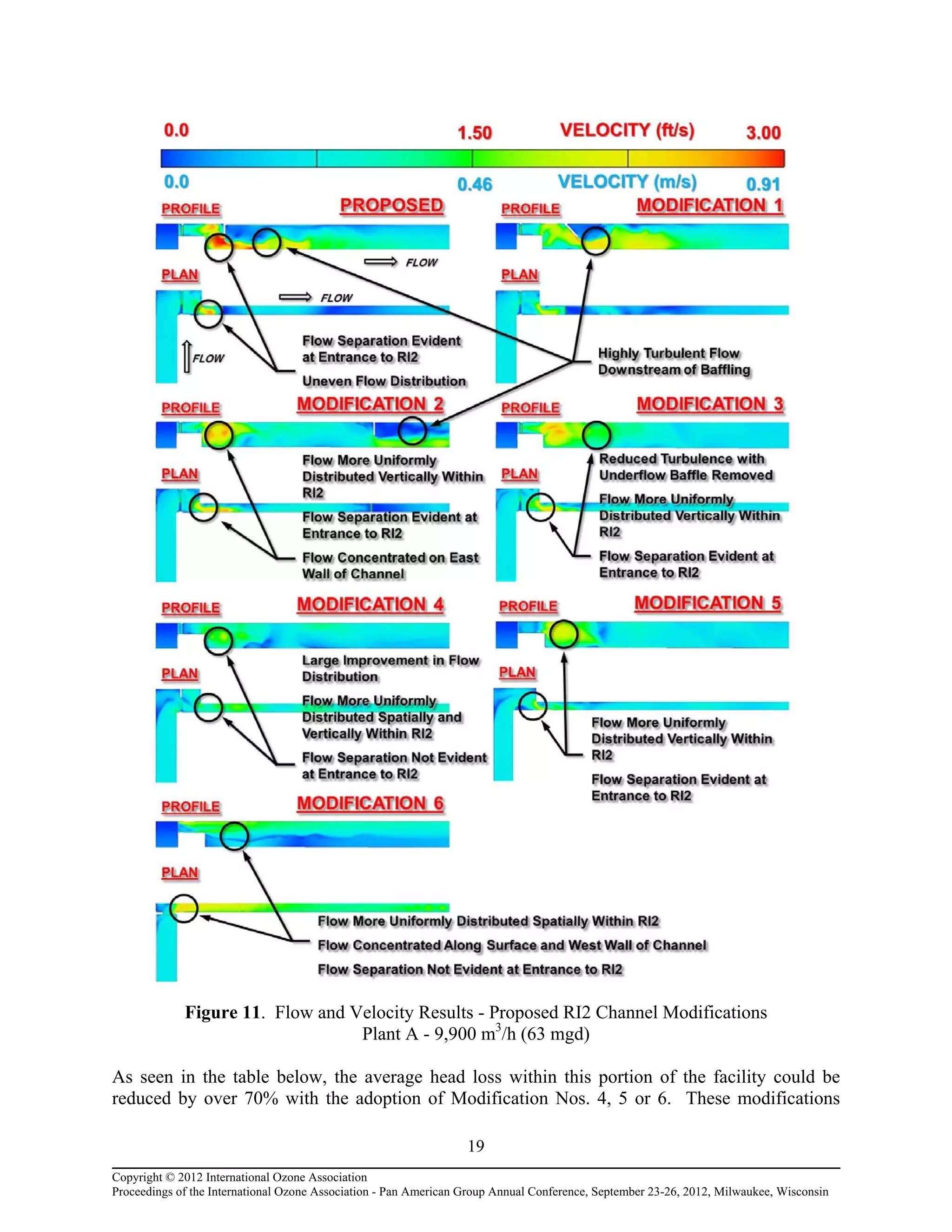
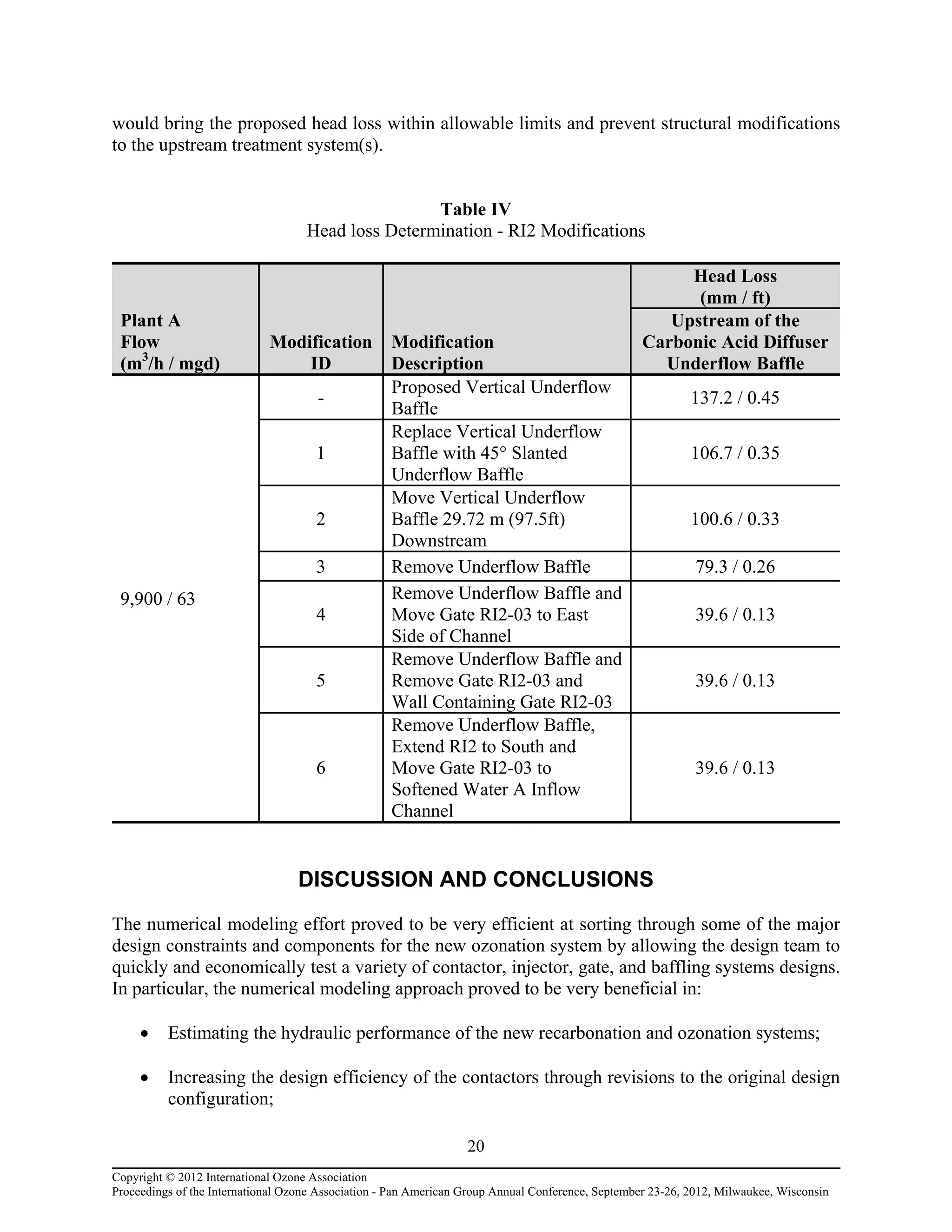
Computational fluid dynamic (CFD) modeling was used to optimize the design of four new ozone contactors being added to an existing water treatment plant. The CFD analysis identified design improvements that increased contactor performance while meeting constraints. Specifically, it minimized dead zones and improved flow transitions, resulting in more uniform flow distribution and reduced head loss. The modified design achieved excellent flow characteristics and contact times within design criteria. The optimized contactor design is expected to provide more effective ozone use and minimize residual levels.

