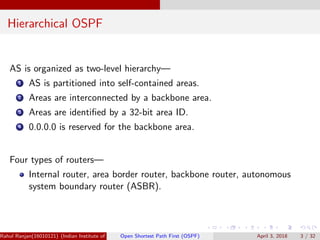
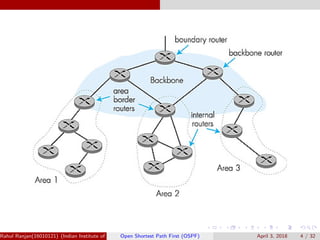
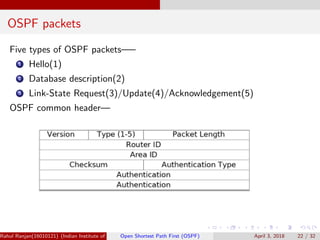
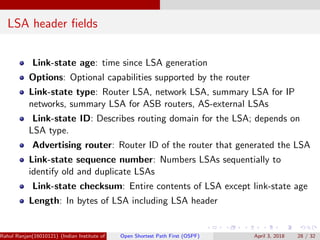
The document provides an overview of Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), a link-state routing protocol used in computer networks. It explains how routers exchange link-state information to construct a complete link-state database and build routing tables using algorithms like Dijkstra's. The document also covers OSPF's hierarchical structure, types of link-state advertisements, packet types, and performance considerations.