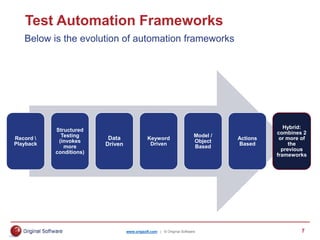
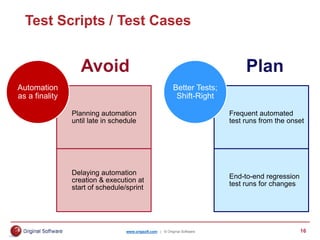
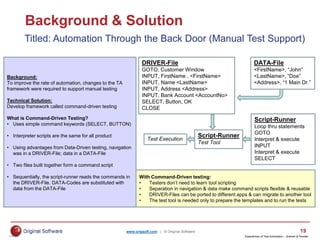
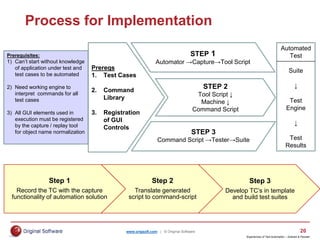
The document summarizes a presentation on transforming manual testing processes to incorporate test automation. It discusses automation models and frameworks, incorporating automation into standard testing processes, typical test activities and deliverables for agile and waterfall SDLCs. It provides a deep dive into testing artifacts and how to better plan for automation. It also presents a case study where a command-driven testing framework was adopted to help automate manual testing processes and limit concurrent work by testers on the same templates. The presentation aims to provide best practices for planning and implementing test automation.