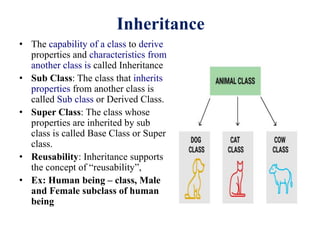
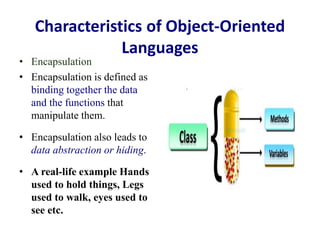
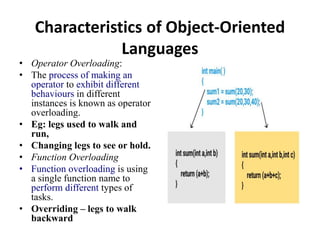
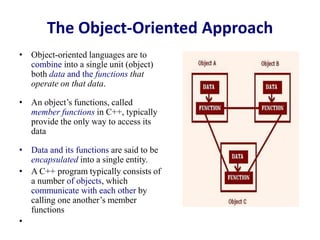
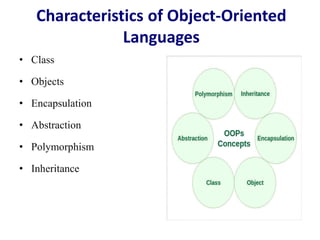
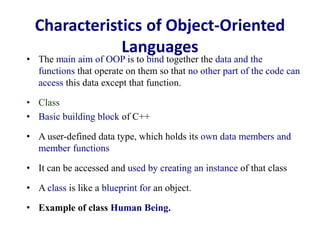
This document discusses the key concepts of object-oriented programming including classes, objects, encapsulation, inheritance, polymorphism, and abstraction. It provides examples like the human being class with male and female subclasses to illustrate these concepts. The main characteristics of OOP are to combine data and functions into single units called objects, and to define classes that act as templates for creating objects that can communicate by passing messages. Real-world analogies are used throughout to explain OOP concepts.



![Characteristics of Object-Oriented
Languages
• Object
• An object is an identifiable
entity with some
characteristics and
behaviour.
• An object is an instance of a
Class.
• When a class is defined, no
memory is allocated
• But when it is instantiated
(i.e. an object is created)
memory is allocated.
class person
{
char name[20];
int id;
public:
void getdetails(){}
};
int main()
{
person p1; // p1 is a object
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oopsconcepts-200728104255/85/Oops-concepts-7-320.jpg)