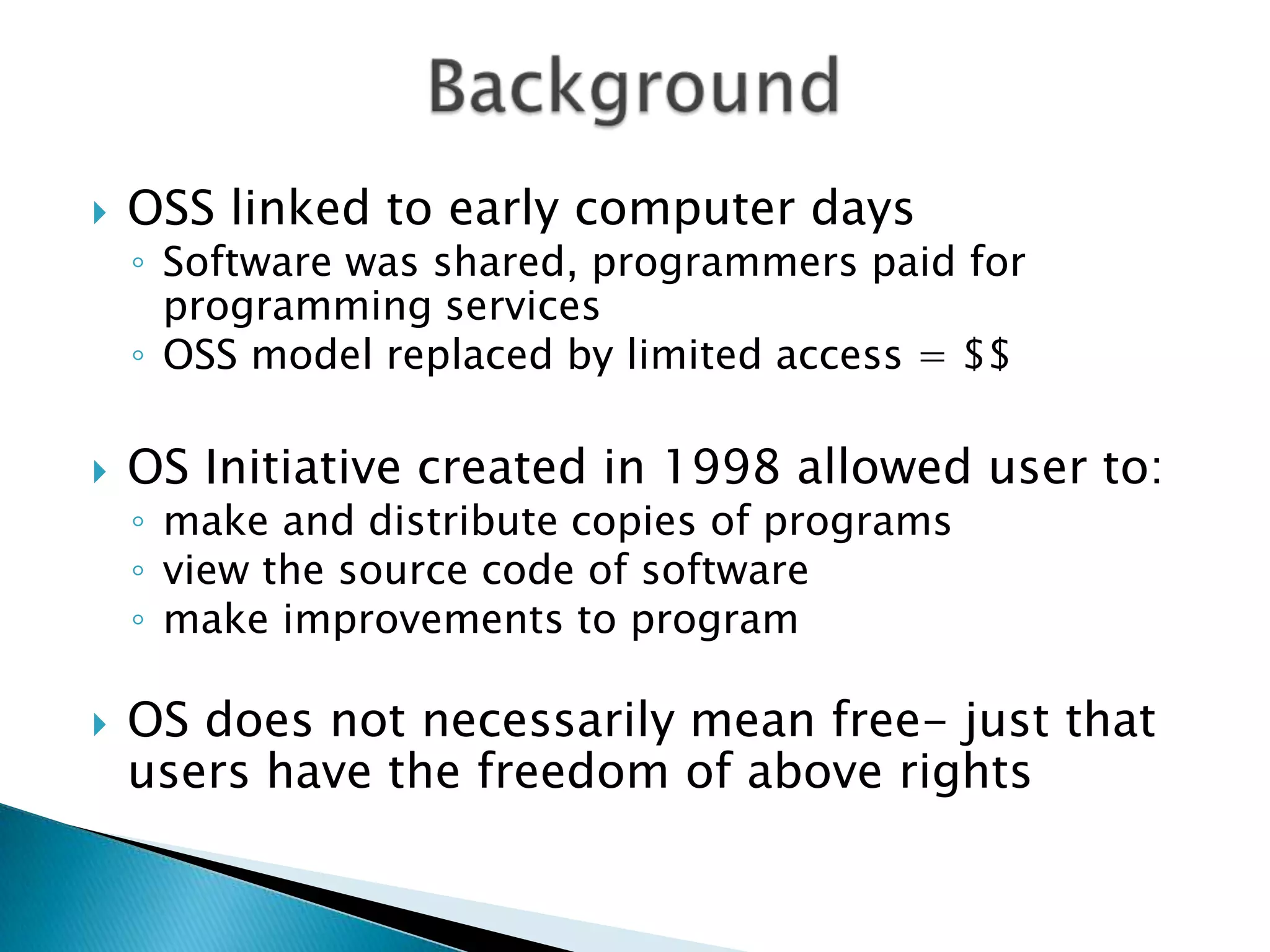
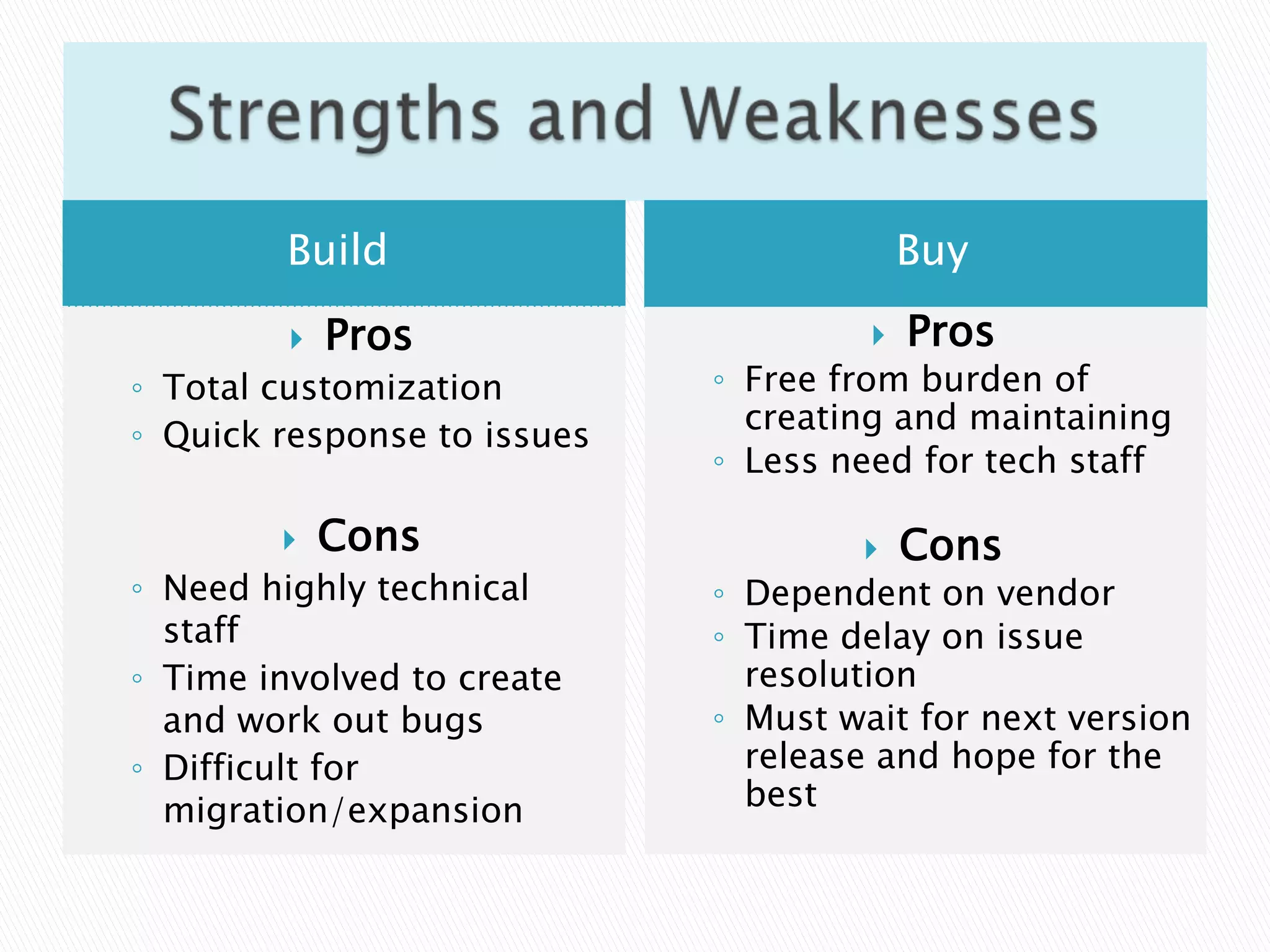
Open source software has become widely adopted by libraries as both integrated library systems and other applications. There are strengths and weaknesses to both developing open source software internally ("build") versus purchasing commercial options or borrowing existing open source code to customize ("buy" or "borrow"). Building requires significant technical resources but allows for total customization, while buying relies on vendors for support but reduces the technical burden. Overall, open source aligns with library values of sharing knowledge and being open to all.