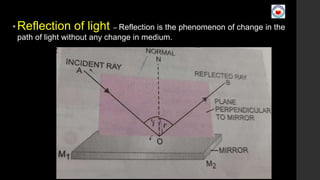
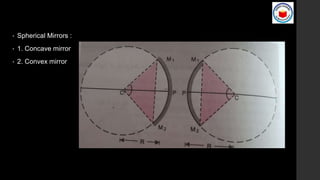
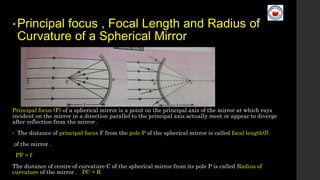
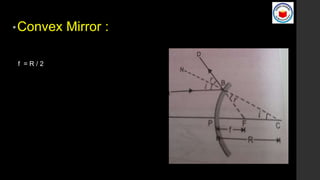
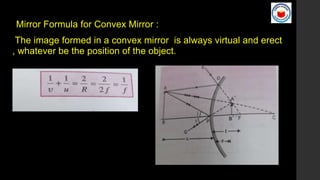
This document covers Chapter 9 on Ray Optics and Optical Instruments, focusing on key concepts such as reflection and refraction, spherical mirrors, and their properties including focal length and radius of curvature. It also presents formulas for image formation in concave and convex mirrors, with specific conditions for real and virtual images. Additionally, it touches on natural phenomena caused by sunlight, such as mirages and rainbows.