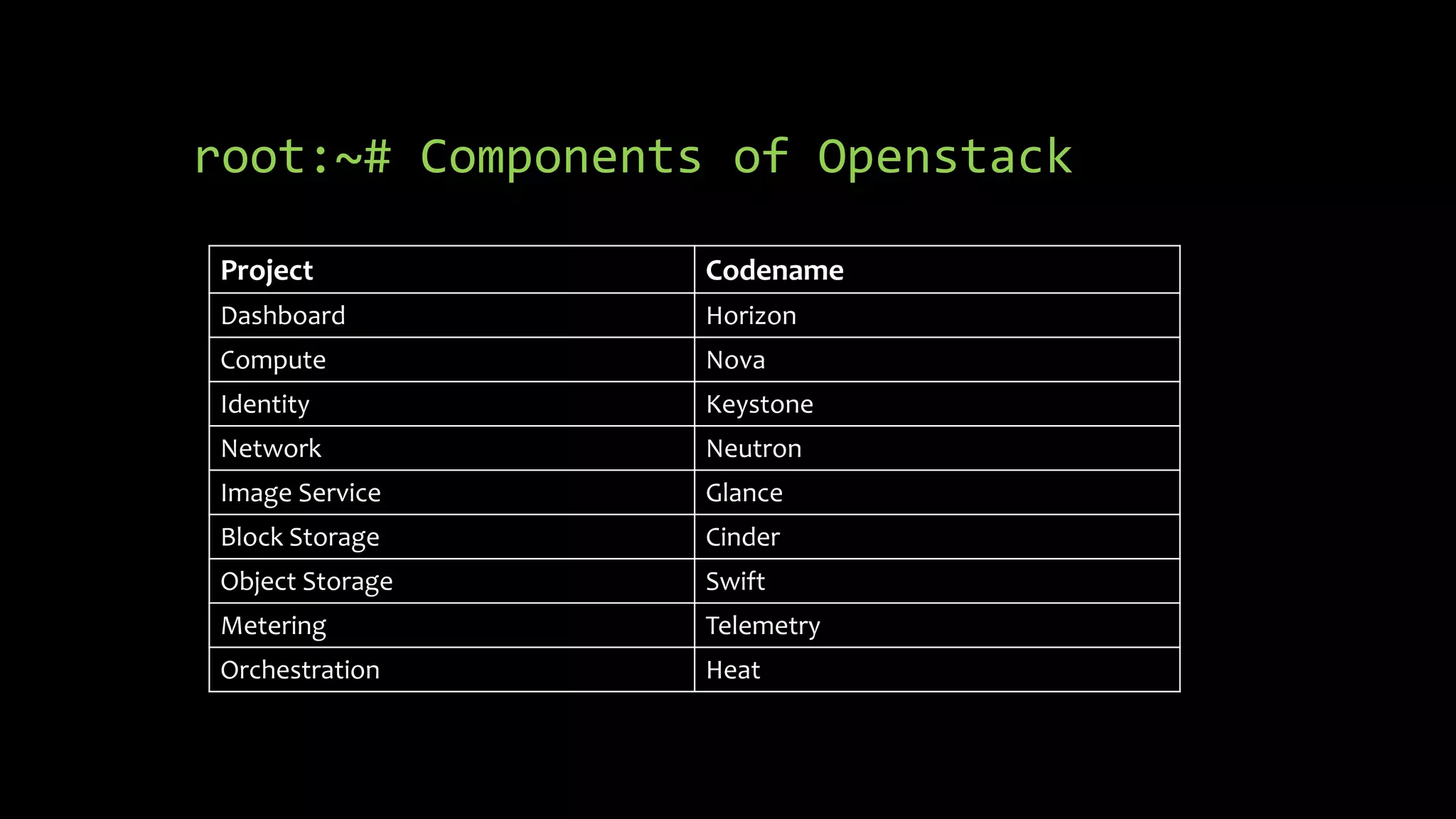
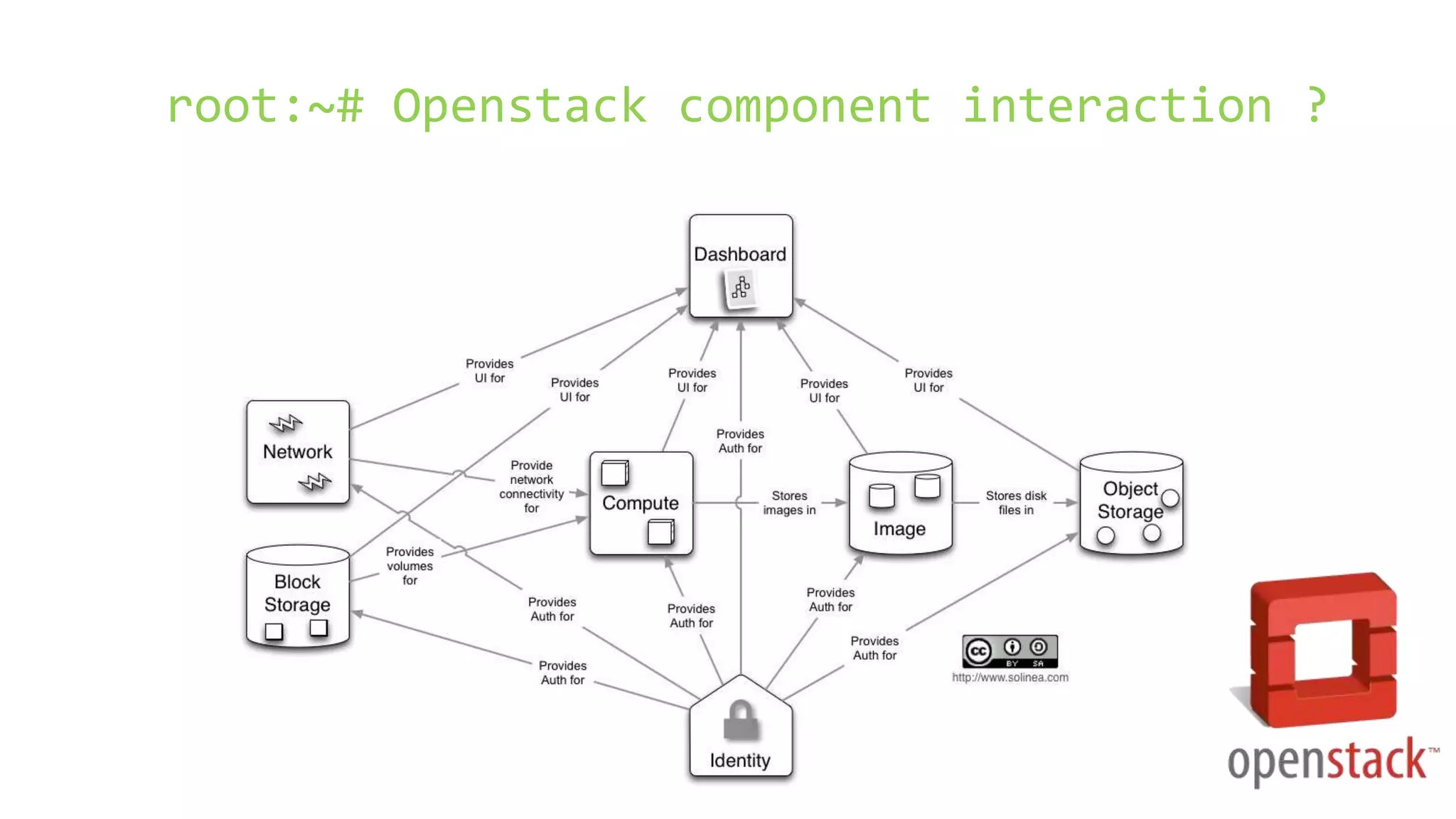
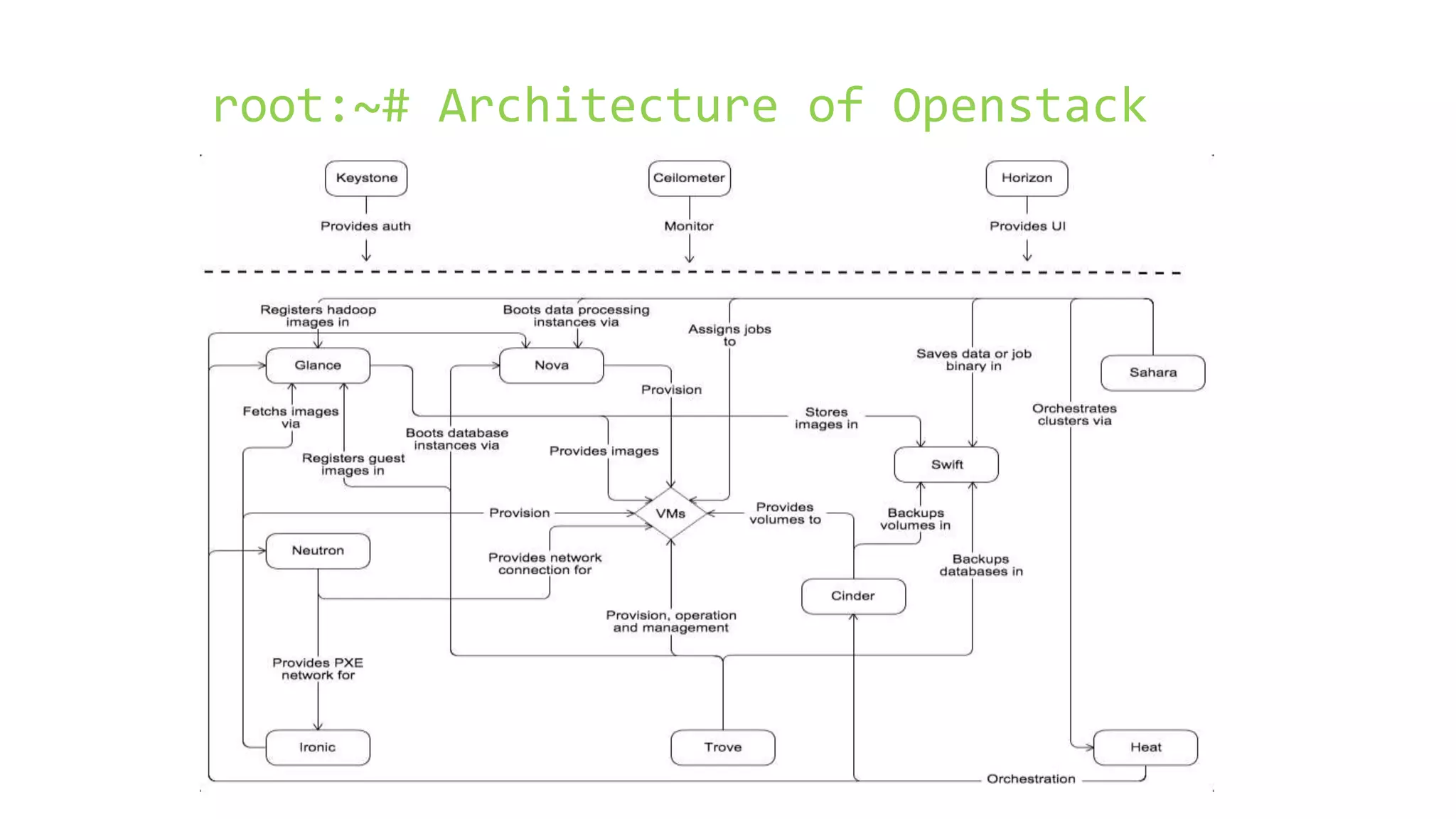
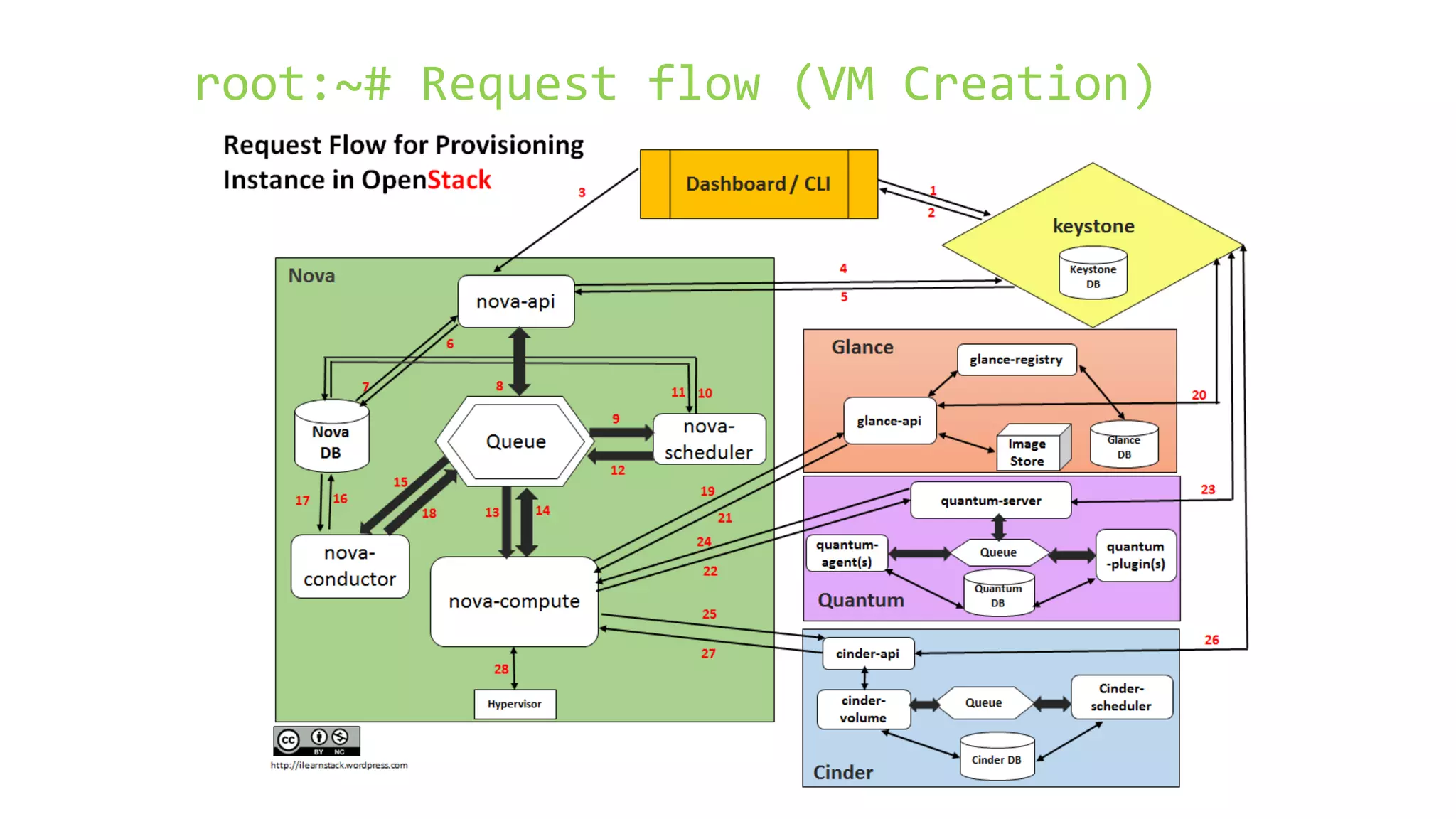
OpenStack is an open source cloud computing platform that consists of several components including Nova (compute), Glance (images), Keystone (identity), Neutron (networking), Swift (object storage), and Horizon (dashboard). It aims to be scalable, feature-rich, and simple to implement. OpenStack began as a collaboration between NASA and Rackspace to develop open source cloud computing software. It has since grown significantly with over 2000 companies contributing to its development and adoption.