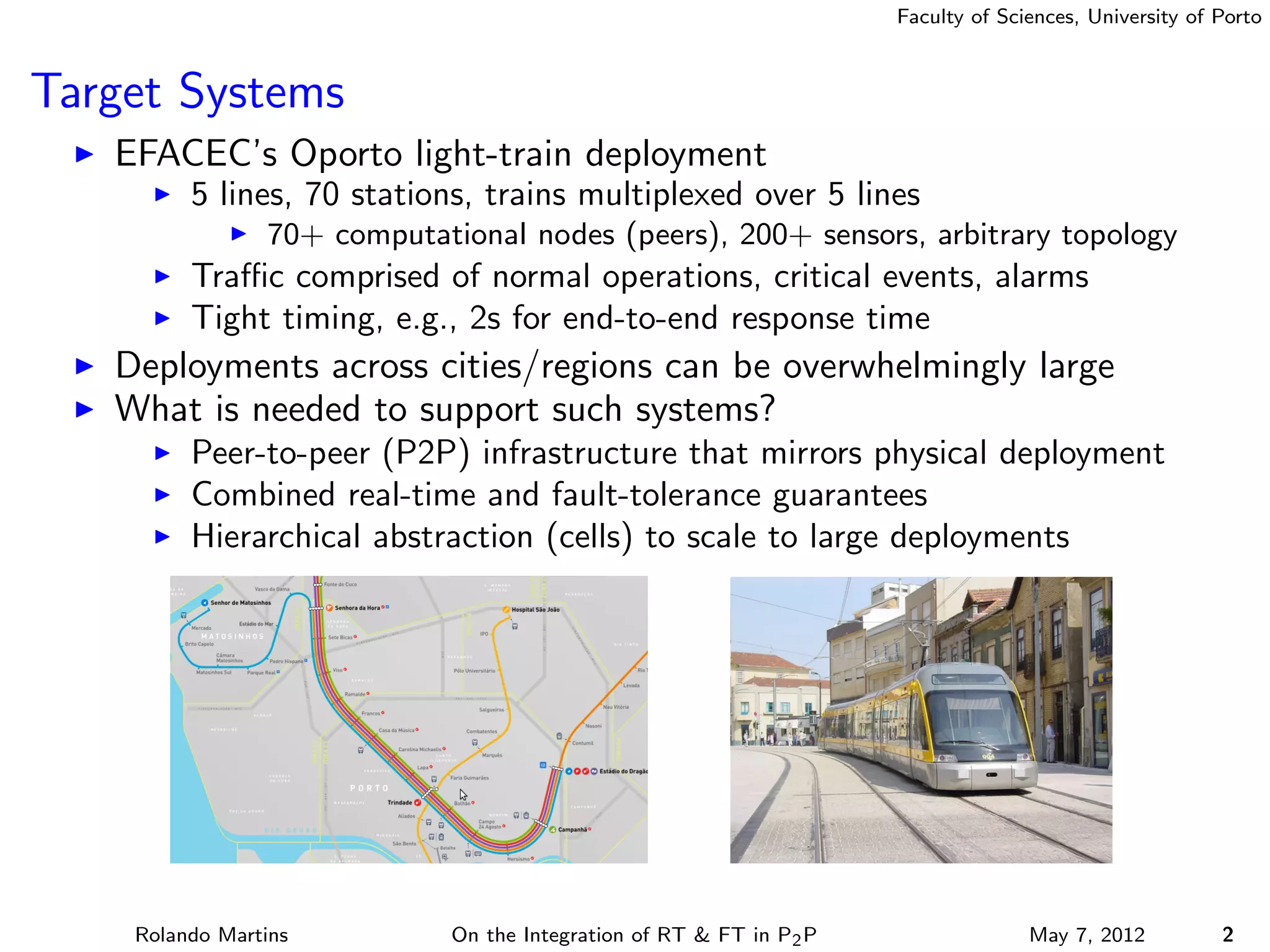
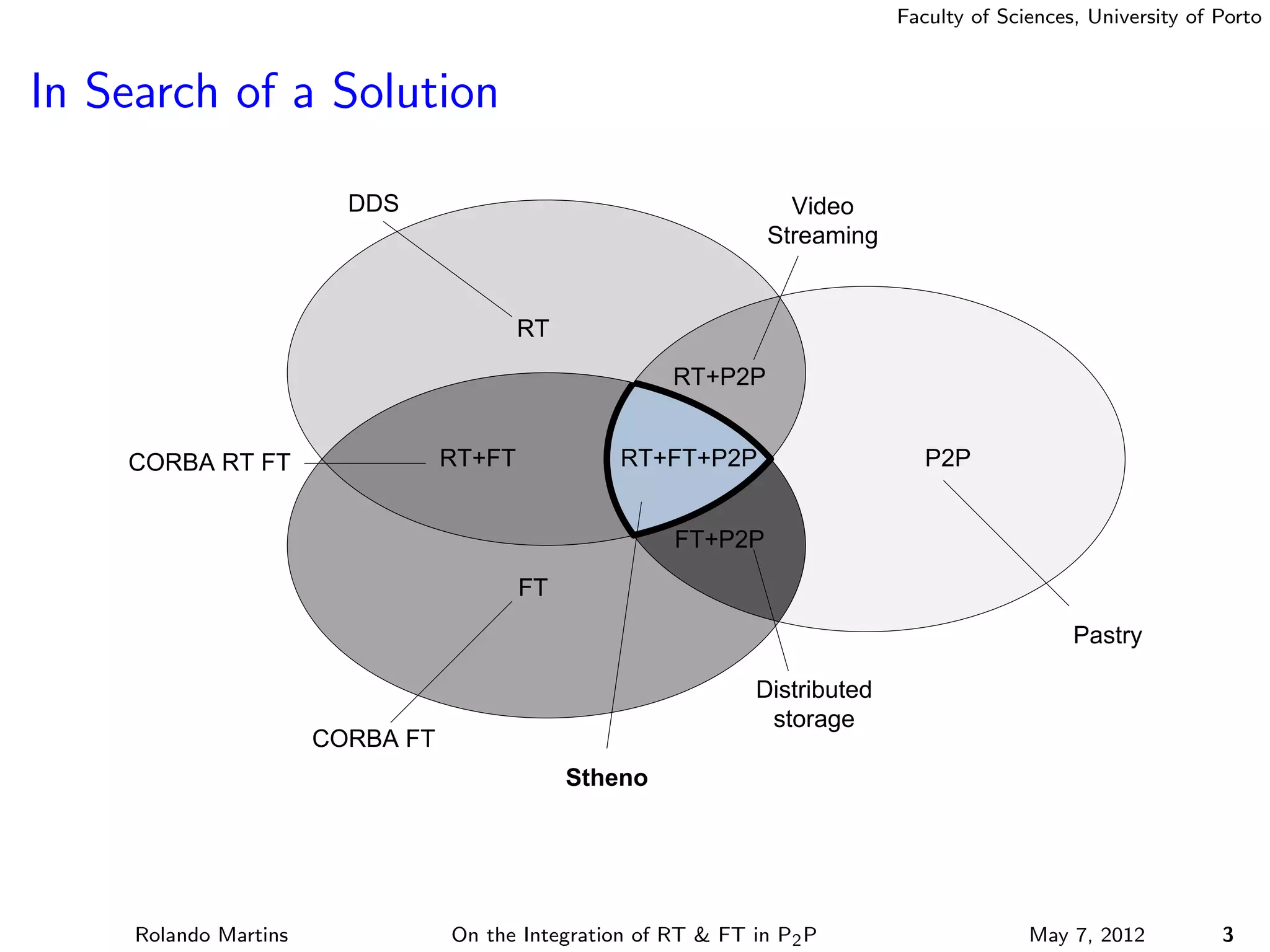
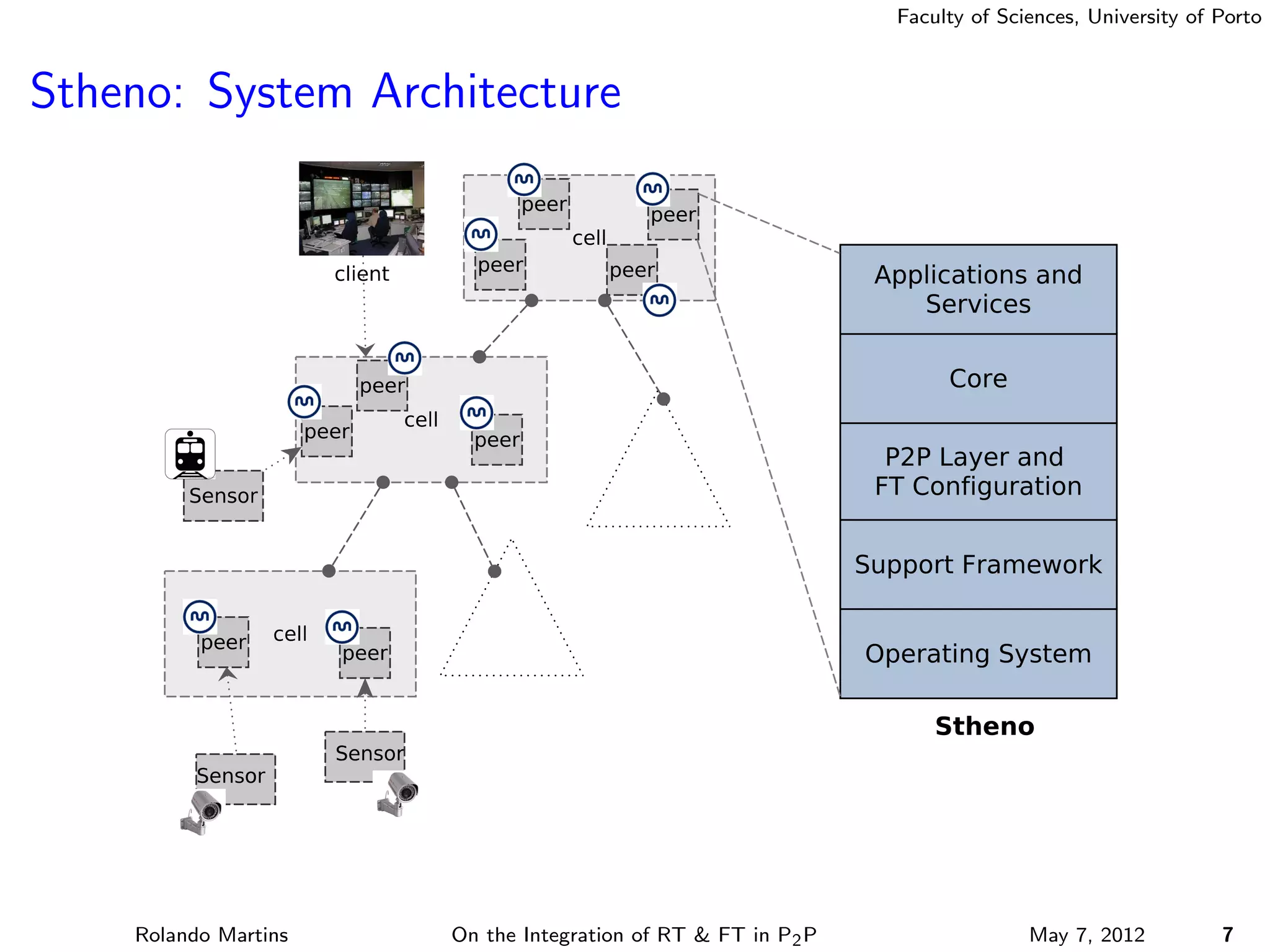
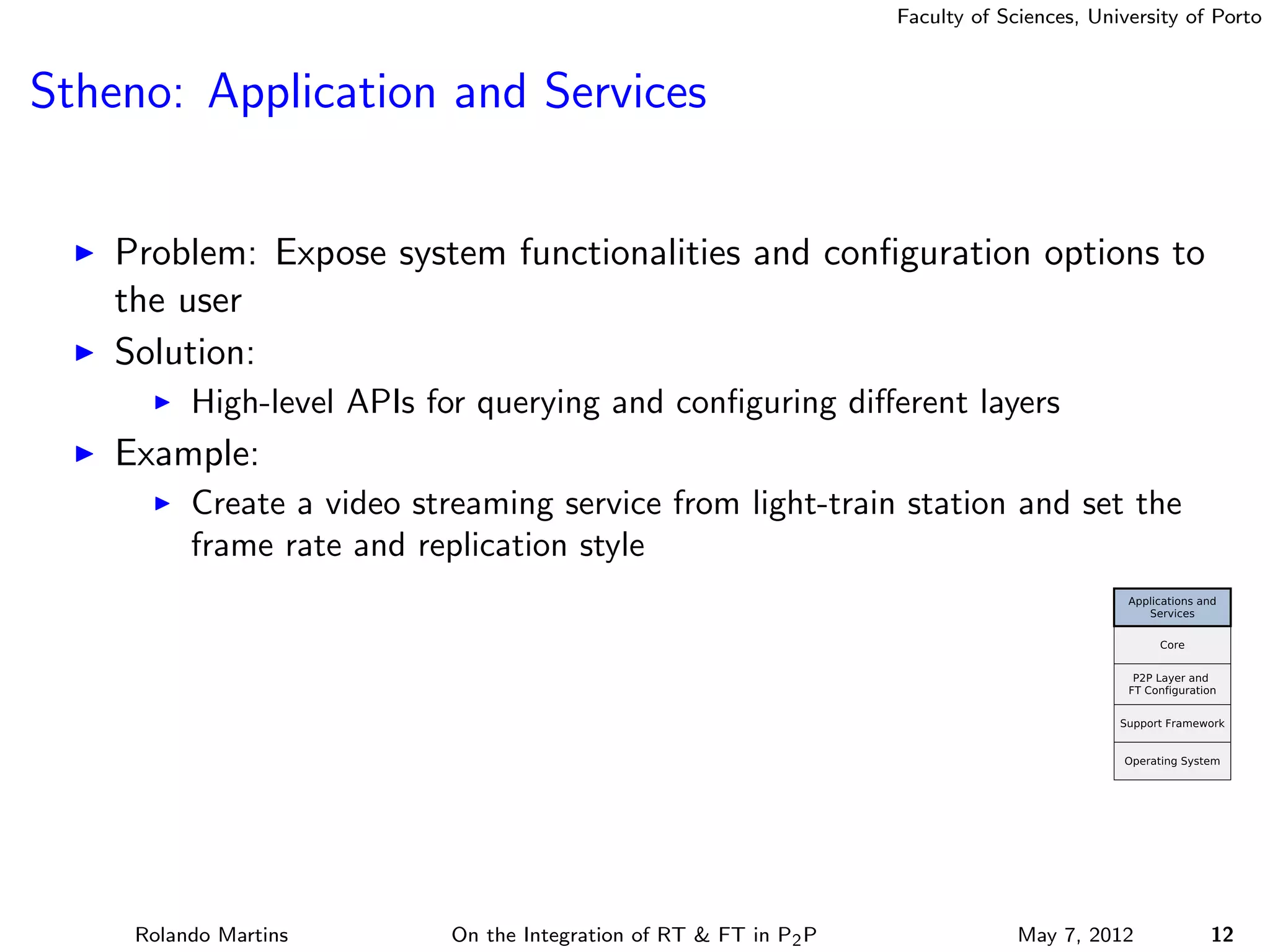
