The document simulates different file allocation strategies including sequential, indexed, and linked allocation and shows sample code to implement each. It also simulates different file organization techniques including single-level and two-level directory structures, providing sample code and outputs for each approach. The code samples provide a way to test and understand how these different file allocation and organization techniques work.
![Simulate all Page Replacement Algorithms
a) FIFO Page Replacement Algorithm
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int str[30],z,count,fs,p[100],pf=0;
main()
{
int i,j,k,temp;
printf("n Enter the No.of frames:");
scanf("%d",&fs);
printf("n Enter string (-1 to stop):");
i=0;
while(1)
{
scanf("%d",&temp);
if(temp==-1)
break;
str[i++]=temp;
}
count=i;
for(i=0;i<fs;i++)
p[i]=-1;
printf("nt Pages t Frames");
i=j=0;
while(i<count)
{
if(!check(str[i]))
{
pf++;
p[j]=str[i];
j=(j+1)%fs;
}
printf("nt <%d> t",str[i]);
for(k=0;k<fs;k++)
if(p[k]!=-1)
printf("%3d",p[k]);
i++;
}
z=pf-fs;
printf("nt Page Faults:%d",z);
}
check(int key)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<fs;i++)
if(key==p[i])
return 1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/75/Os-2-cycle-1-2048.jpg)

![b) LRU Page Replacement Algorithm
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int str[30],count,fs,p[100],pf;
main()
{
int i,j,k,z,temp;
printf("n Enter the No.of frames:");
scanf("%d",&fs);
printf("n Enter string (-1 to stop):");
i=0;
while(1)
{
scanf("%d",&temp);
if(temp==-1)
break;
str[i++]=temp;
}
count=i;
for(i=0;i<fs;i++)
p[i]=-1;
printf("n Pages tt Frames");
i=0;
while(i<count)
{
if(!check(str[i]))
{
pf++;
j=lru(i);
p[j]=str[i];
}
printf("n %3d tt",str[i]);
for(k=0;k<fs;k++)
if(p[k]!=-1)
printf("%3d",p[k]);
i++;
}
z=pf-fs;
printf("nn Page Faults:%d",z);
}
check(int key)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<fs;i++)
if(key==p[i])
return 1;
return 0;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-3-320.jpg)
![}
lru(int pos)
{
int i,j=0,r=0;
for(i=0;i<fs;i++)
{
if(p[i]==-1)
return i;
if(rec(i,pos)>=r)
{
j=i;
r=rec(i,pos);
} }
return j;
}
rec(int fn,int pn)
{
int i,c=0;
for(i=pn-1;i>=0;i--)
{
c++;
if(p[fn]==str[i])
return c;
}
}
OUTPUT
1) Enter the No. of frames: 3
Enter string (-1 to stop):2 3 2 1 5 2 4 5 3 2 5 2 -1
Pages Frames
2 2
3 2 3
2 2 3
1 2 3 1
5 2 5 1
2 2 5 1
4 2 5 4
5 2 5 4
3 3 5 4
2 3 5 2
5 3 5 2
2 3 5 2
Page Faults:4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-4-320.jpg)
![c) LFU page replacement Algorithm
#include<stdio.h>
int i,j=1,s,k,l,re[30],p[10],ch,no,nr,c,a1=0,a,line=6,nk;
struct
{
int st,l,ps,pos;
}opr;
main()
{
clrscr();
printf("Enter length of reference string:");
scanf("%d",&nr);
printf(" Enter reference string:");
for(i=1;i<=nr;i++)
scanf("%d",&re[i]);
printf("n Enter number of frames:");
scanf("%d",&no);
clrscr();
for(i=1;i<=no;i++)
p[i]=-1;
opr.st=100;
for(i=1;i<=nr;i++)
{
a1=0;
opr.st=100;
opr.pos=100;
for(c=1;c<=no;c++)
if(re[i]==p[c])
a1++;
if(a1==0)
{
if(j<=no)
{
p[j]=re[i];
j++;
}
else
{
for(k=1;k<=no;k++)
{
a=0;
for(ch=i-1;ch>0;ch--)
{
if(p[k]==re[ch])
{
a++;
nk=ch;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-5-320.jpg)
![}
if(a>1)
{
if(opr.st>a)
{
opr.st=a;
opr.ps=k;
}
else
if(opr.st==a)
{
if(opr.pos>ch)
opr.ps=k;
}
}
else
if(a==1)
{
if(opr.pos>nk)
{
opr.pos=nk;
opr.ps=k;
opr.st=a;
}
}
}
p[(opr.ps)]=re[i];
}
}
display(no,p,i);
}
printf("n");
getch();
}
display(int no,int p[],int i)
{
int k;
if(i==1)
{
printf("ttt");
for(k=1;k<=no;k++)
printf("_ _");
}
printf("n%d",re[i]);
gotoxy(25,line++);
for(k=1;k<=no;k++)
{ printf("|");
printf("_");
if(p[k]!=-1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-6-320.jpg)
![printf("%d",p[k]);
else
printf(" ");
