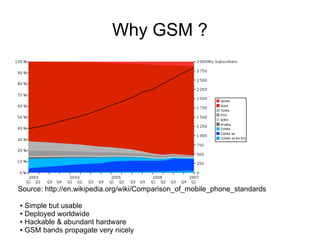
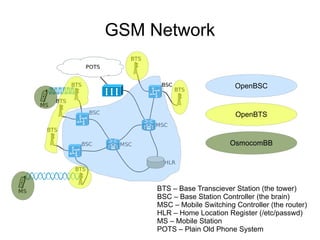
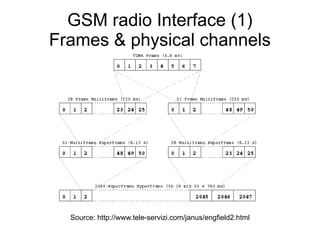
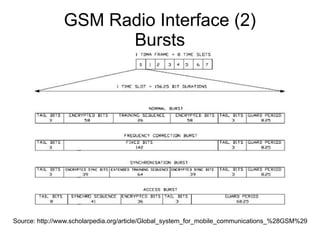
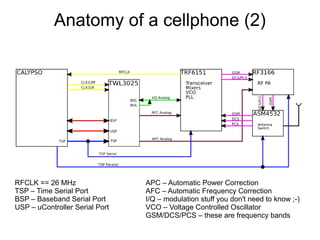
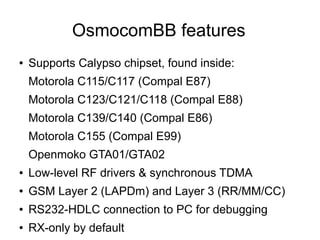
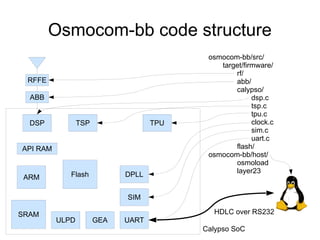
This document discusses open sourcing GSM baseband firmware to allow for free cellphone firmware, security research of cellphone networks, and disruptive competition. It notes challenges include closed chipset and network equipment industries and lack of learning materials. It promotes GSM due to its simplicity, worldwide deployment, and hackable hardware. It introduces the Osmocom project which produces open source GSM baseband software and describes its features and code structure.