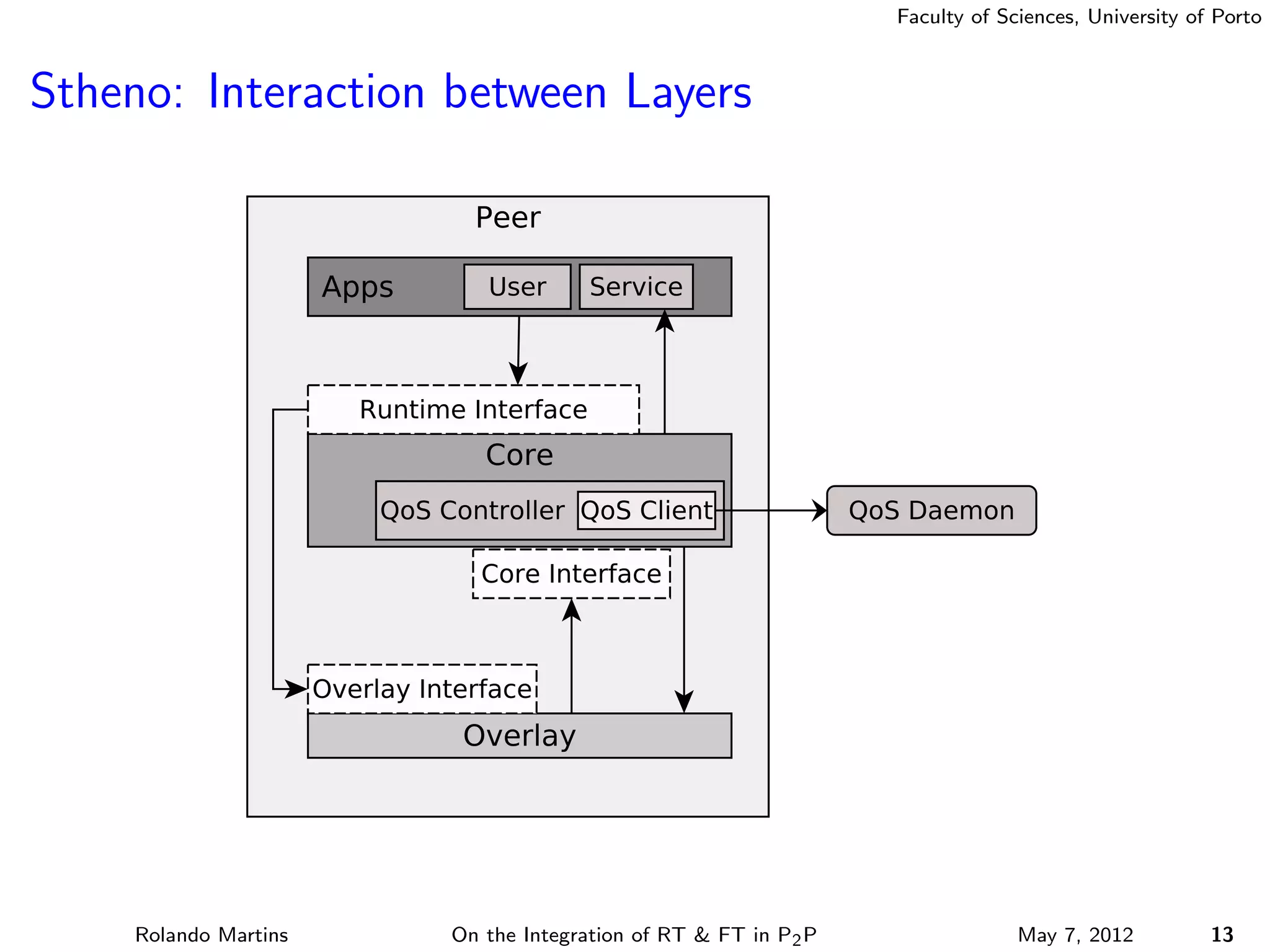
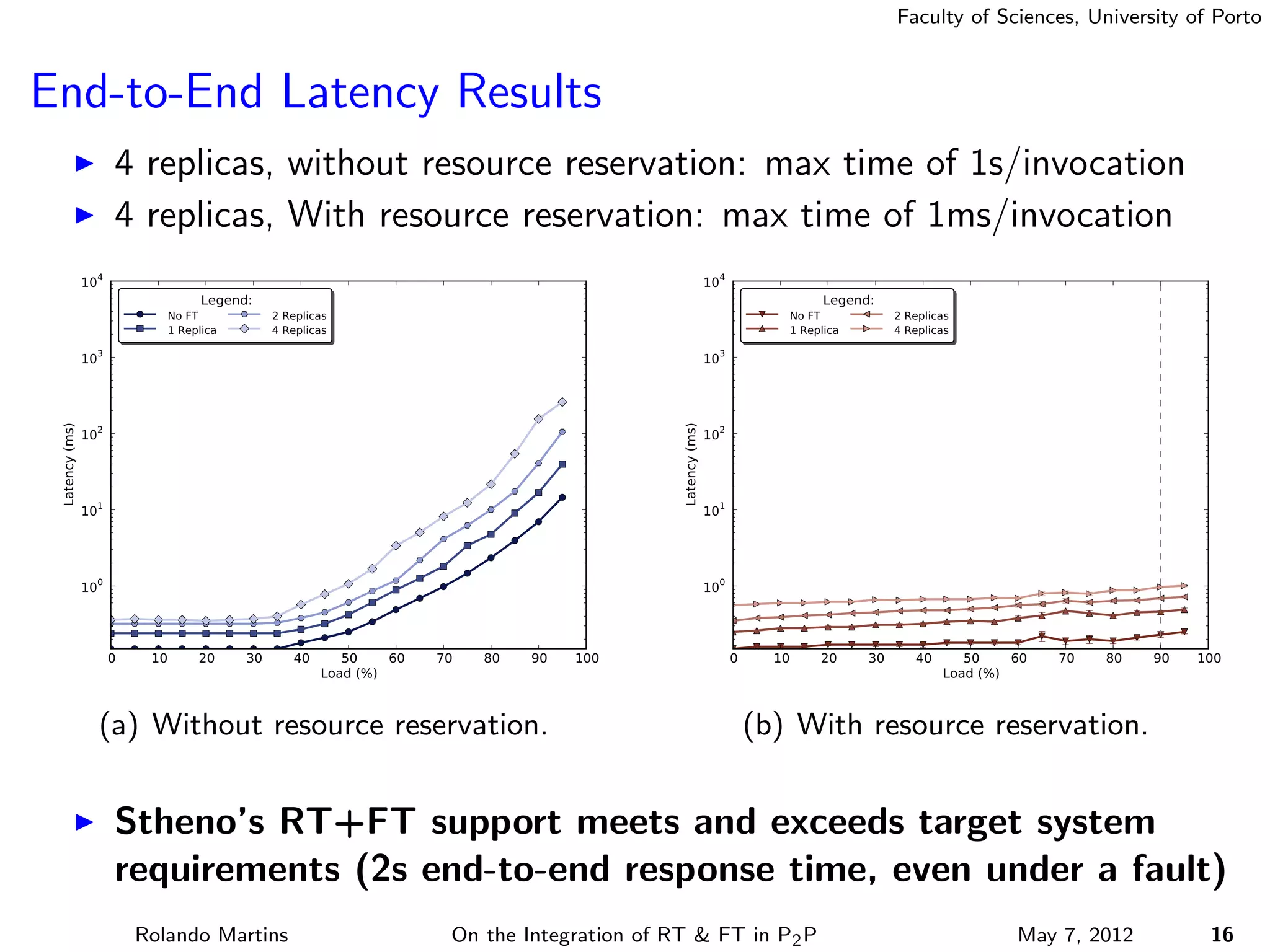
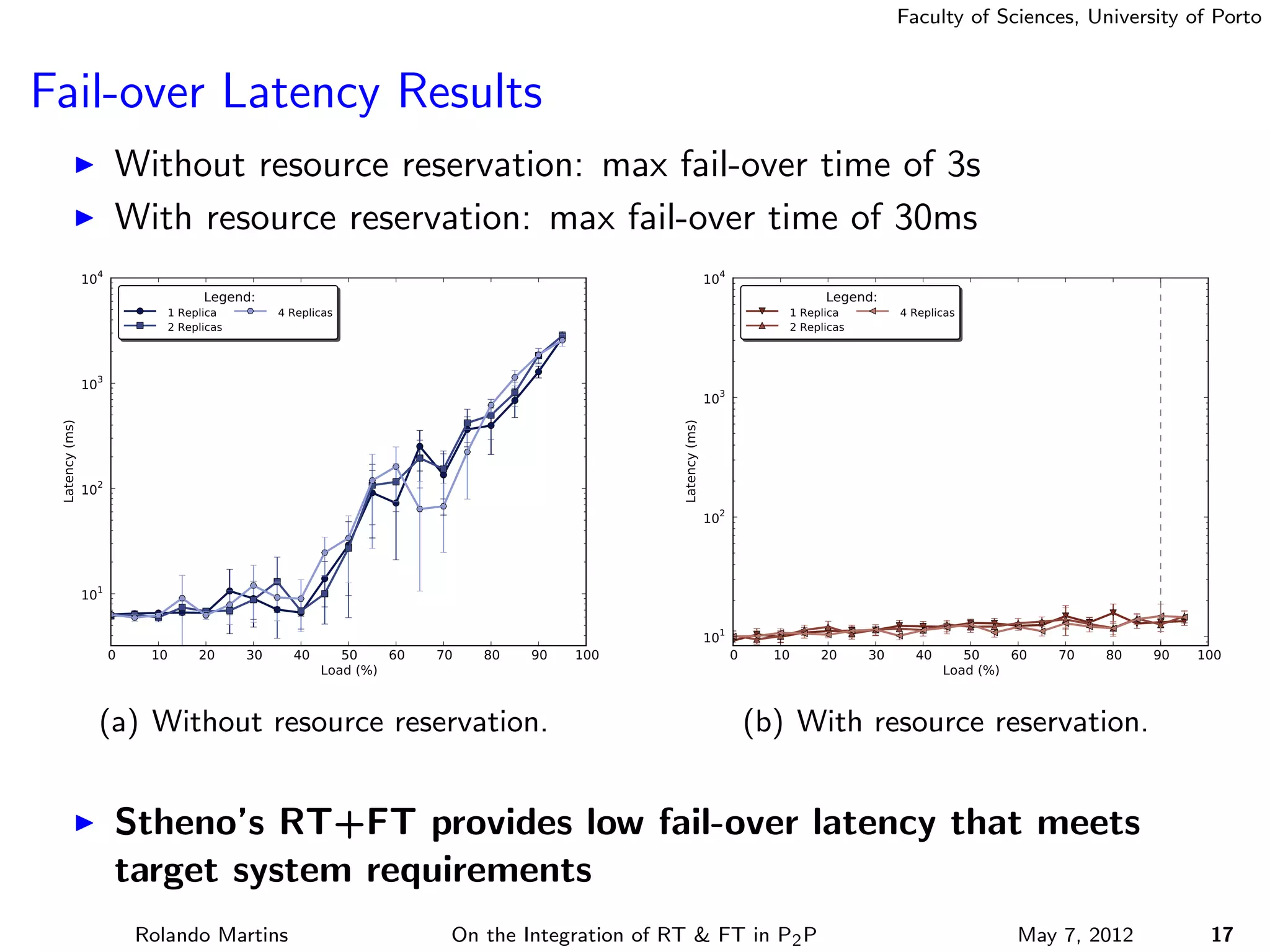