![2
Copyright © 2012 International Ozone Association
Proceedings of the International Ozone Association - Pan American Group Annual Conference, September 23-26, 2012, Milwaukee, Wisconsin
Introduction
The existing Hap Cremean Water Plant (HCWP) is located east of I-270 off Morse Road in
Columbus, Ohio. It is currently the largest water treatment facility in the City of Columbus
(City), serving a population of more than 500,000 people. The treatment facility consists of two
parallel treatment trains, Plant A and Plant B, beginning at a raw water influent screening station
and continuing through all treatment processes including mechanical screening, low‐service
pumping, alum coagulation/ flocculation/sedimentation, lime softening, recarbonation, dual-
media rapid sand filtration, and chlorine disinfection. Flows for Plants A and B each have an
approved rated capacity of 236.6 cubic meters per hour (m3
/h) (62.5 million gallons per day
[mgd]) and are typically segregated although flow streams can be periodically joined and then re‐
divided during routine maintenance activities.
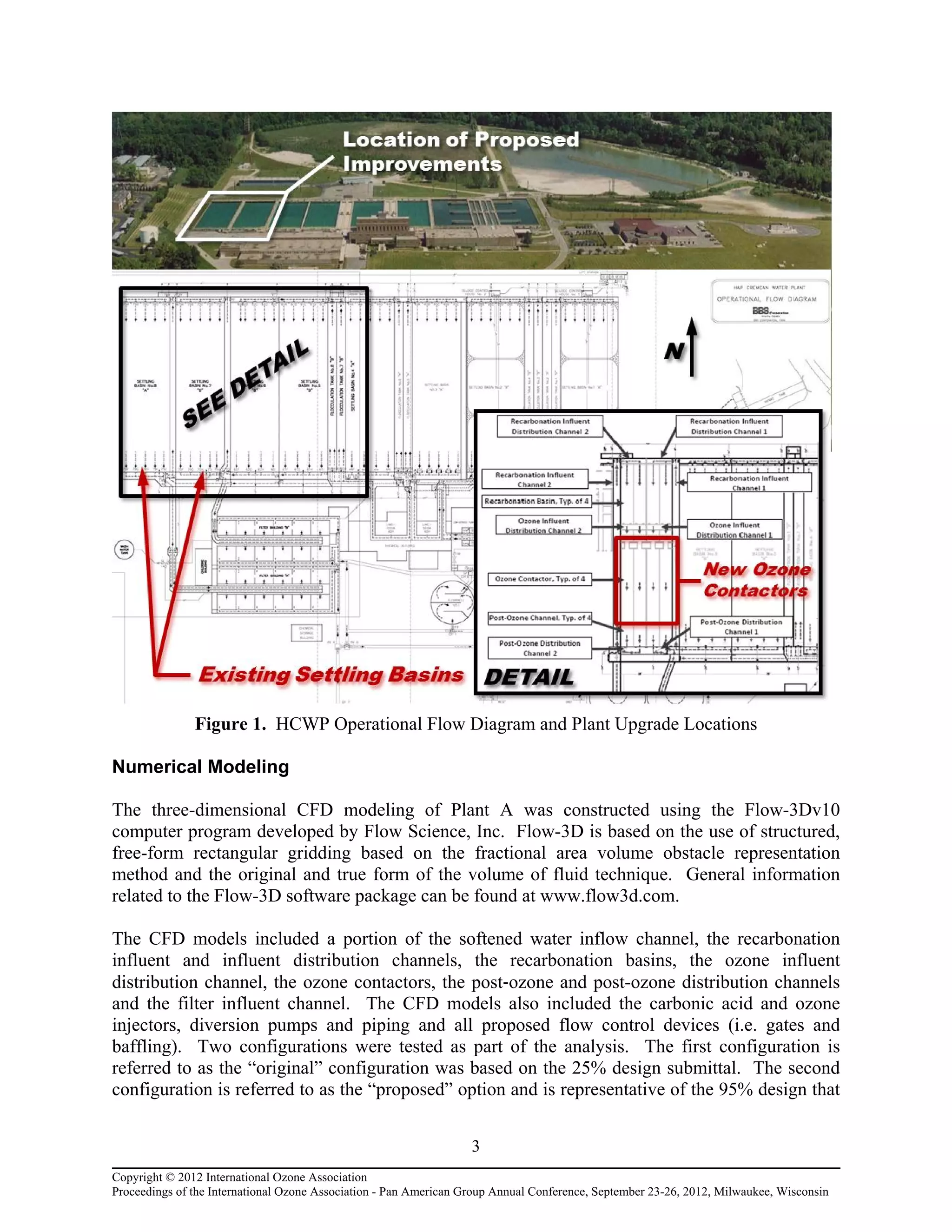
In April 2010 the City authorized a capital improvement project that included an upgrade of the
existing recarbonation system, addition of intermediate ozonation following recarbonation, and
conversion/rehabilitation of the existing sand filters for operation as biologically active filters.
