More Related Content
PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
Understanding Groups and Teams PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
ch6-foundations-of-group-behavior.ppt Similar to Organizational Behavior ses5amgt500.ppt
PDF
Unit 8 - The nature of Groups and Teams.pdf PPT
Chapter 11 management (10 th edition) by robbins and coulter PPT
Chapter 11management10theditionbyrobbinsandcoulter-130822073629-phpapp01 PDF
Managing teams by Stephen P Robbins .pdf PPT
PPT
Management 11th Edition - Chapter 13 - Managing Teams PPT
9.Groups & Teams.ppt teaming for working PPT
PPT
PDF
Session 8 - The nature of Groups and Teams.pdf PPT
PPT
(Mb asubjects.com)ob11 08st PPT
(Mb asubjects.com)ob11 08st PPTX
groupommunicationob of 7th sem mba cmmon.pptx.pptx PPT
PPT
Chapter 8_ Foundations of Group Behavior.ppt PPT
PPT
PPT
PPT
Foundations of group behavior More from samirba0196c
PPTX
Organizational Behavior Chapter one.pptx PPTX
Organizational Behavior Chapter Three.pptx PPT
Organizational Behavior Topic 7 and Chapter 8 (1).ppt PPTX
organizational behavior chapter6.pptx PPTX
Marketing Management Marketing Research 3.pptx PPTX
Marketing Management Marketing Research 4.pptx PPTX
Marketing Management Ch-2_Adapting-words.pptx PPTX
Marketing Management Case4 Fabulous fashion .pptx PPTX
marketing management .....MKT MGT 7.pptx PPTX
MARkrting mgt Marketing Research 16.pptx PPT
Human Resource Management- Conflict Management.ppt PPTX
entreprenuereship-Business Pitching.pptx PPTX
Strategic Marketing in business studies.pptx PPTX
Types of Communication in business .pptx Recently uploaded
DOCX
Buy Instagram Account Purchase_ A Safe and Secure Approach.docx PDF
Iryna Rudenko: Follow the Money: How Investment Trends Define IT Niches (UA) DOCX
8 Best Places to Buy Facebook Accounts at Wholesale Prices.docx DOCX
What Are Telegram Accounts and Why Are They Important for Global Communicatio... PDF
Top Platform to Buy Facebook Accounts in Bulk Safely.pdf PDF
Serhii Herasymov: Expert sales in outsource companies: your technical special... DOCX
How to Buy Verified Bybit Accounts in 2026 not risk .docx PPTX
Sewage Treatment Plant in Bangalore |Best STP Plant Manufacturers in Tamilna... PDF
What Is the Fastest Way to Buy Facebook Accounts.pdf PDF
Intangible (Knowledge) Assets and Dynamic Capabilities: New Paradigms for Ana... DOCX
Buy Old Gmail Accounts in 2026_ Complete Buyer’s Guide PDF
Your presence tells your story in real time PDF
ICv2 White Paper - Navigating the New World of Comics PDF
KGA - Governing administration in a consolidated market PDF
Comments on Ultra Map Section II Multifaceted Second Edition.pdf PDF
Rami Tawasha - Specializes In High-Impact Work PDF
rf_mccaffrey_stocksforthelongrun_revisited_online.v2 (1).pdf PDF
𝐋𝐚𝐮𝐧𝐜𝐡 𝐘𝐨𝐮𝐫 𝐎𝐰𝐧 𝐀𝐥𝐥 𝐢𝐧 𝐎𝐧𝐞 𝐃𝐞𝐥𝐢𝐯𝐞𝐫𝐲 𝐀𝐩𝐩 𝐏𝐥𝐚𝐭𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦 𝐋𝐢𝐤𝐞 𝐆𝐥𝐨𝐯𝐨 PDF
Precision Agriculture 2026: Using Drones for Targeted Insecticide and Herbici... PDF
A Brief Introduction About Xin Yi Hoo Organizational Behavior ses5amgt500.ppt
- 1.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 1
Defining and
Classifying Groups
Formal
Formal
Command Groups
Command Groups
Task Groups
Task Groups
Interest Groups
Interest Groups
Friendship Groups
Friendship Groups
Informal
Informal
- 2.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 2
1. FORMING
Member Questions - What is expected of me?
- What are our goals and why?
- Who are these other people?
- How do I fit in?