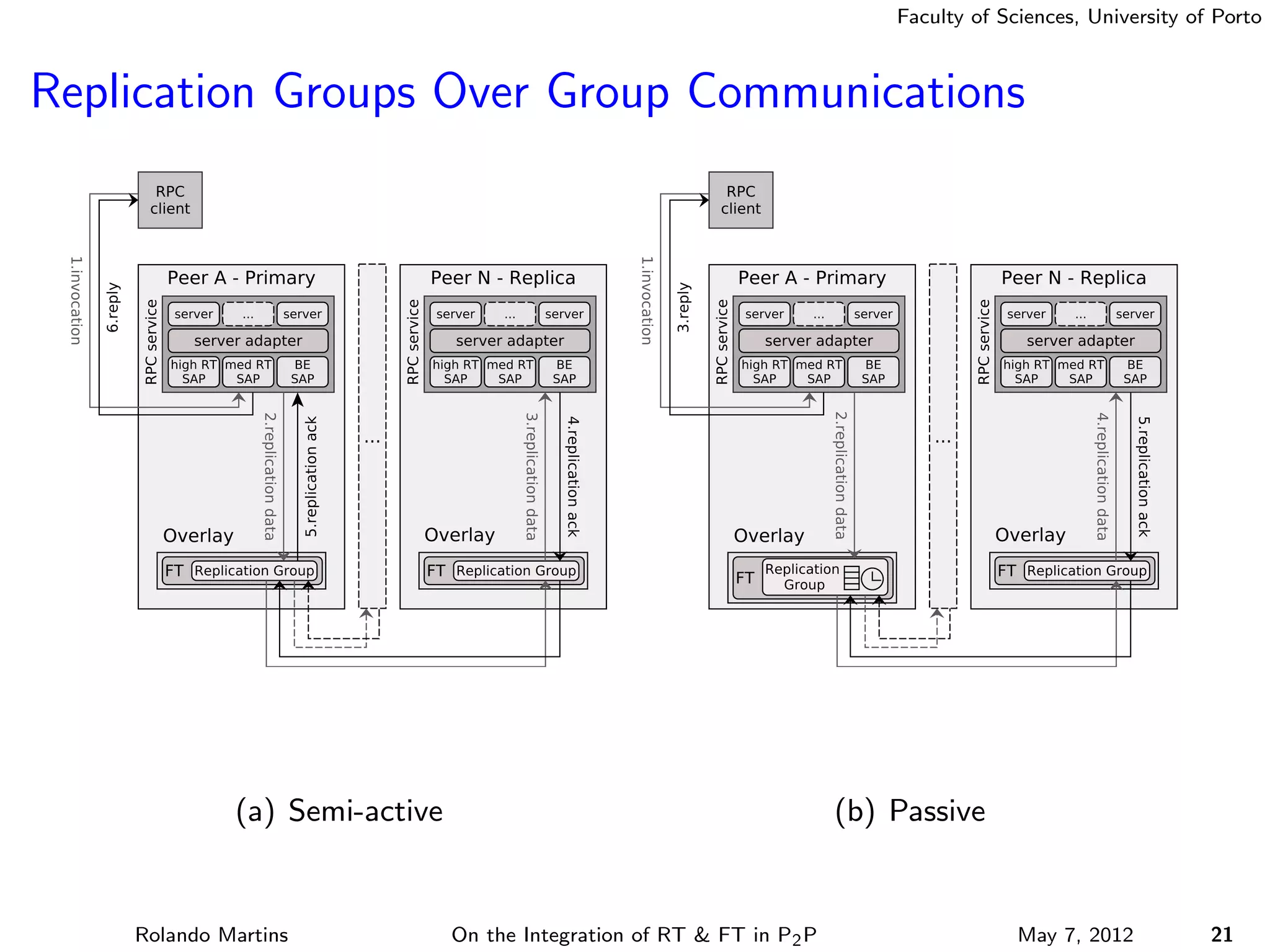
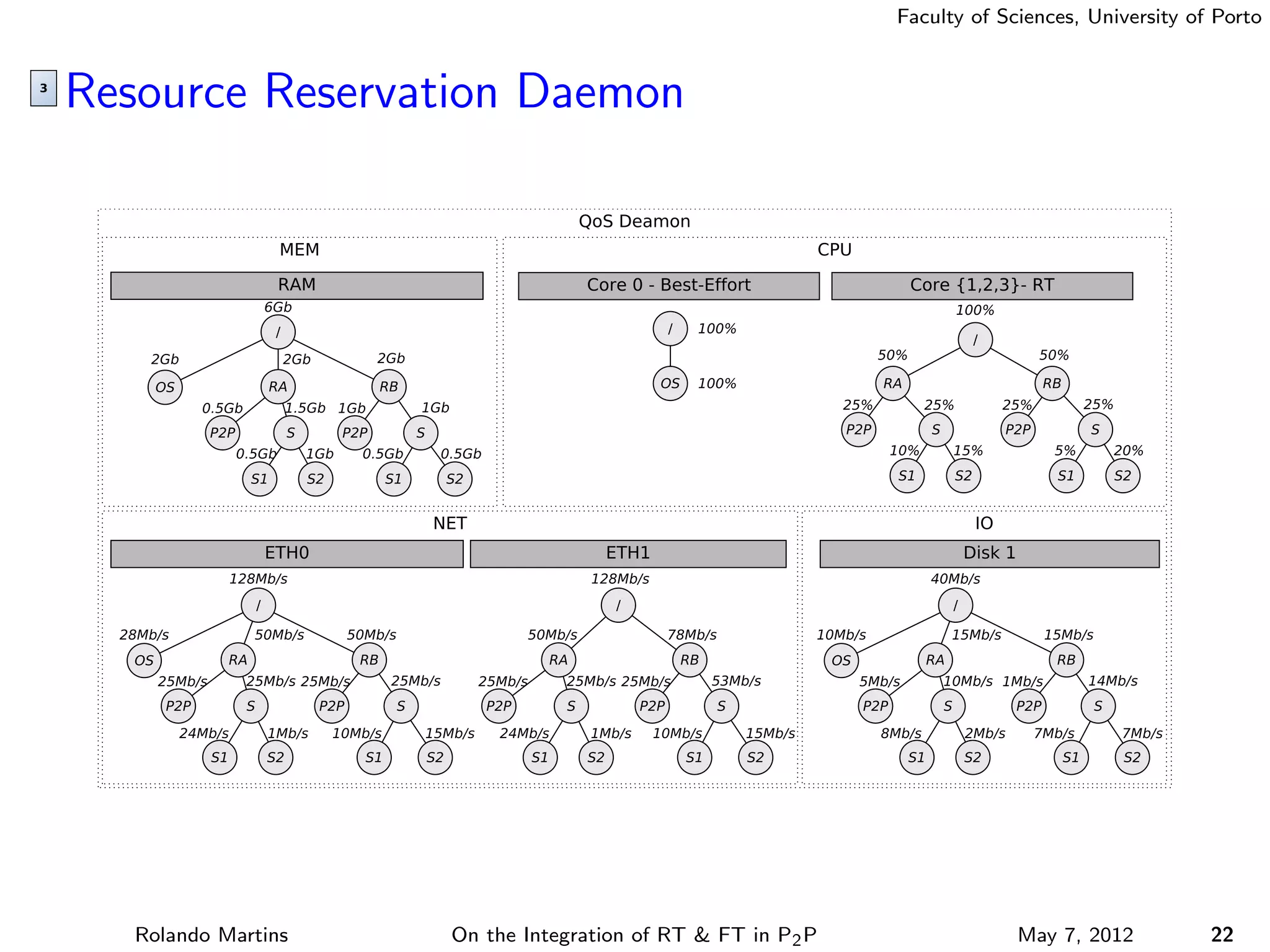
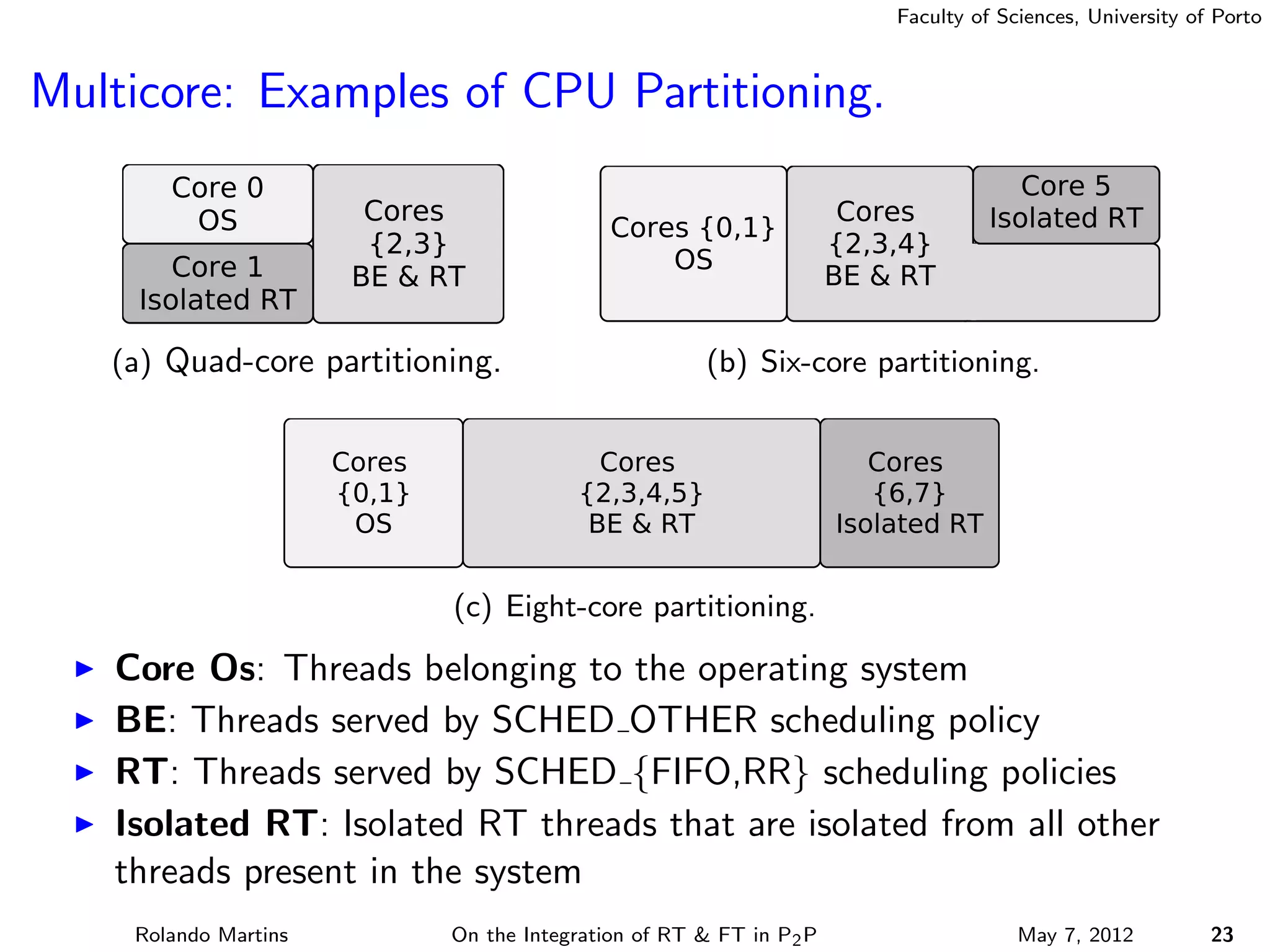
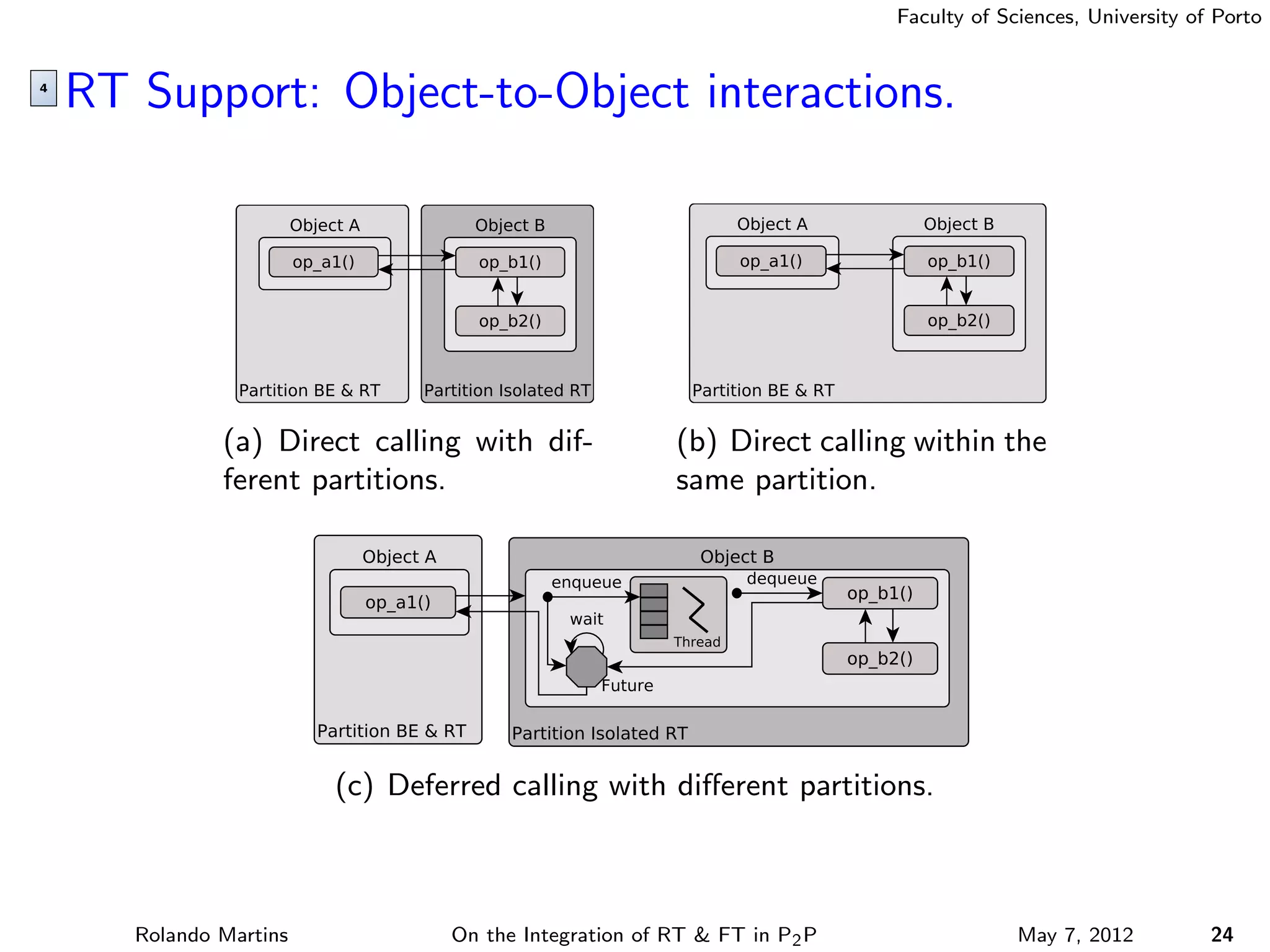
