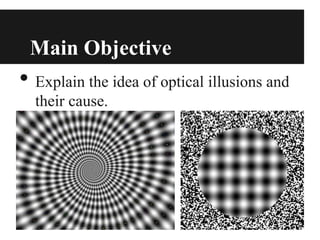
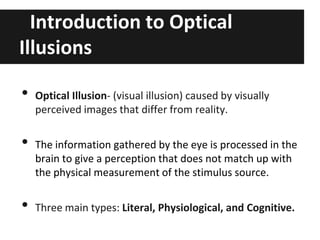
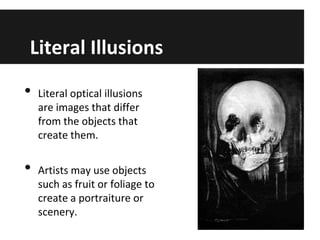
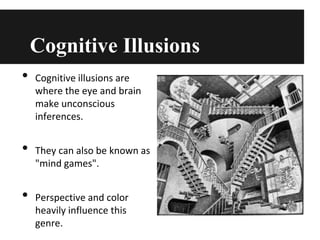
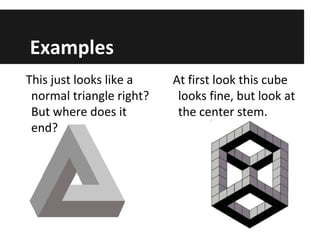
This document discusses optical illusions, explaining that they are visual illusions caused when the brain's perception does not match physical reality. There are three main types of optical illusions - literal, physiological, and cognitive - which use different techniques to confuse the eyes and brain. While illusions trick our senses, hallucinations involve perceiving something that is not really there, often due to drugs, illness, or lack of sleep. Some experiments show that other species can also experience optical illusions. In the end, illusions are different from hallucinations or delusions and are almost universally experienced by people in the same way.