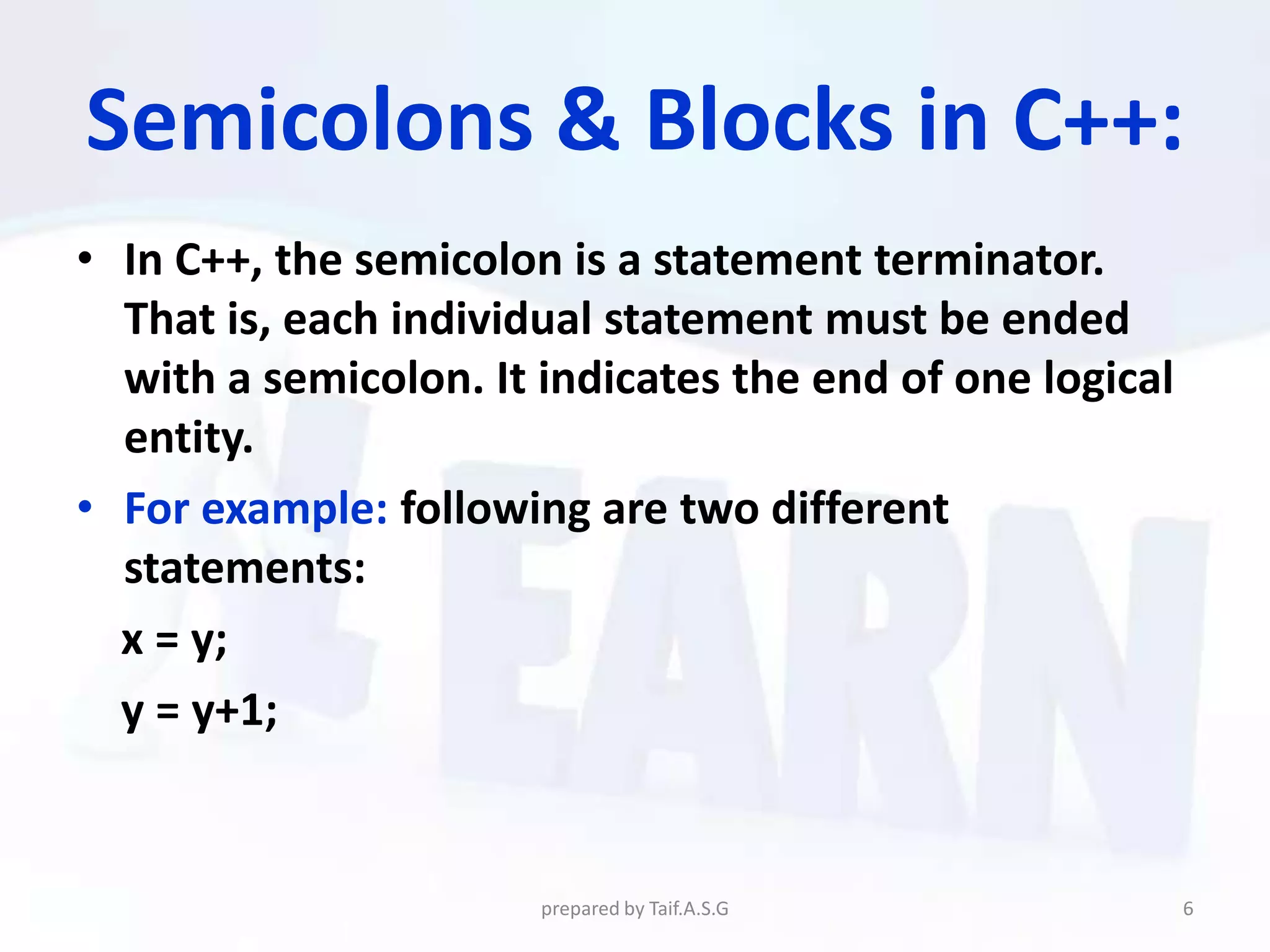
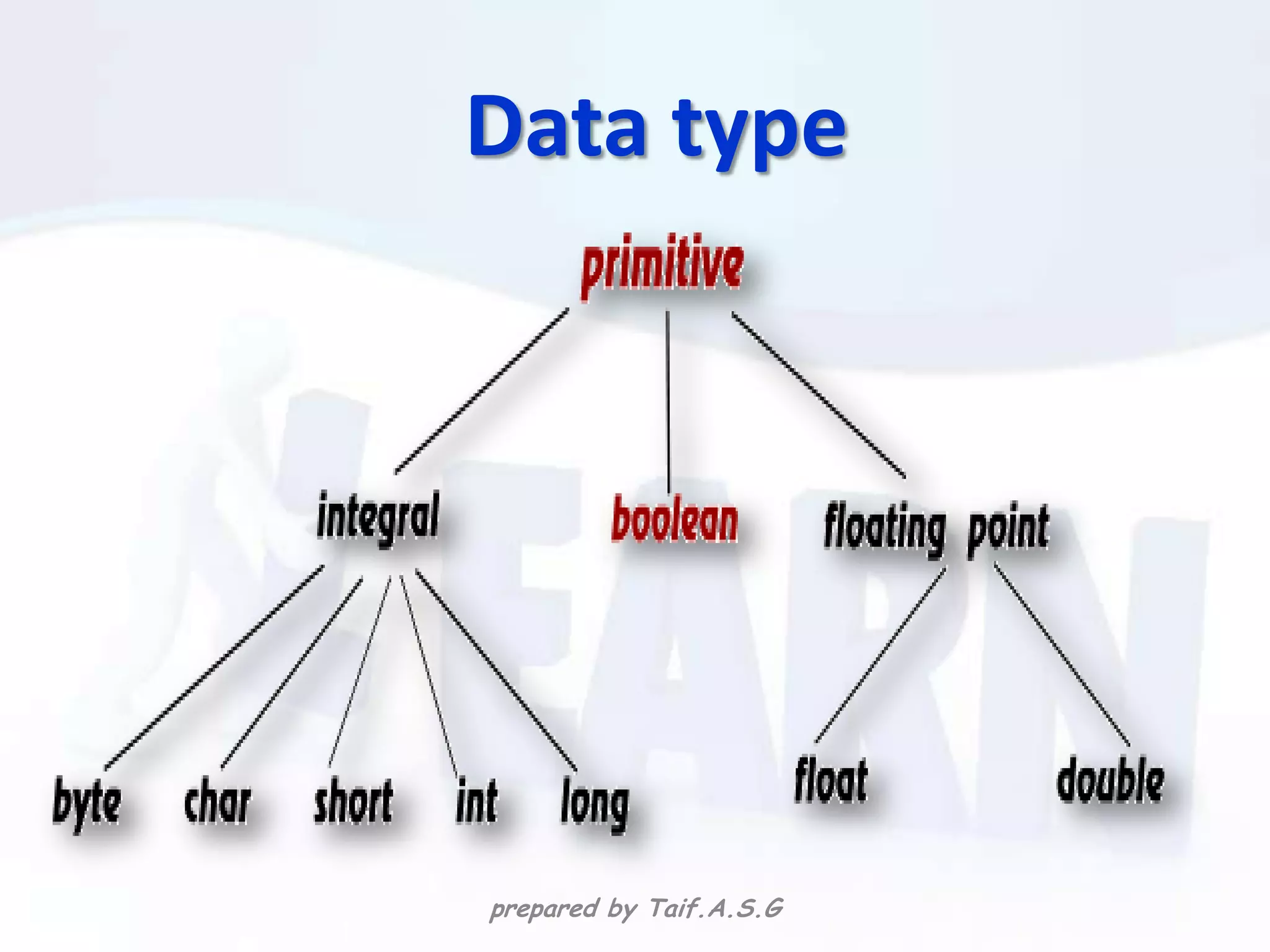