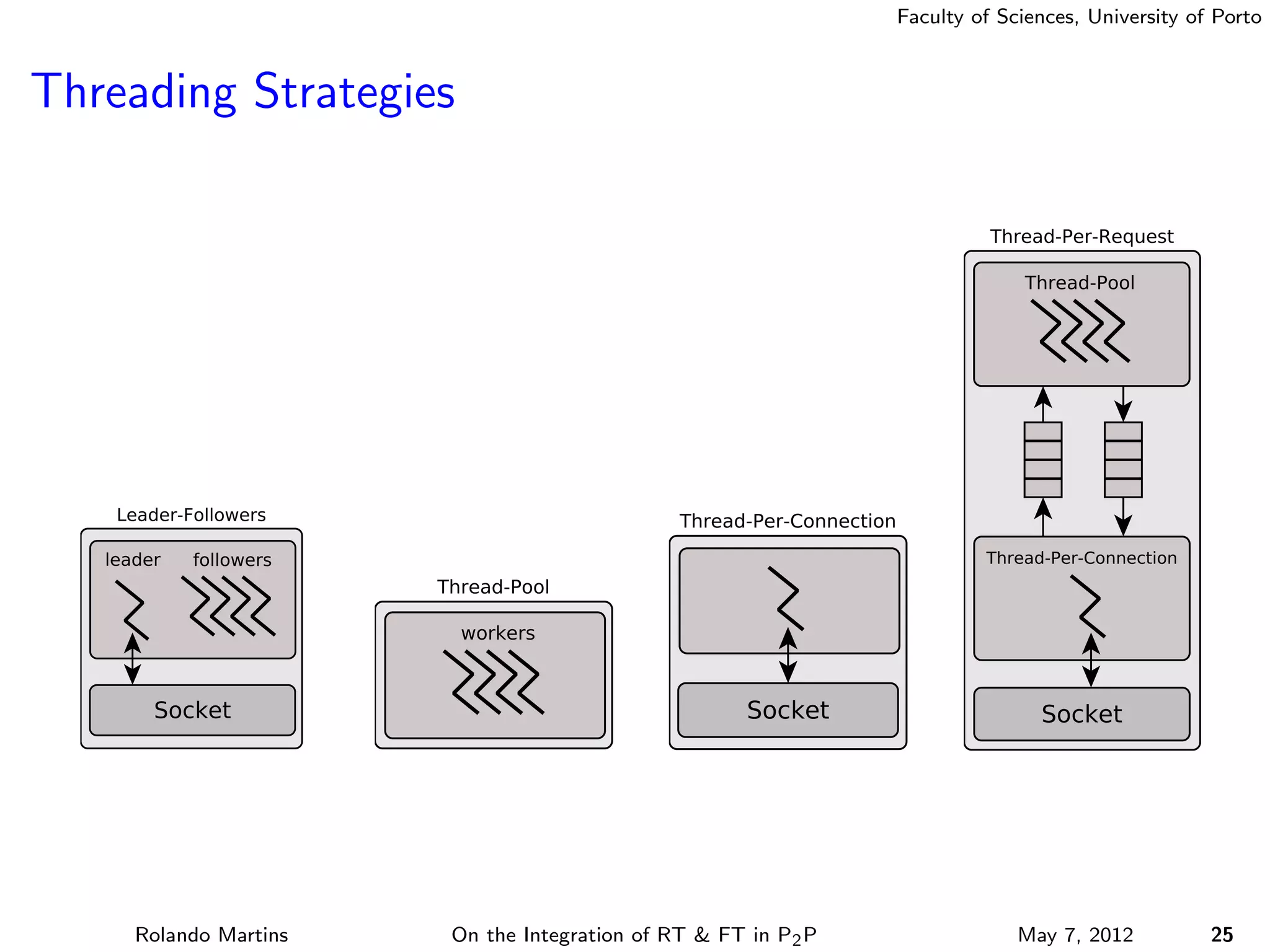
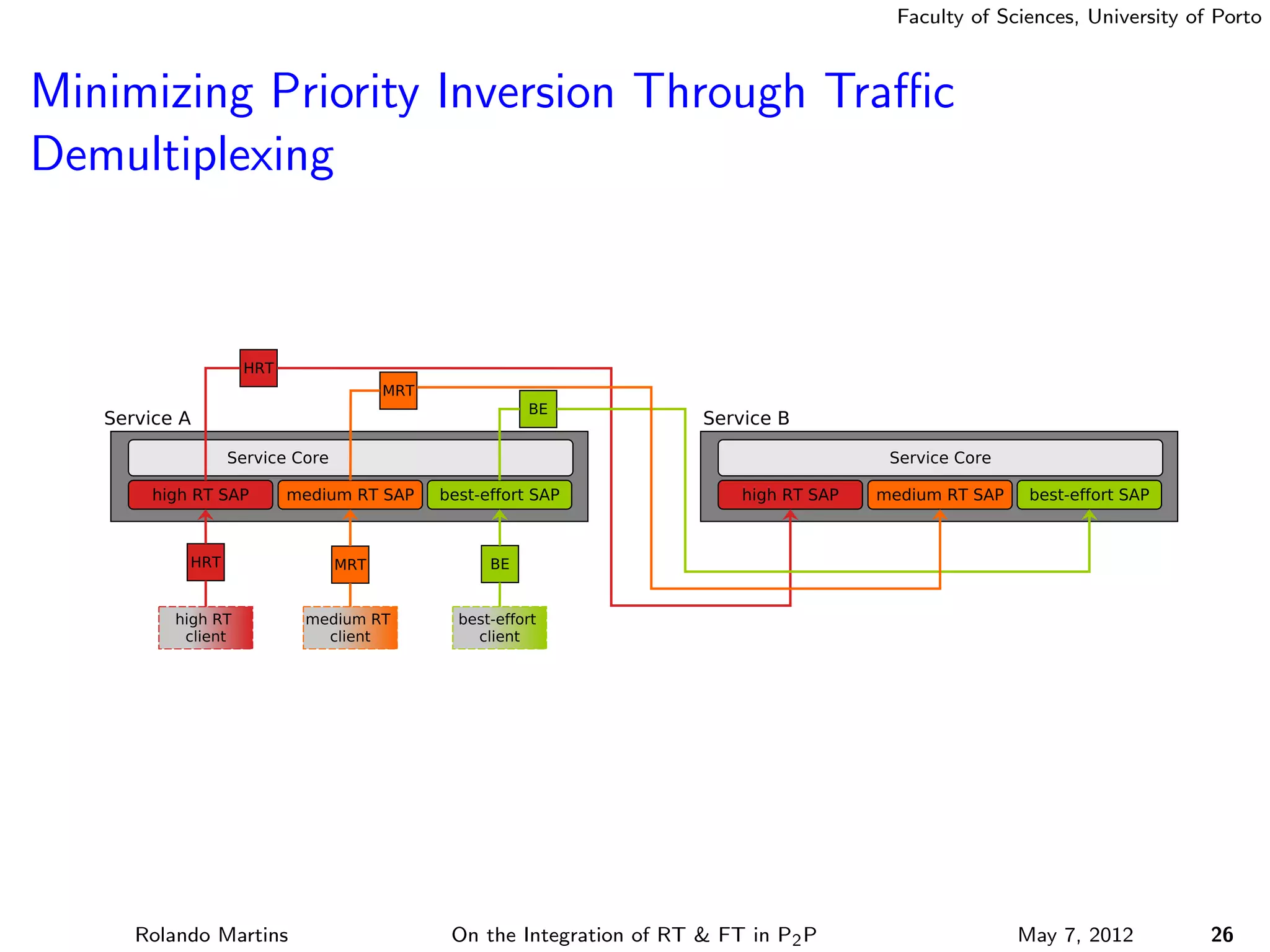
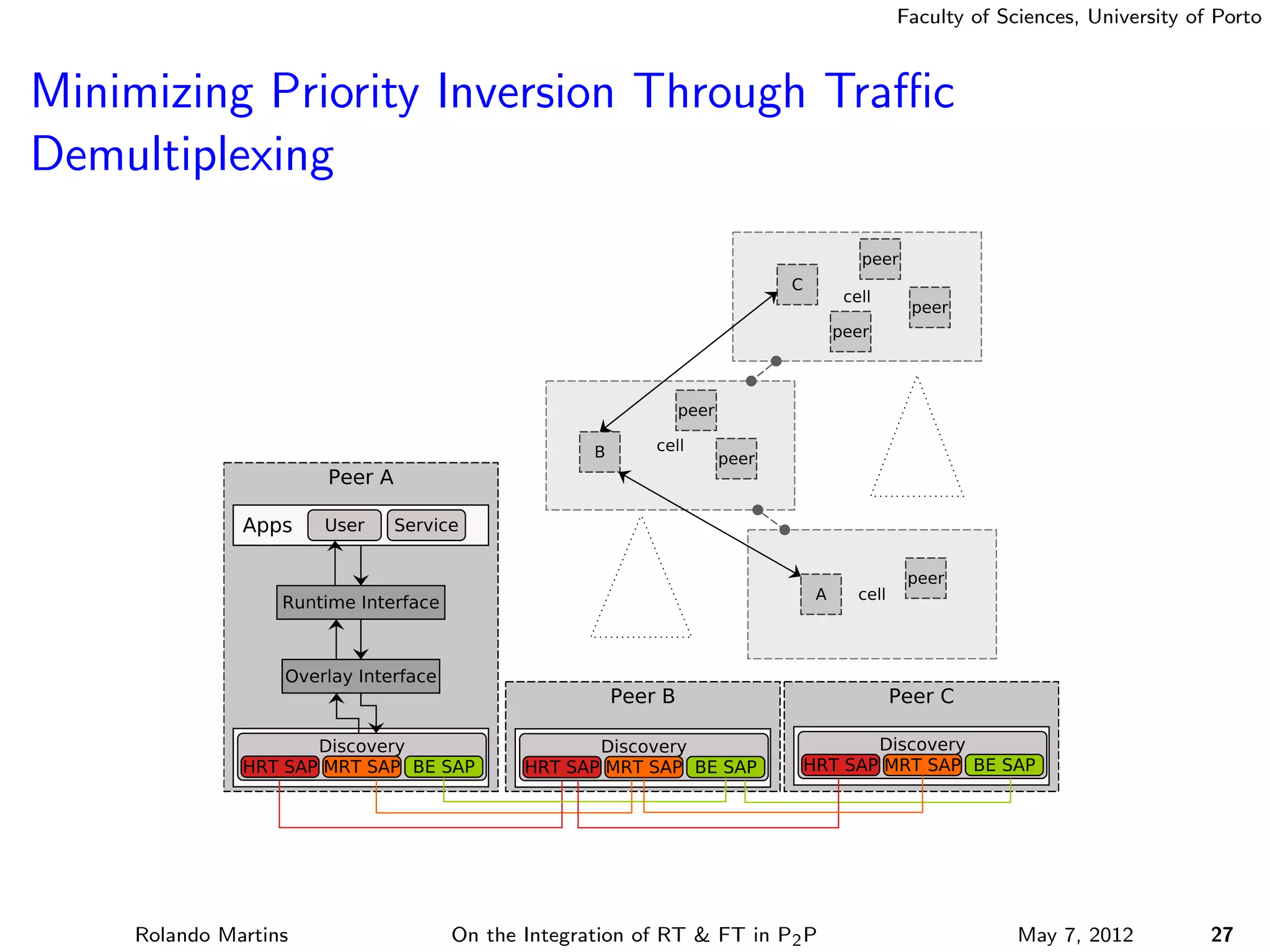
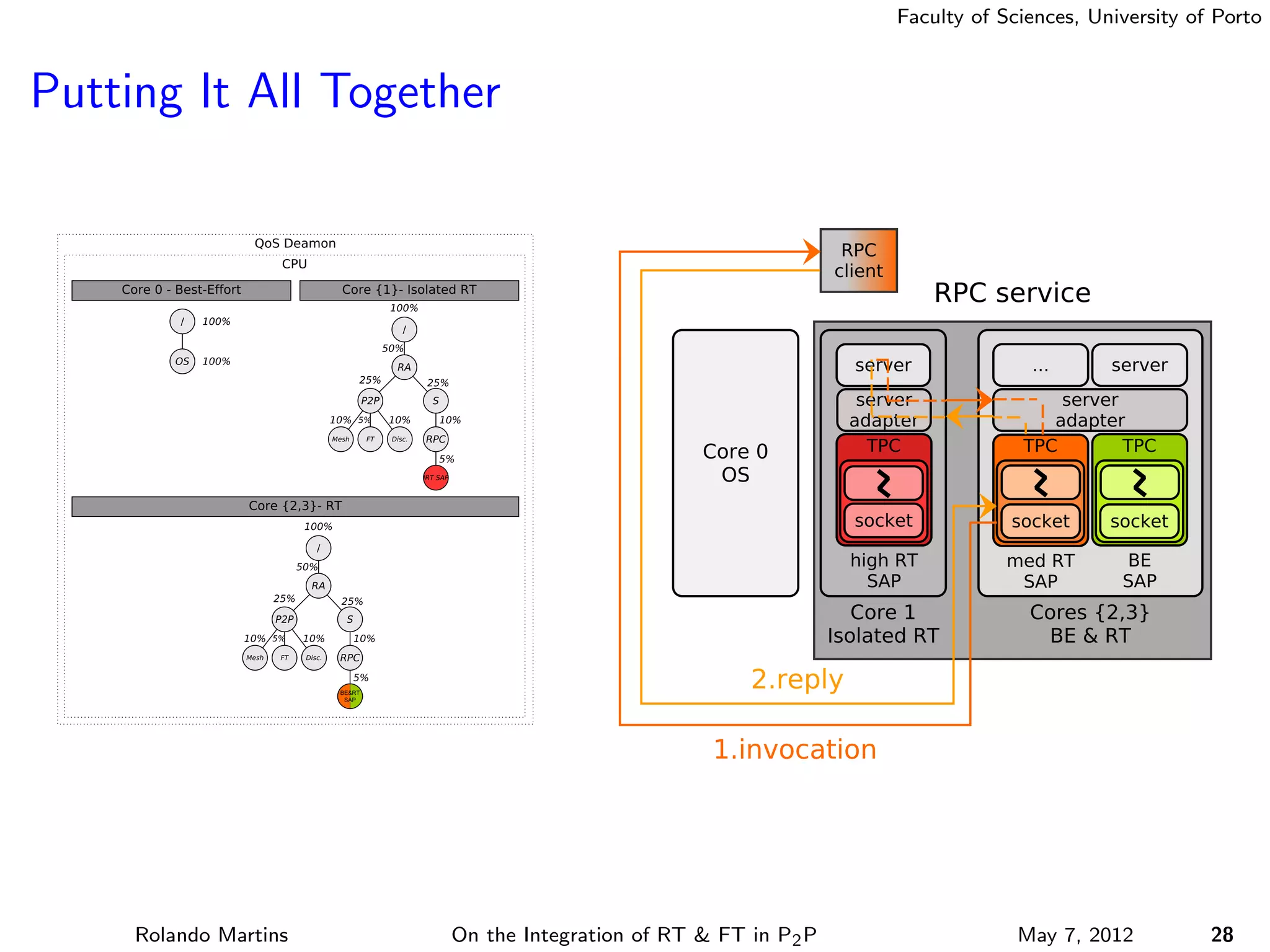
