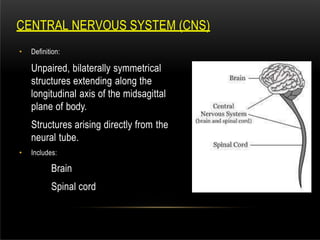
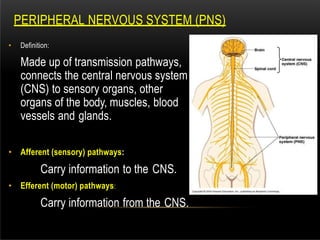
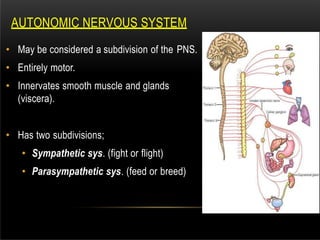
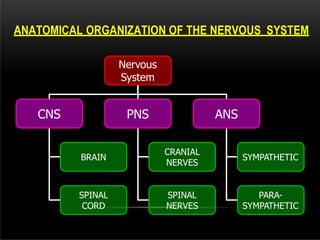
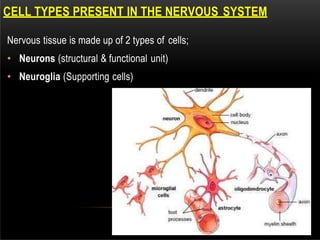
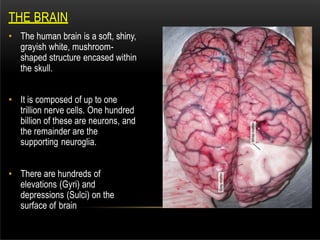
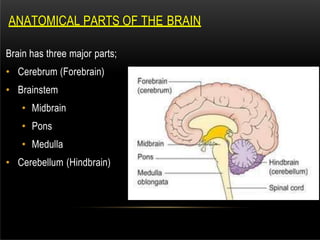
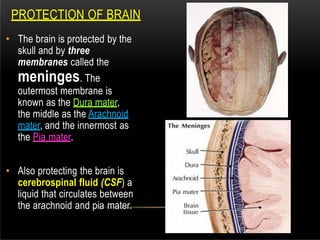
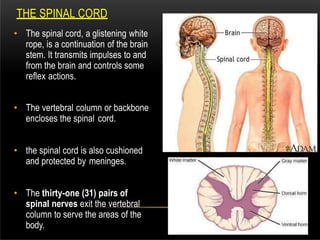
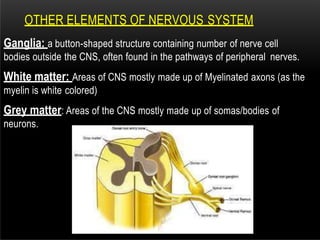
The nervous system is composed of the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS contains neurons and neuroglia, as well as three main parts of the brain - the cerebrum, brainstem, and cerebellum. The brain and spinal cord are protected by membranes and cerebrospinal fluid. The PNS connects the CNS to organs and muscles through the autonomic nervous system and somatic nerves. Key cell types in the nervous system include neurons, which transmit signals, and neuroglia, which provide support.