Figure 1 shows the operational flow diagram of the plant with the location of the proposed
upgrades. The new treatment plant improvements were designed to ensure compliance with
upcoming water quality regulations, specifically addressing the Stage 2 Disinfection By-Products
Rule. The new ozonation system is the focus of this paper.
Due to the location and nature of the modifications within the existing system (i.e. converting
existing settling basins to ozone contactors), the main focus of the HCWP design became its
ability to maximize the efficiency of the ozonation process and limiting head loss trough the
plant.
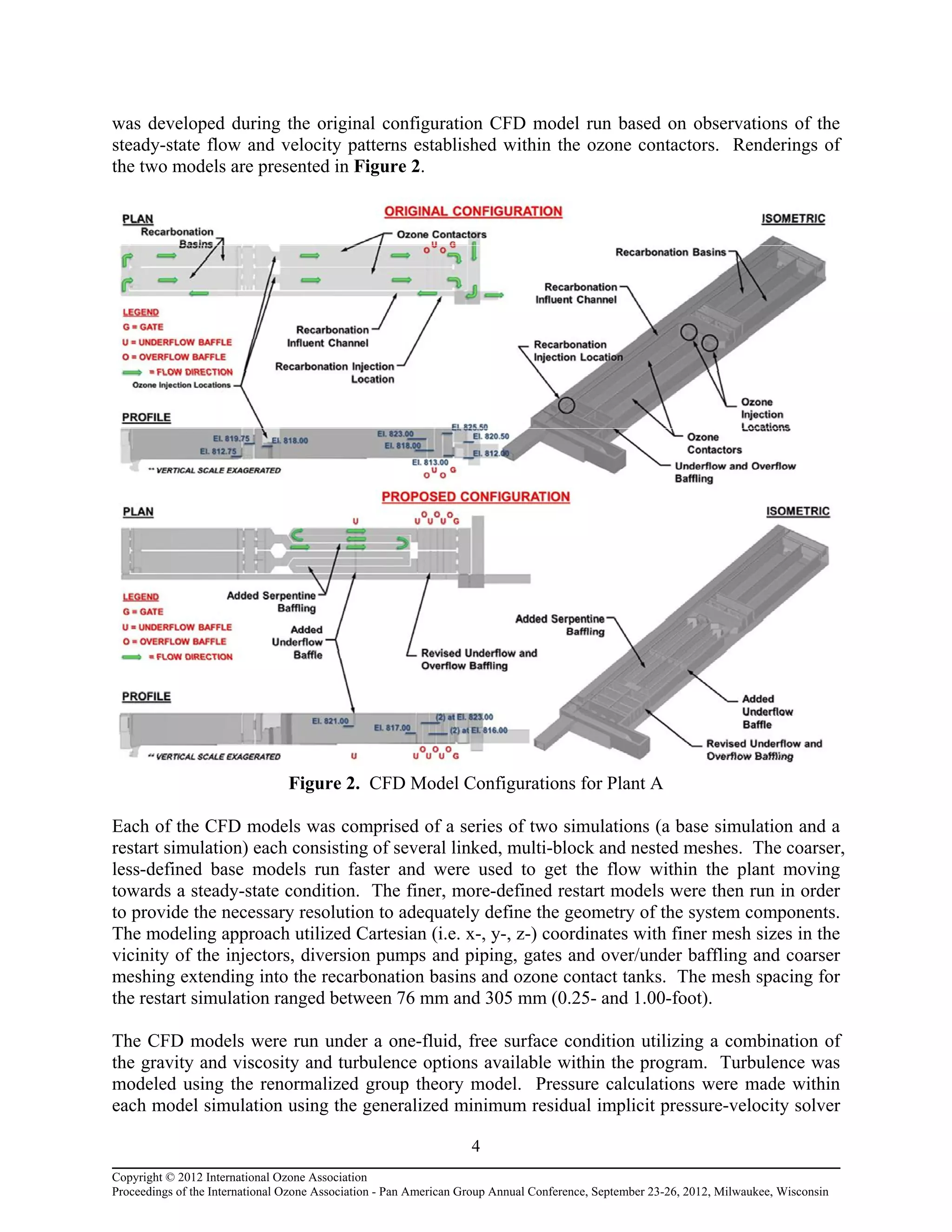
To confirm that the new ozonation system would meet performance requirements, the design
team determined that Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) modeling was required in order to
develop the final locations and configurations of the new contactors, injectors, gates, and baffling
system(s). This conclusion was based on the site constraints at the plant and considered the
potential for the City to pursue post-construction treatment credits.