printf("_");
} printf("|"); }
OUTPUT:
Least frequently used
Enter no of frame 3
Enter no of pages 4
Enter page sequence 4 5 8
400F
450F
458F
No of page faults 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-7-320.jpg)
![3.Simulate all File Allocation Strategies
a) Sequential file allocation
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct
{
int bno,flag;
}block;
block b[200];
void main()
{
int rnum();
int n,p[30],i,j,r,k[20][20],s,s1;
printf("n input");
printf("n enter no of files");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("n-------------------------------");
printf("n enter memory requirements");
printf("n------------------------------");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("n enter %d file requirements:",i);
scanf("%d",&p[i]);
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
s1=rnum();
j=0;
for(s=s1;s<(s1+p[i]);s++)
{
j=j+1;
b[s].bno=s;
b[s].flag=1;
k[i][j]=s;
}
}
printf("n output");
printf("n ---------------------------------");
printf("n program blocka allocated");
printf("n----------------------------------");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-8-320.jpg)
![{
printf("%5dt",i);
for(j=1;j<=p[i];j++)
printf("%5d",k[i][j]);
printf("'n");
}
printf("n------------------------------------");
printf("n allocated blocks:");
printf("n-----------------------------------");
for(i=1;i<=200;i++)
if(b[i].flag==1)
printf("%5dt",b[i].bno);
}
int rnum()
{
int i,k=0;
for(i=1;i<=200;i++)
{
k=rand()%200;
if(k%2==0)
k=k+10;
if(b[k].flag!=1)
break;
return k;
}
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the no of input files : 3
Input the requirements:
Enter the no of blocks needed in file 1: 2
Enter the no of blocks needed in file2 :4
Enter the no of blocks needed in file3: 3
Allocation
Allocate for file1: 8386
Allocate for file2: 77159335
Allocate for file3:924921](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-9-320.jpg)
![b) Indexed File allocation
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct block
{
int bno,flag;
};
struct block b[100];
int rnum();
void main()
{
int p[10],r[10][10],ab[10],i,j,n,s;
printf("n INPUT");
printf("enter no of files:");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("n enter the size of block %d:",i);
scanf("%d",&p[i]);
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
s=rnum();
ab[i]=s;
for(j=0;j<p[i];j++)
{
s=rnum();
r[i][j]=s;
}
}
printf("n output:");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("n file %d n block %d contains:",i,ab[i]);
for(j=0;j<p[i];j++)
{
printf("%6d",r[i][j]);
}
}
}
int rnum()
{
int k=0,i;
for(i=1;i<=100;i++)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-10-320.jpg)
![k=rand()%100;
if(b[k].flag!=-1)
break;
}
return k;
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the no of files: 3
Enter the memory requirements:
Enter the 1 file requirement: 3
Enter the 2 file requirement: 2
Enter the 3 file requirement: 4
Program blocks allocated
1 70 71 72
2 115 116
3 212 213 214 215
Allocated blocks
70 71 72 115 116 212 213 214 215](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-11-320.jpg)
![c) Linked File Allocation
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct
{
int bno,flag,bn[20];
}block;
block b[100],b1;
void main()
{
int rnum();
int p[30],kk[20],i,n,t,s1,s,r,j,c=1;
printf("n enter no of i/p files");
scanf("%d",&n);
printf("n input the requirements");
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("n enter the no of blocks needed for file%d",i);
scanf("%d",&p[i]);
}
t=1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=p[i];j++)
{
s=rnum();
b[s].flag=1;
b[c].bno=s;
r=p[i]-1;
kk[i]=s;
t=1;
c++;
}
}
while(r!=0)
{
s1=rnum();
b[s].bn[t]=s1;
b[s1].flag=1;
b[c].bno=s1;
r=r-1;
t=t+1;
c++;
}