- How much work will this involve?
Interpersonal Issues Uncertainty, self-consciousness,
Silence, Dependence
Task Issues orient members, establish trust,
establish clear purpose
Leader Behaviors - Make introductions
- Establish foundation of trust
- Model expected behaviors
- Clarify goals and expectations
- 3.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 3
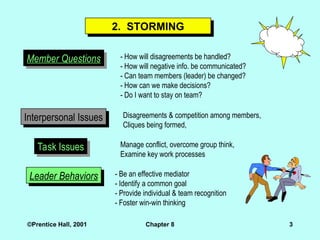
2. STORMING
Member Questions - How will disagreements be handled?
- How will negative info. be communicated?
- Can team members (leader) be changed?
- How can we make decisions?
- Do I want to stay on team?
Interpersonal Issues Disagreements & competition among members,
Cliques being formed,
Task Issues Manage conflict, overcome group think,
Examine key work processes
Leader Behaviors - Be an effective mediator
- Identify a common goal
- Provide individual & team recognition
- Foster win-win thinking
- 4.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 4
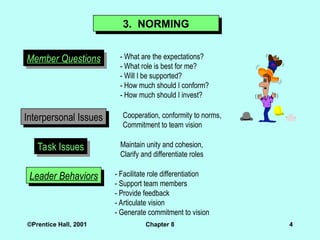
3. NORMING
Member Questions - What are the expectations?
- What role is best for me?
- Will I be supported?
- How much should I conform?
- How much should I invest?
Interpersonal Issues Cooperation, conformity to norms,
Commitment to team vision
Task Issues Maintain unity and cohesion,
Clarify and differentiate roles
Leader Behaviors - Facilitate role differentiation
- Support team members
- Provide feedback
- Articulate vision
- Generate commitment to vision
- 5.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 5
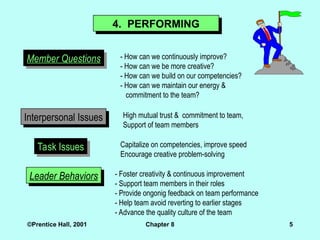
4. PERFORMING
Member Questions - How can we continuously improve?
- How can we be more creative?
- How can we build on our competencies?
- How can we maintain our energy &
commitment to the team?
Interpersonal Issues High mutual trust & commitment to team,
Support of team members
Task Issues Capitalize on competencies, improve speed
Encourage creative problem-solving
Leader Behaviors - Foster creativity & continuous improvement
- Support team members in their roles
- Provide ongonig feedback on team performance
- Help team avoid reverting to earlier stages
- Advance the quality culture of the team
- 6.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 6
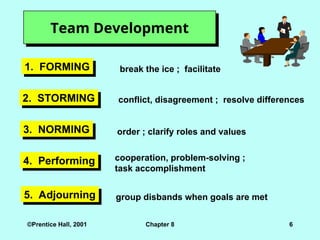
Team Development
1. FORMING break the ice ; facilitate
2. STORMING conflict, disagreement ; resolve differences
3. NORMING order ; clarify roles and values
4. Performing cooperation, problem-solving ;
task accomplishment
5. Adjourning group disbands when goals are met
- 7.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 7
Who Should be on Team?
Questions to be Asked?
What are we trying to accomplish?
Task vs. Growth & Development
Need for Functional Expertise
- Engineering types
- Operations / manufacturing
- Marketing / sales
- Finance / accounting
When are people needed?