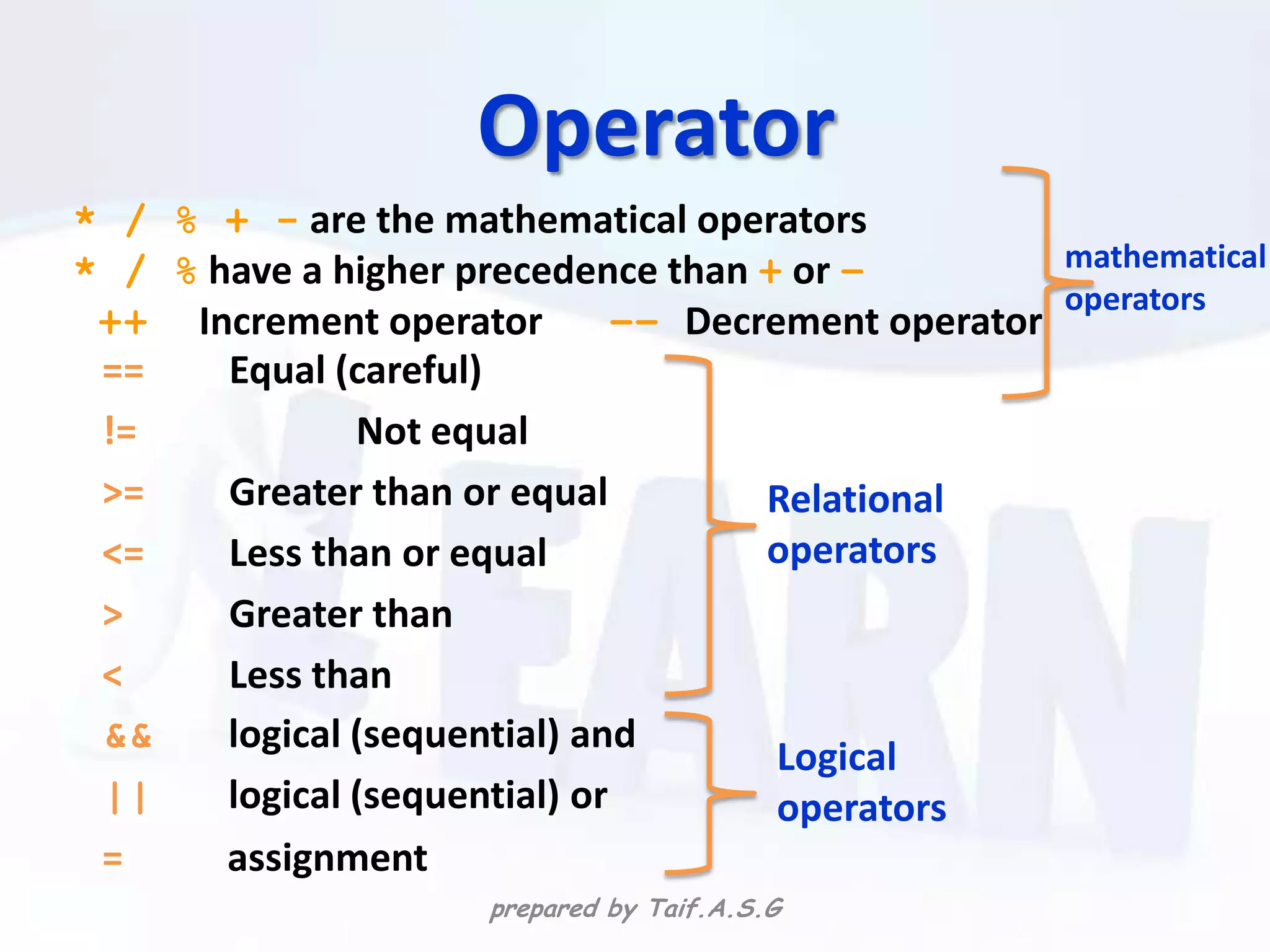
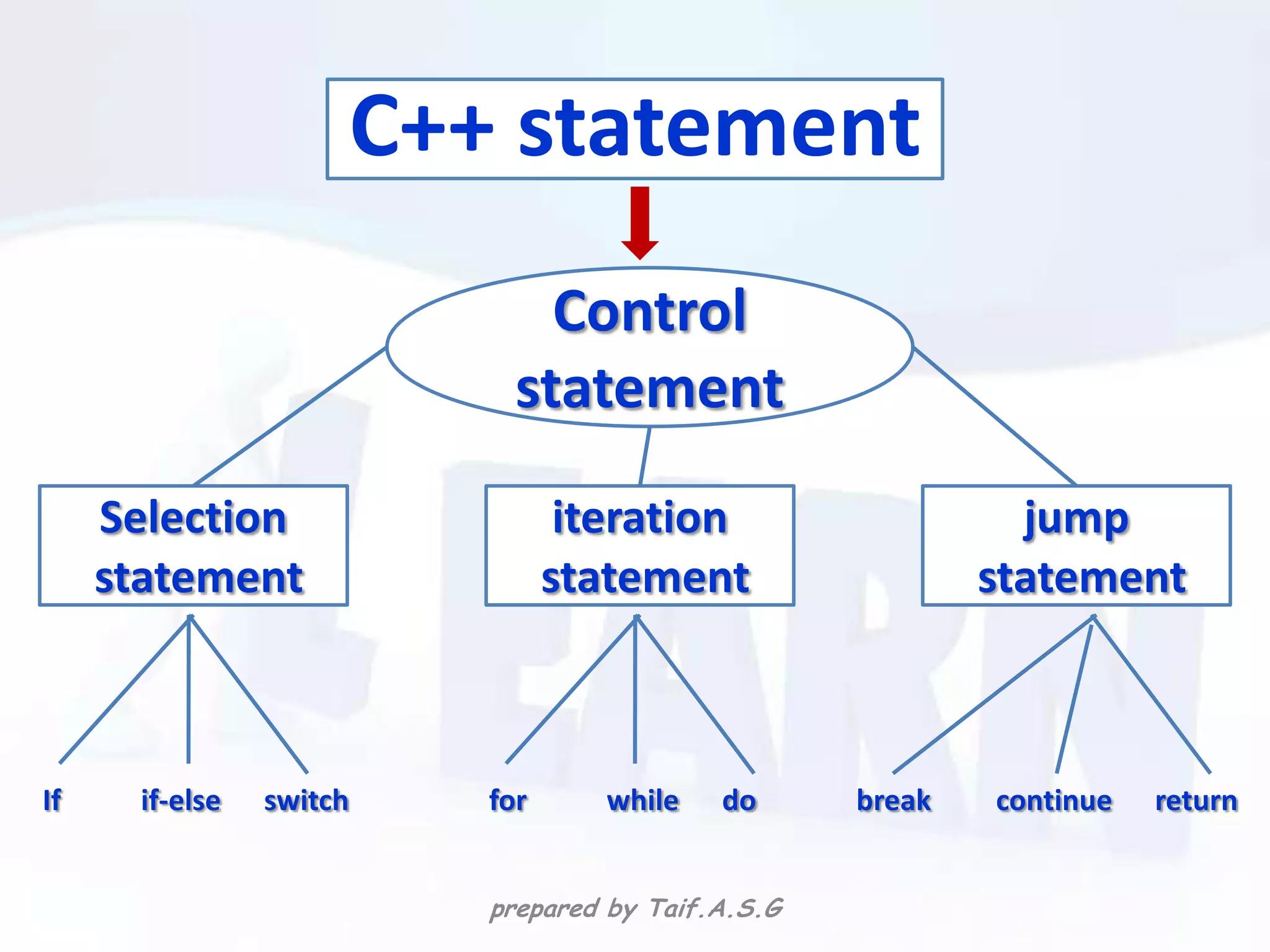
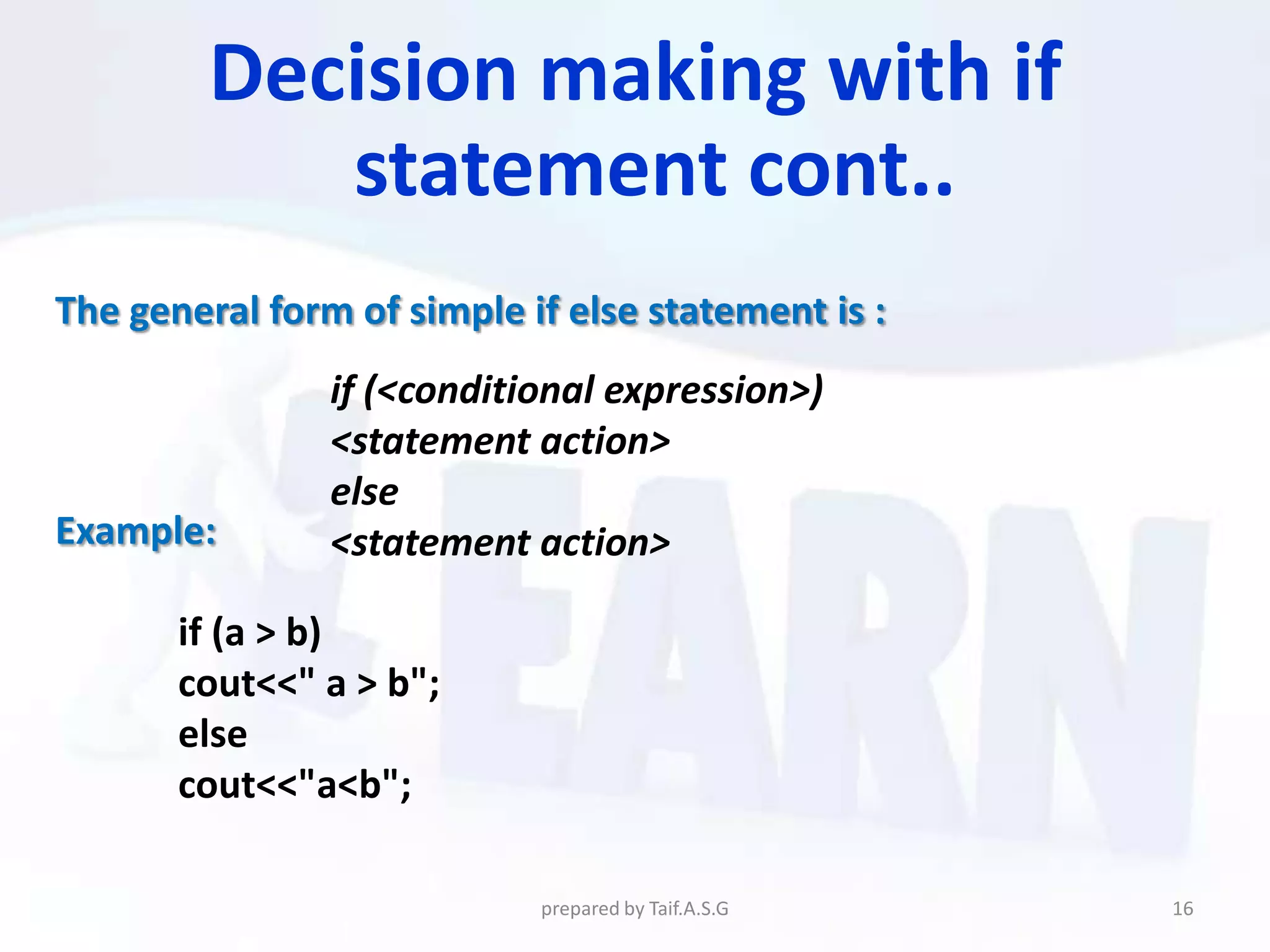
