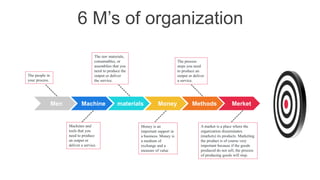
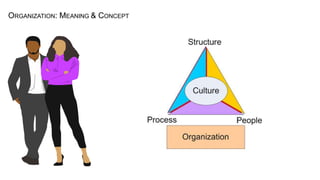
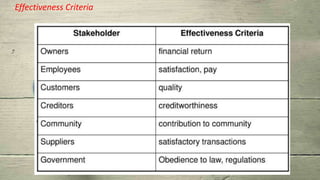
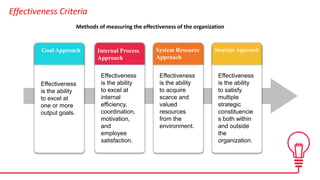
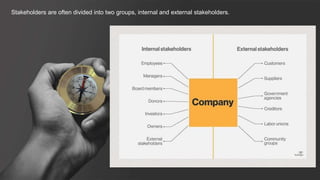
The document discusses organizational concepts including the meaning of organizations, their structures, effectiveness, stakeholders, management, ethics, and relationships with the external environment. It defines an organization as a collection of people working together in a coordinated way to achieve goals. Organizational structures determine relationships and assign roles. Effectiveness refers to achieving objectives and solving problems. Stakeholders include internal groups like managers and employees, and external groups like customers and suppliers. Top managers are responsible for setting goals and allocating resources. Business ethics concerns principles of right and wrong. Organizations must adapt to forces in their general and task environments.