- 8.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 8
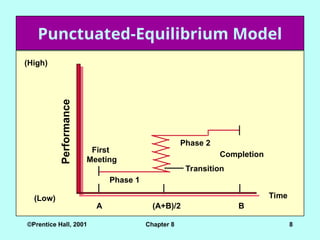
Punctuated-Equilibrium Model
Time
(Low)
(High)
First
Meeting
Phase 1
Phase 2
Transition
Completion
A B
(A+B)/2
Performance
- 9.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 9
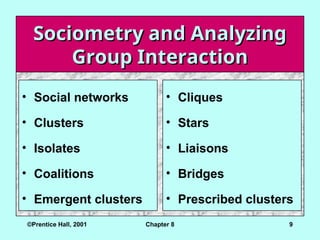
Sociometry and Analyzing
Sociometry and Analyzing
Group Interaction
Group Interaction
• Social networks
• Clusters
• Isolates
• Coalitions
• Emergent clusters
• Cliques
• Stars
• Liaisons
• Bridges
• Prescribed clusters
- 10.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 10
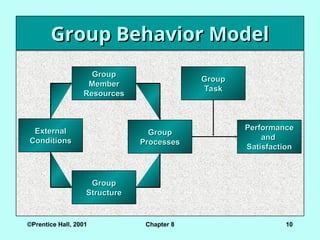
Group Behavior Model
Group Behavior Model
External
External
Conditions
Conditions
Performance
Performance
and
and
Satisfaction
Satisfaction
Group
Group
Task
Task
Group
Group
Structure
Structure
Group
Group
Member
Member
Resources
Resources
Group
Group
Processes
Processes
- 11.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 11
External Conditions
External Conditions
Imposed on the Group
Imposed on the Group
• Overall strategy
• Authority structures
• Formal regulations
• Resources
• Employee selection
• Evaluation-rewards
• Culture
• Work setting
- 12.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 12
The Resources
The Resources
of Group Members
of Group Members
Knowledge,
Knowledge,
Skills, and
Skills, and
Abilities
Abilities
Personality
Personality
Characteristics
Characteristics
- 13.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 13
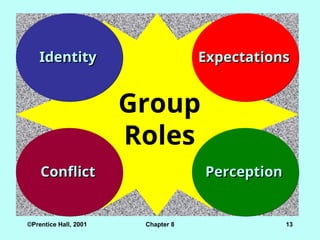
Identity
Identity
Group
Roles
Expectations
Expectations
Conflict
Conflict Perception
Perception
- 14.
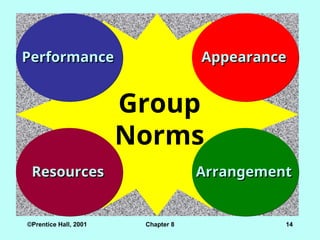
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 14
Performance
Performance
Group
Norms
Appearance
Appearance
Resources
Resources Arrangement
Arrangement
- 15.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 15
Size of the Group
Size of the Group
• Small groups
• Large groups
• Social loafing
• Individual effort
- 16.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 16
The Composition
The Composition
of the Group
of the Group
Diversity
Diversity Cohorts
Cohorts
Demography
Demography
- 17.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 17
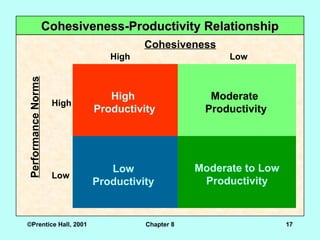
High
Productivity
Moderate
Productivity
Moderate to Low
Productivity
Low
Productivity
Cohesiveness
Performance
Norms
High Low
Cohesiveness-Productivity Relationship
Cohesiveness-Productivity Relationship
High
Low
- 18.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 18
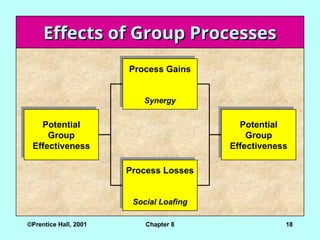
Effects of Group Processes
Effects of Group Processes
Potential
Group
Effectiveness
Potential
Group
Effectiveness
Process Losses
Social Loafing
Process Gains
Synergy
- 19.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 19
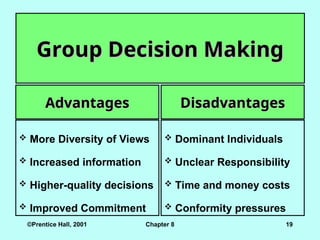
Group Decision Making
Group Decision Making
Advantages
Advantages
More Diversity of Views
Increased information
Higher-quality decisions
Improved Commitment
Disadvantages
Disadvantages
Dominant Individuals
Unclear Responsibility
Time and money costs
Conformity pressures
- 20.
©Prentice Hall, 2001Chapter 8 20
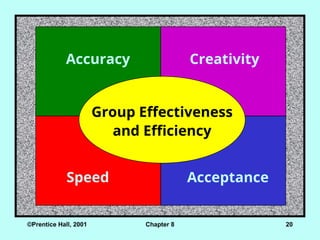
Group Effectiveness
and Efficiency
Accuracy Creativity
Acceptance
Speed