The CFD analysis was performed on the new ozonation system for Plant A. This plant was
chosen due to the symmetrical layout of the two plants and the lower degree of available
freeboard versus Plant B. The key issues to be resolved through the numerical modeling
approach included: 1) Developing necessary modifications to the contactor geometry and gate
and baffling system(s) to minimize short-circuiting and areas of recirculation/stagnation; 2)
Creating uniform flow distribution within the ozone influent and post-ozonation channels to
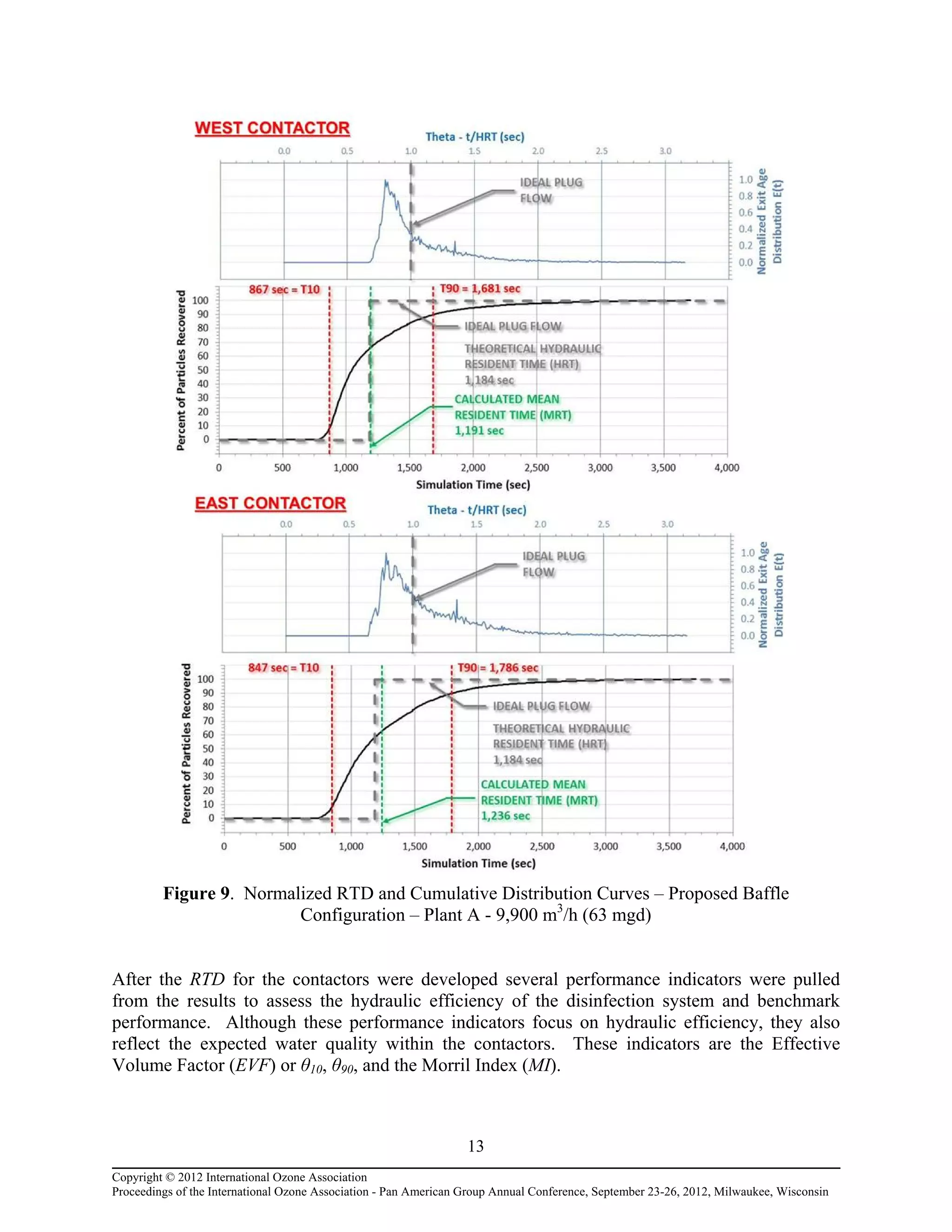
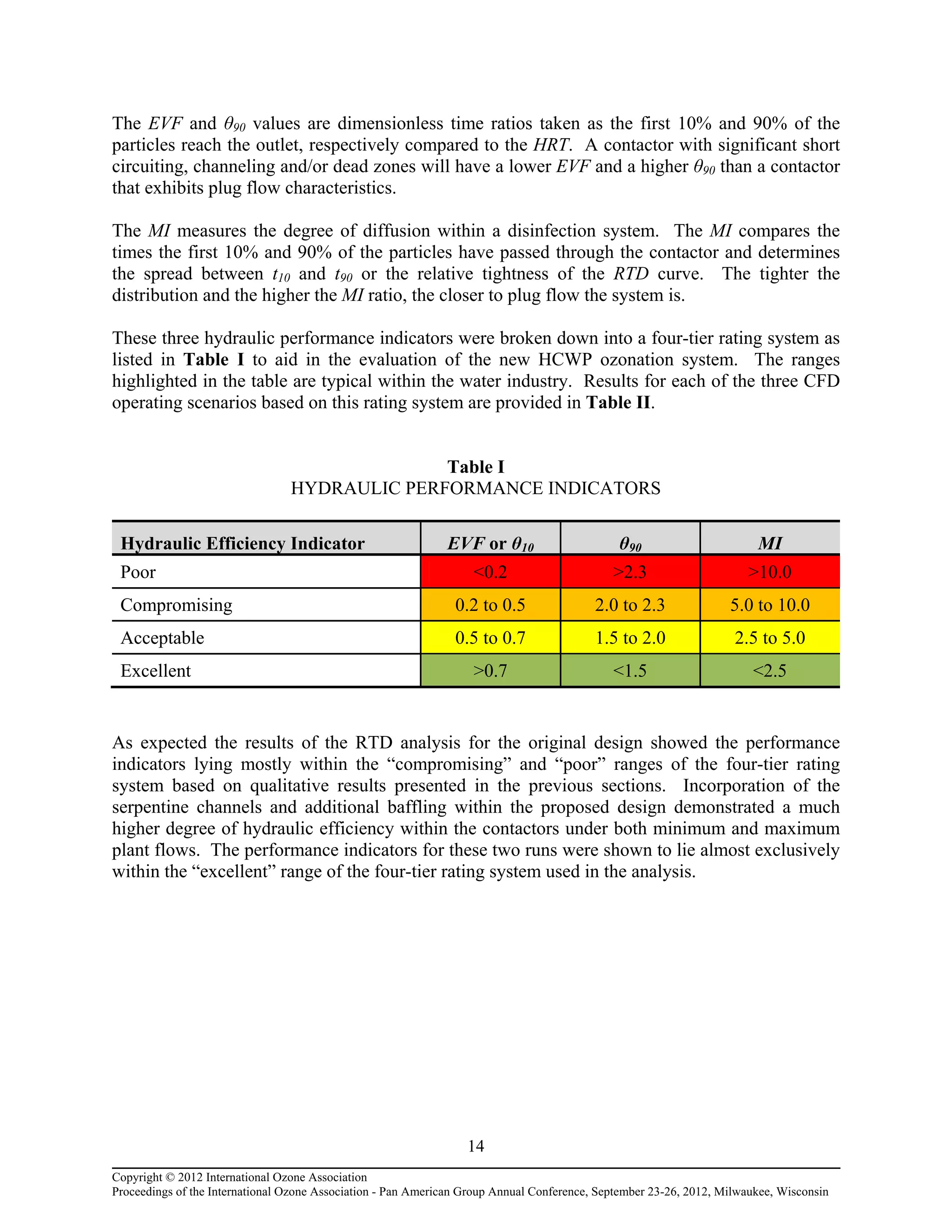