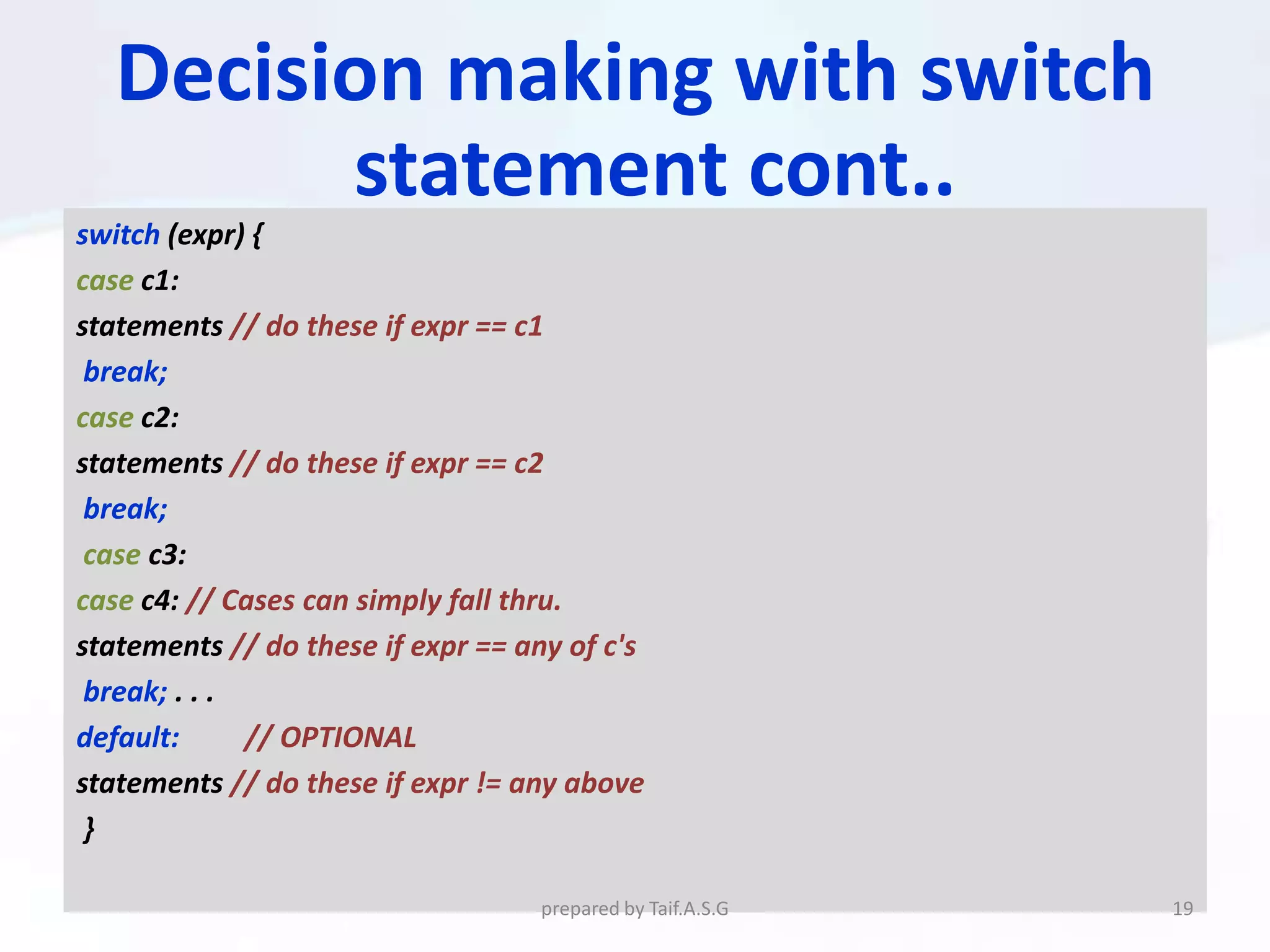
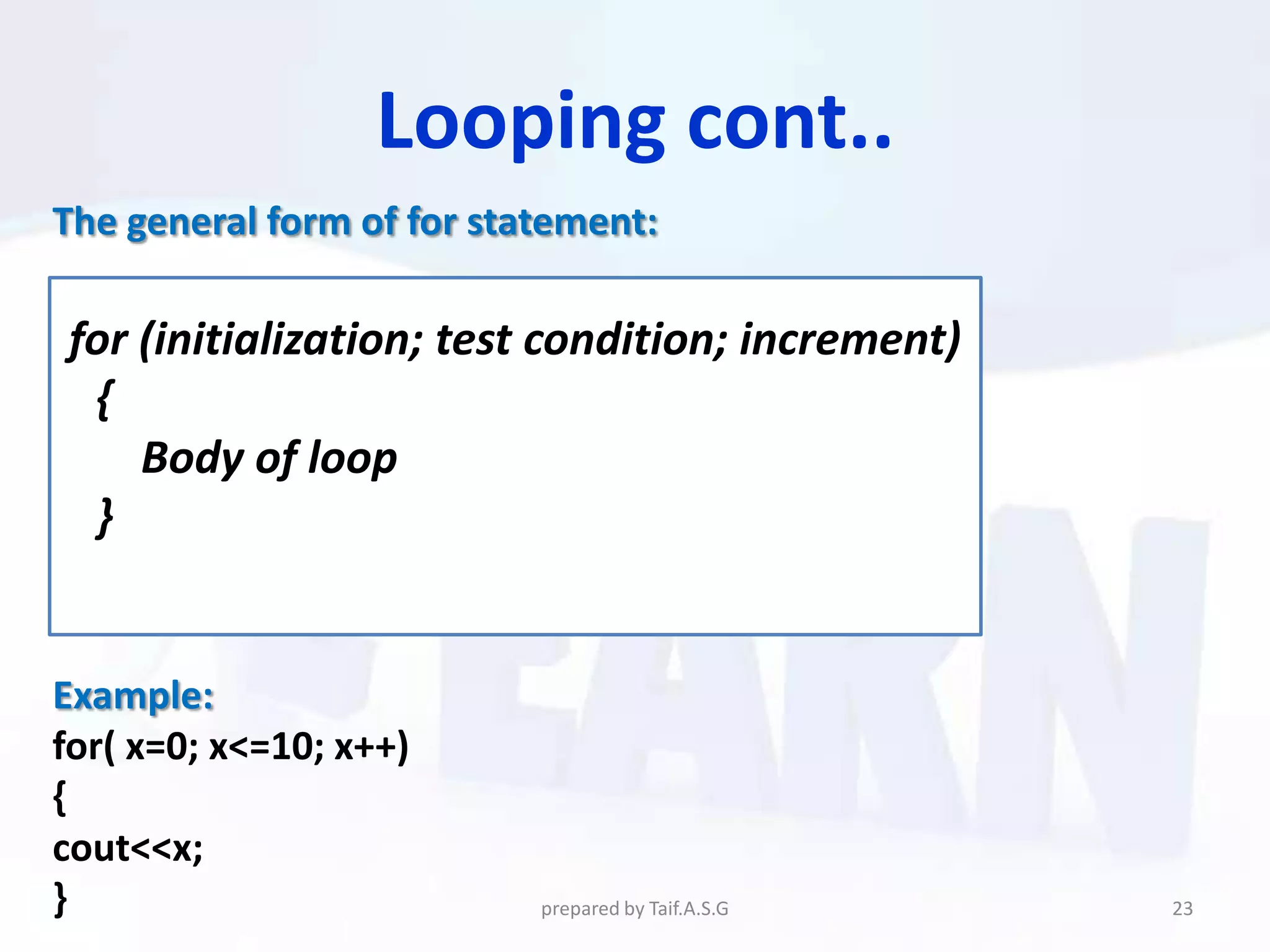