printf("n allocation:n");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-12-320.jpg)
![c=1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
printf("n allocated for file%d",i);
for(j=1;j<=p[i];j++)
{
if(j==1)
{
printf("%3d",b[c].bno);
c++;
}
else
{
printf("---->%3d",b[c].bno);
c++;
}
}
printf("n");
}
}
int rnum()
{
int k=0,i;
for(i=1;i<=100;i++)
{
k=rand()%100;
if(b[k].flag!=1)
break;
}
return k;
}
OUTPUT:
Enter the no of files 3
Enter the size of block 1 2 3
4 3 2
File 1 Block 83 contains 86 77 15 93
File 2 Block 85 contains 86 92 49
File 3 Block 21 contains 62 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-13-320.jpg)
![4. Simulate all File Organization Techniques
a) Single level directory
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<graphics.h>
void main()
{
int gd,gm,count,i,j,mid,cir_x;
char fname[10][20];
gd=DETECT;
clrscr();
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"c:/turboc");
cleardevice();
setbkcolor(GREEN);
puts("n Enterno.of files do u have?");
scanf("%d",&count);
for(i=0;i<count;i++)
{
cleardevice();
setbkcolor(GREEN);
printf("Enter file %d name ",i+1);
scanf("%s",fname[i]);
setfillstyle(1,MAGENTA);
mid=640/count;
cir_x=mid/3;
bar3d(270,100,370,150,0,0);
settextstyle(2,0,4);
settextjustify(1,1);
outtextxy(320,125,"Root Directory");
setcolor(BLUE);
for(j=0;j<=i;j++,cir_x+=mid)
{
line(320,150,cir_x,250);
fillellipse(cir_x,250,30,30);
outtextxy(cir_x,250,fname[i]);
}
getch();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-14-320.jpg)
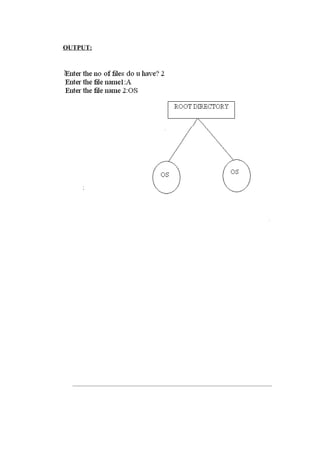
![b) Two level Directory
//two level directory structure
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#include<graphics.h>
#define SX 250
#define SY 200
#define BL 30
#define BW 15
#define SY1 250
int SX1=100;
int n,m[10];
char a[10][10];
int cols[]={2,5,1,3,4,6,8,7,9};
typedef struct
{
char name[10];
struct
{
char file[10];
}k[10];
}file_info;
file_info f[10];
void readfiles()
{
int i,j;
printf("nEnter no. of directories:");
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("Enter %d directory:",i+1);
scanf("%s",&f[i].name);
printf("enter no.of files:");
scanf("%d",&m[i]);
for(j=0;j<m[i];j++)
{
printf("enter %d file name:",j+1);
scanf("%s",&f[i].k[j].file);
}
}
}
void fillspace()
{
int x1,y1,i,j;
outtextxy(70,205,"Directory");
outtextxy(100,255,"Files");
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-16-320.jpg)
![setfillstyle(1,cols[i]);
x1=SX+(i%10)*50;
y1=SY+(i/10)*40;
bar(x1,y1,x1+BL+20,y1+BW);
outtextxy(x1+BL/4,y1+BW/4,f[i].name);
line(x1+BL/2,y1+BW,SX1+50,SY1);
SX1=SX1+50;
for(j=0;j<m[i];j++)
{ setfillstyle(1,cols[i]);
x1=SX1+(j%10)*40;
y1=SY1+(j/10)*40;
bar(x1,y1,x1+BL+10,y1+BW);
outtextxy(x1+BL/4,y1+BW/4,f[i].k[j].file);
line(x1+BL/2,y1+BW,x1+BL/2,y1+50);
circle(x1+BL/2,y1+60,7);
}
SX1=SX1+100;
}
}
void main()
{
int gm,gd=DETECT;
initgraph(&gd,&gm,"c:tcbgi");
readfiles();
cleardevice();
getch();
fillspace();
getch();
closegraph();
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-17-320.jpg)
![5.Interprocess Communication
a) Pipes
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<error.h>
#define MAXBUFF 1024
main()
{
int childpid,pipe1[2],pipe2[2];
if(pipe(pipe1)<0||pipe(pipe2)<0)
printf("error");
if((childpid=fork())<0)
{
printf("error");
}
else if(childpid>0)
{
close(pipe1[0]);
close(pipe2[1]);
client(pipe2[0],pipe1[1]);
while(wait((int *)0)!=childpid)
close(pipe1[1]);
close(pipe2[0]);
exit(1);
}
else
{
close(pipe1[1]);
close(pipe2[0]);
server(pipe1[0],pipe2[1]);
close(pipe1[0]);
close(pipe2[1]);
}
}
client(readfd,writefd)
int readfd,writefd;
{
char buff[MAXBUFF];
int n;
if(fgets(buff,MAXBUFF,stdin)==NULL)
printf("client filename read error");
n=strlen(buff);
if(buff[n-1]=='n')