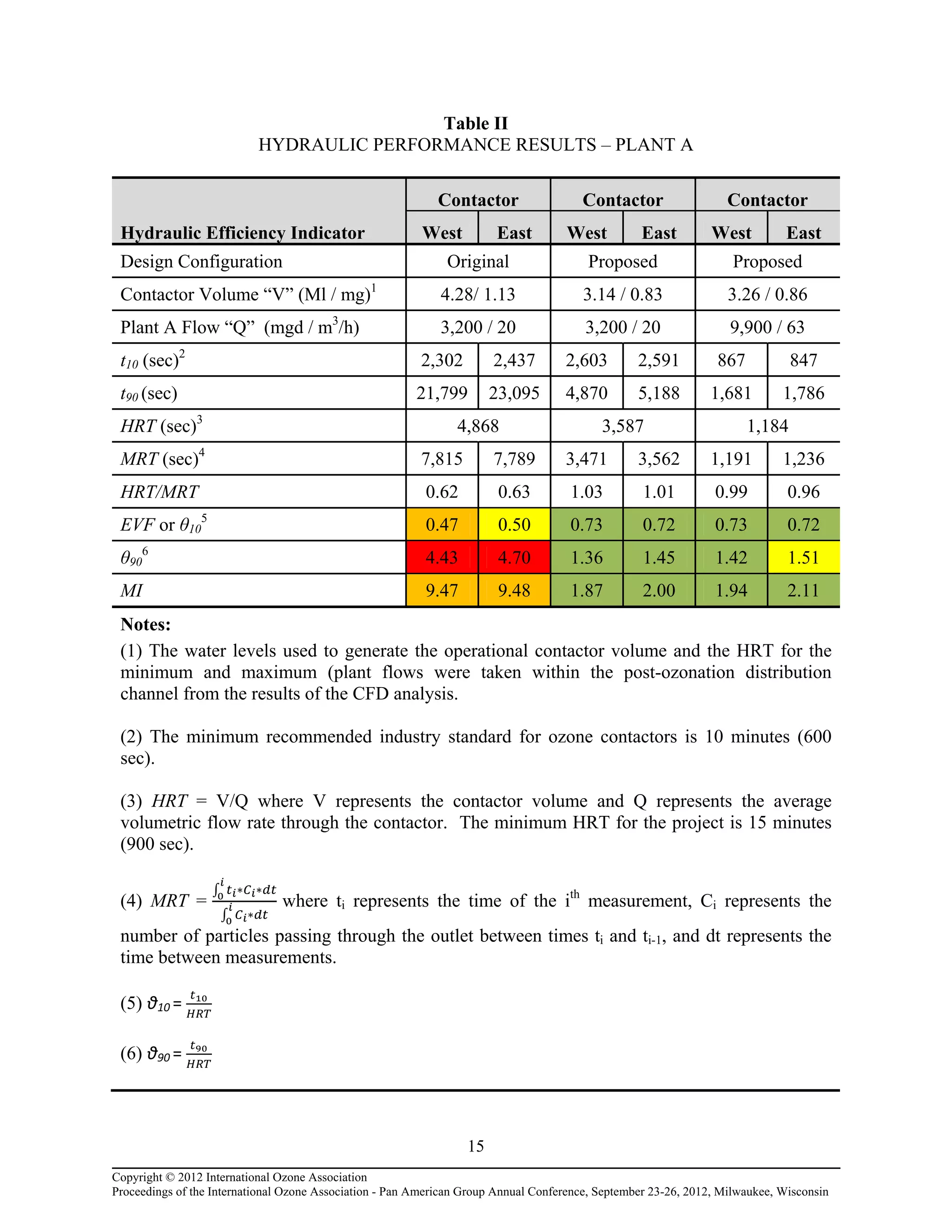
maximize dosing efficiency; 3) Determining the resident time distribution (RTD), mean resident
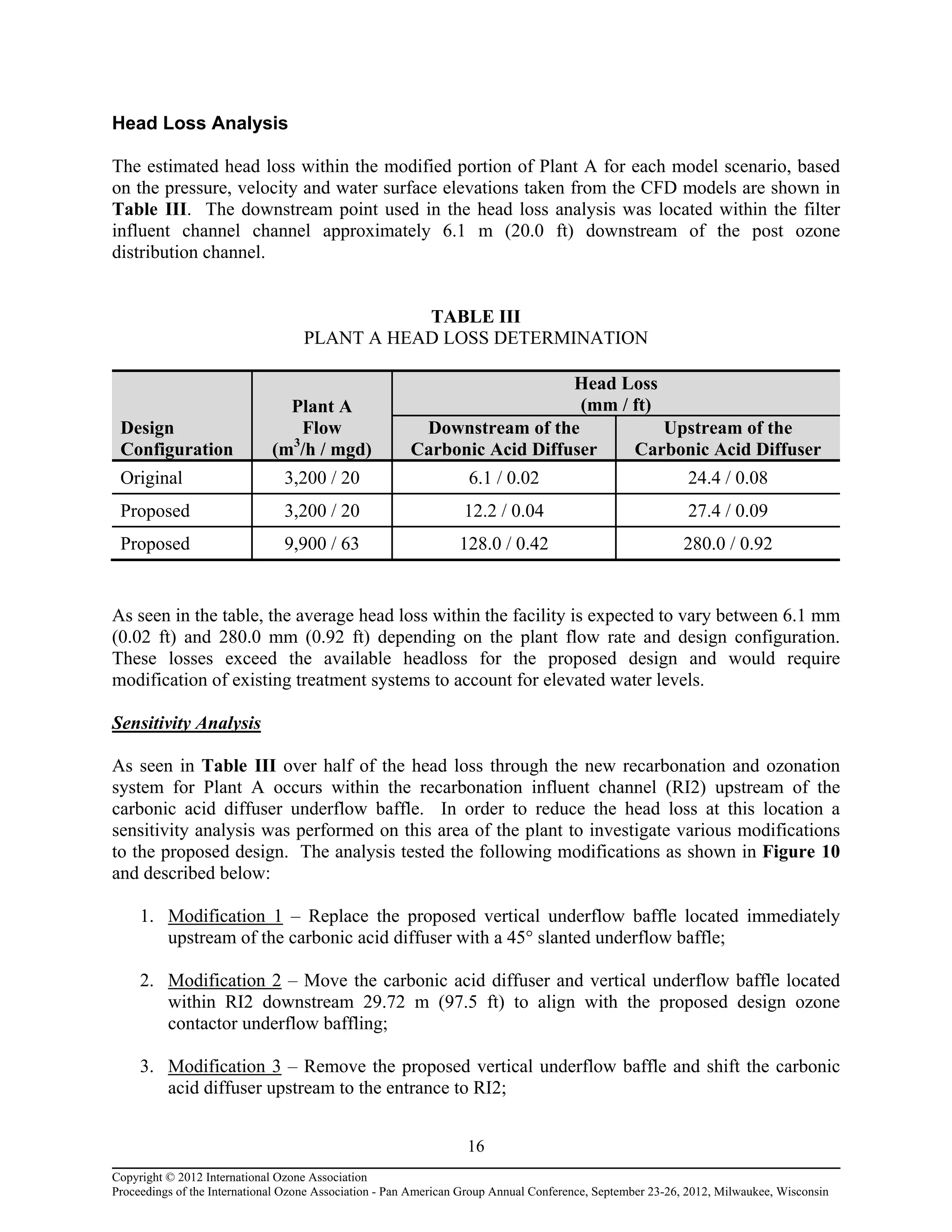
time (MRT) and the hydraulic efficiency of the new ozone contactors; and 4) Minimizing head
loss through the recarbonation and ozonation systems to limit structural modifications to the
upstream portion of the plants.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/755241d1-464d-4a1b-a9ae-298016ab20b9-150413080802-conversion-gate01/75/Ozone-Contactor-Design-Improvements-using-CFD-Modeling-2-2048.jpg)