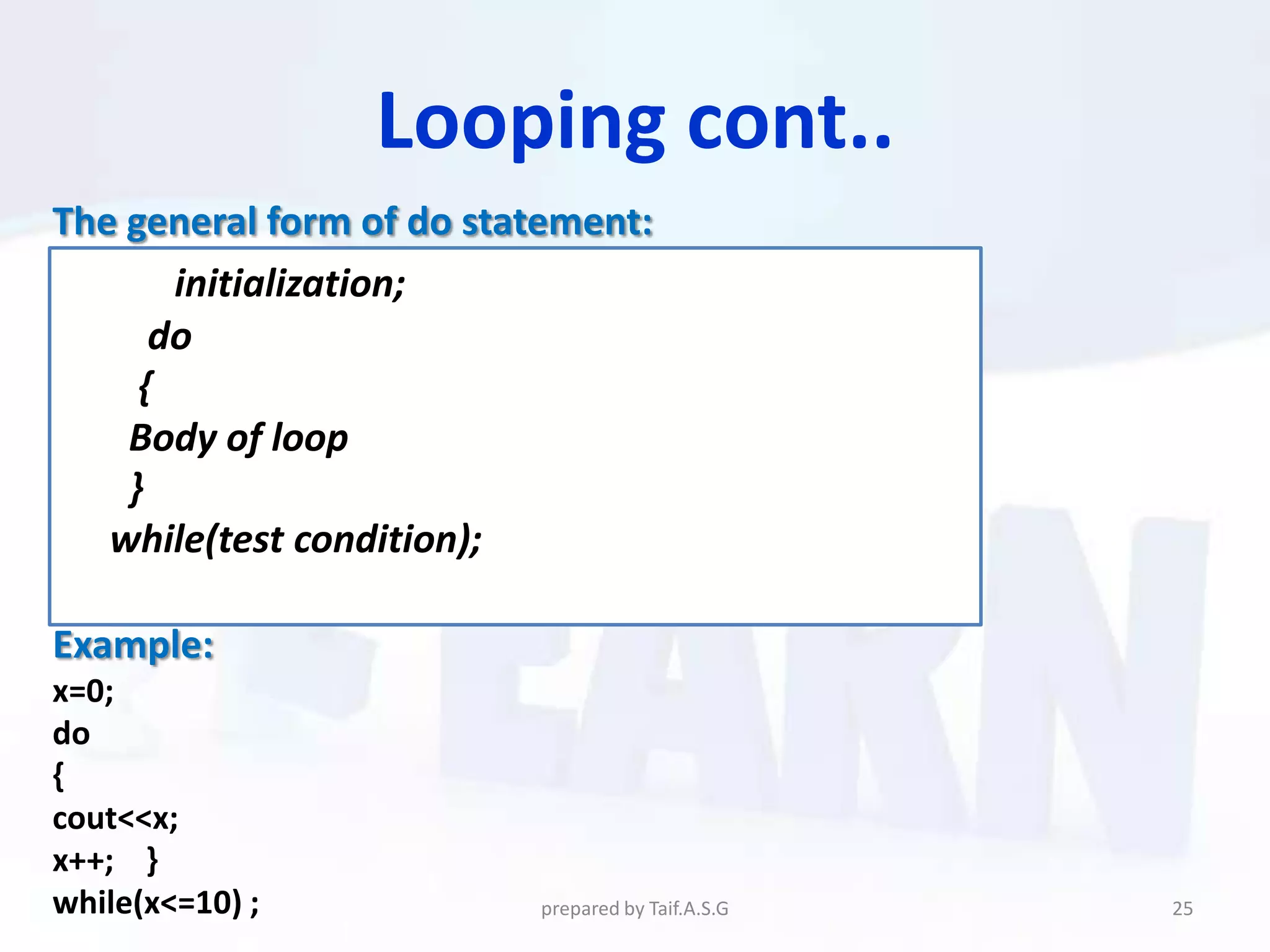
The document provides an overview of the C++ programming language. It discusses what C++ is, its history and features. It then outlines various C++ concepts like identifiers, constants, data types, comments, operators, variables, and statements. It also covers control structures like decision making statements (if-else, switch), looping (for, while, do-while), and functions. The document is intended as a lecture on the basic elements of the C++ language.