n--;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-18-320.jpg)
![if(write(writefd,buff,n)!=n)
printf("client filename error");
while((n=read(readfd,buff,MAXBUFF))>0)
if(write(1,buff,n)!=n)
printf("client data write error");
if(n>0)
printf("client: data read errror");
}
server(readfd,writefd)
int readfd,writefd;
{
char buff[MAXBUFF];
int n,fd;
if((n=read(readfd,buff,MAXBUFF))<0)
printf("srever filename read error");
buff[n]='0';
if((fd=open(buff,0))<0)
{
n=strlen(buff);
if(write(writefd,buff,n)!=n)
printf("server :error msg");
}
else
{
while((n=read(fd,buff,MAXBUFF))>0)
if(write(writefd,buff,n)!=n)
printf("server data write error");
if(n>0)
printf("server read error");
}
}
OUTPUT:
vi a.txt
welcome to NP
]$ ./a.out
a.txt
welcome to NP](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-19-320.jpg)




![d) Message Queues
/*server*/
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/ipc.h>
#include<sys/msg.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define BUFSZ 4096
struct msg
{ 10 long int type;
char text[BUFSZ];
};
int main()
{
struct msg data;
int msgid;
char buff[BUFSZ];
msgid=msgget((key_t)4321,0666|IPC_CREAT);
while(1)
{ 21 printf("n enter some data:nn");
fgets(buff,BUFSZ,stdin);
data.type=1;
strcpy(data.text,buff);
msgsnd(msgid,(void *)&data,BUFSZ,0);
exit(1);
} 28 }
OUTPUT: enter some data
hai
/*client*/
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/ipc.h>
#include<sys/msg.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MSGKEY1 4321L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-24-320.jpg)
![#define MAX 5700
typedef struct msgbuf{
long mtype;
char mtext[MAX];
}my_msgbuff;
main()
{
my_msgbuff buffer;
int msgID,myID;
int temp;
if((msgID=msgget(MSGKEY1,0666|IPC_CREAT))<0)
{
perror("error getting msg queue");
exit(1);
}
if(msgrcv(msgID,&buffer,sizeof(buffer),0L,0)<0)
{
perror("error receiving msg from queue");
exit(1);
}
printf("n msg read from queue:nn");
printf("MESSAGE:%sn",buffer.mtext);
while(msgsnd(msgID,&buffer,sizeof(buffer.mtext),0)>0);
if(msgctl(msgID,IPC_RMID,0)<0)
{
perror("error detecting msg queue");
exit(1);
}
msgctl(myID,IPC_RMID,0);
exit(0); }
OUTPUT:
msg read from queue:
MESSAGE:hai](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-25-320.jpg)


![Banker’s Algorithm for Deadlock avoidance and Prevention
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int C[4][3],A[4][3],RQ[4][3],V[3],R[3],K[4],sum=0,np,nr;
main()
{
void fun();
int i,j,count=0,pcount=0;
clrscr();
printf("nEnter the total number of resources : ");
scanf("n%d",&nr);
for(i=0;i<nr;i++)
{
printf("nEnter the no of resources int R%d : ",i+1);
scanf("%d",&R[i]);
}
printf("nEnter the no of processes to be executed : ");
scanf("%d",&np);
printf("nEnter the claim matrix:n");
for(i=0;i<np;i++)
for(j=0;j<nr;j++)
scanf("%d",&C[i][j]);
printf("nEnter the allocation matrix:n");
for(i=0;i<np;i++)
for(j=0;j<nr;j++)
scanf("%d",&A[i][j]);
for(i=0;i<np;i++)
for(j=0;j<nr;j++)
RQ[i][j] = C[i][j] - A[i][j];
fun();
for(i=0;i<np;i++)
{
count=0;
f(K[i] == i+1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-28-320.jpg)
![continue;
for(j=0;j<nr;j++)
{
if(V[j] >= RQ[i][j])
count++;
}
if(count == nr)
{
K[i] = i+1;
for(j=0;j<nr;j++)
C[i][j] = A[i][j] = RQ[i][j] = 0;
pcount++;
count = 0;
i=-1;
fun();
}
}
if(pcount == np)
printf("nThere is no chance of deadlock.nIt is a safe state.");
else
printf("nThere is a chance of deadlock.nIt isn't a safe state.");
getch();
}
void fun()
{
int i1,j1;
for(i1=0;i1<nr;i1++)
{
for(j1=0;j1<np;j1++)
{
sum = sum + A[j1][i1];
}
V[i1] = R[i1] - sum;
sum = 0;
}
}
OUTPUT
Enter the total number of resources
2
Enter the total number of resources in R1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os2cycle-120422132802-phpapp02/85/Os-2-cycle-29-320.jpg)