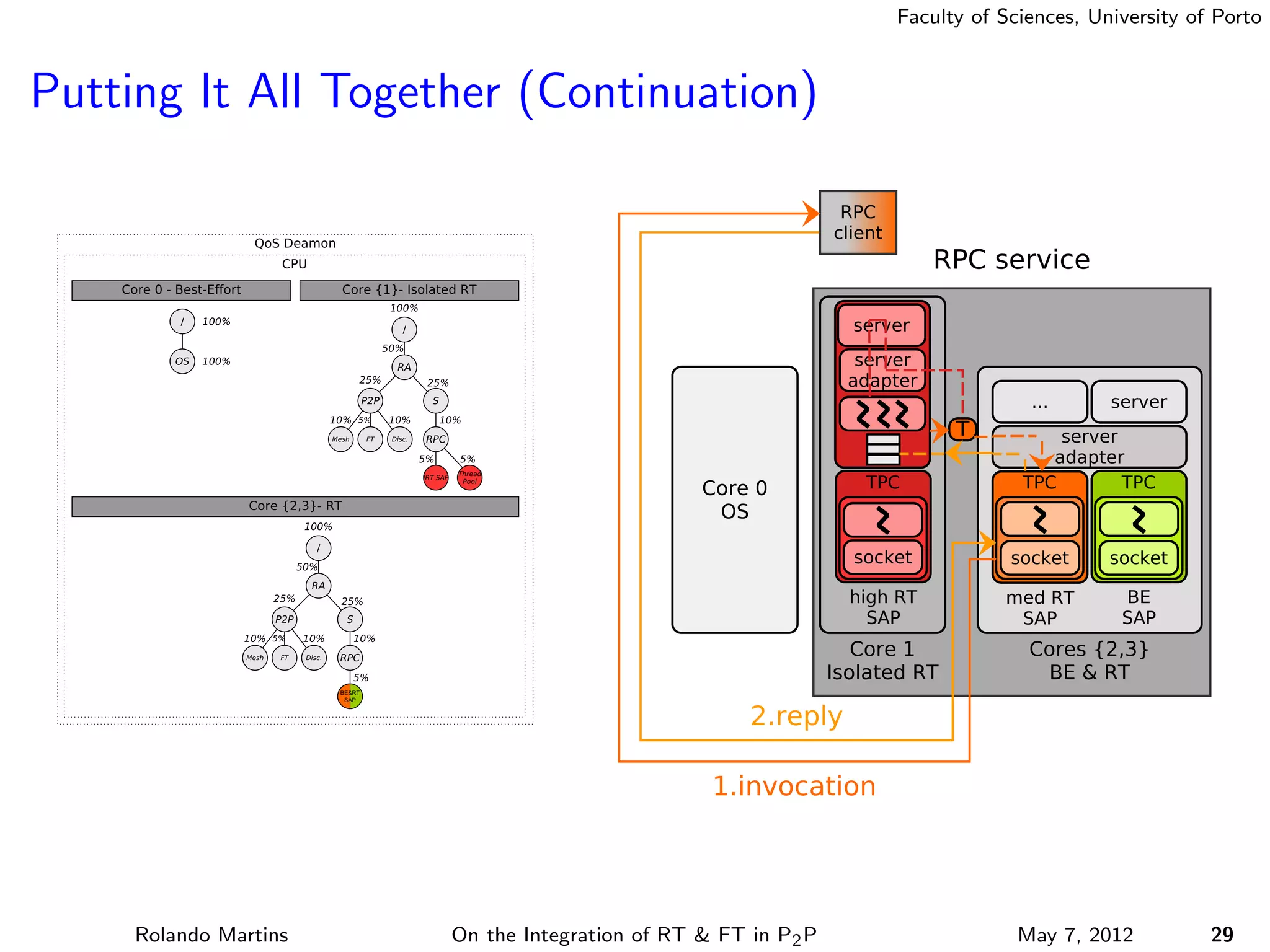
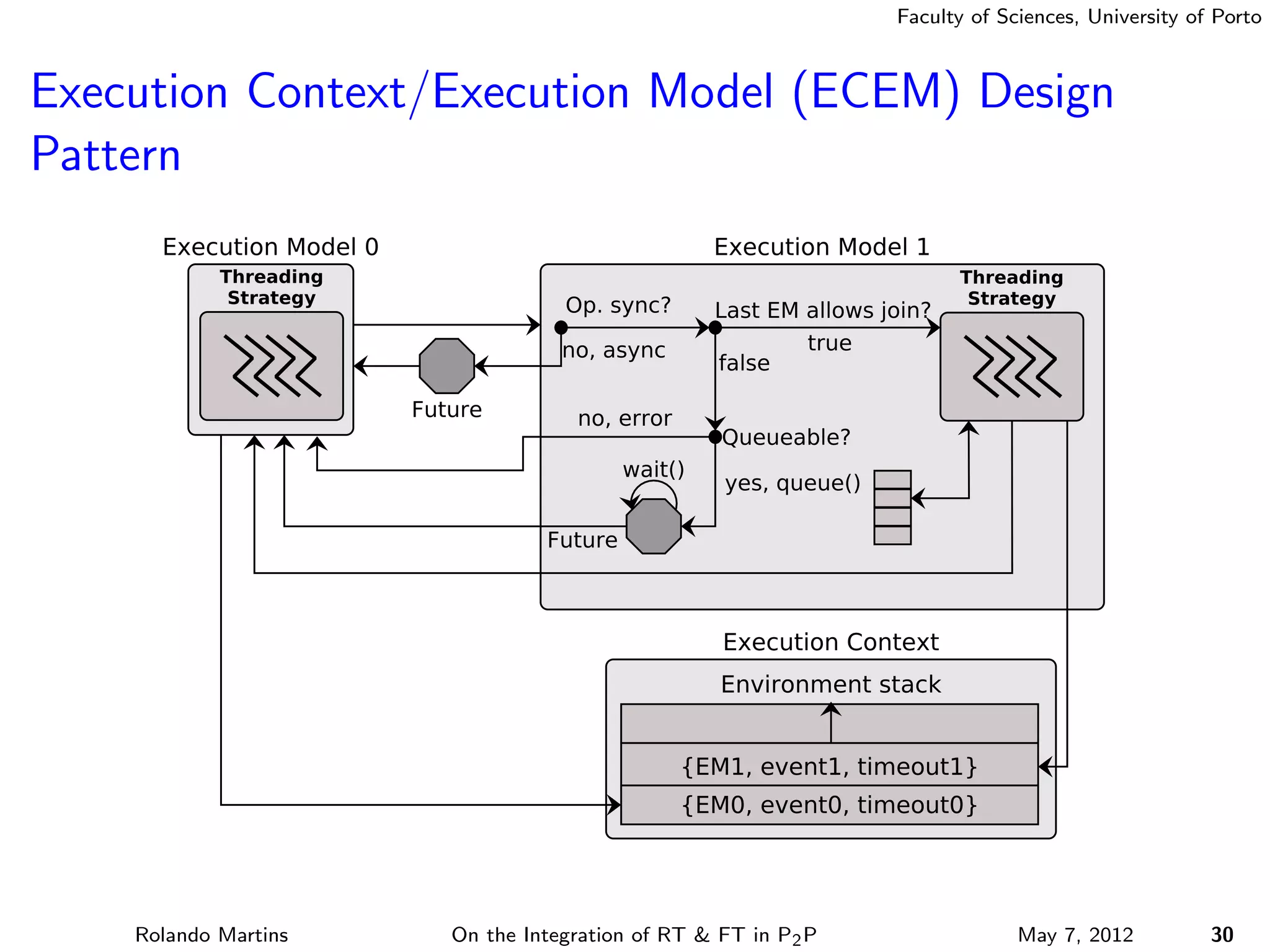
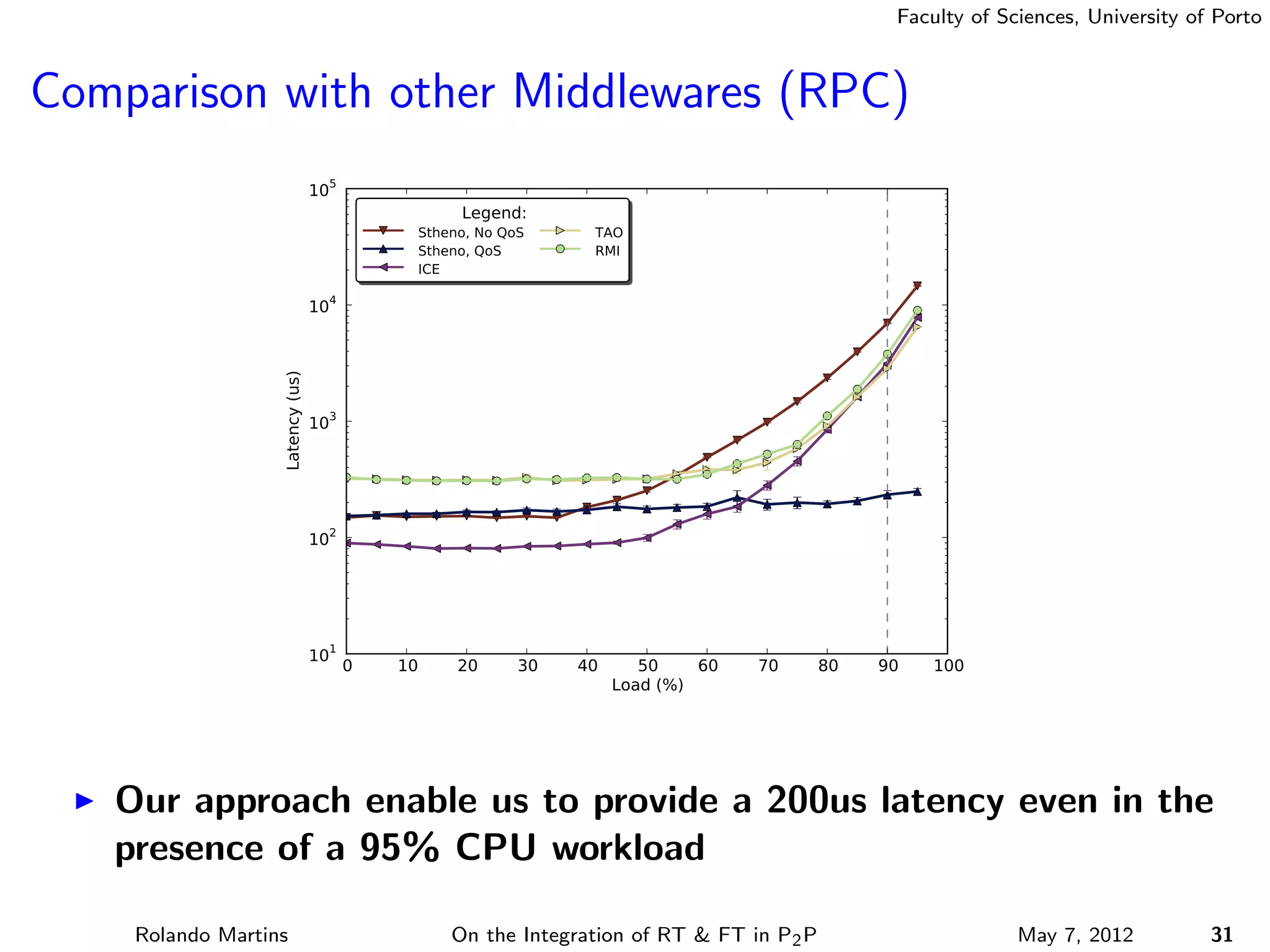
The document discusses the integration of real-time (RT) and fault-tolerance (FT) in peer-to-peer (P2P) middleware, particularly in the context of Efacec’s Oporto light-train deployment, which features a vast architecture with multiple computational nodes and sensors. It addresses the challenges and opportunities of achieving RT and FT, presenting a system named Stheno that effectively supports varying soft-RT requirements and fault configurations while demonstrating superior end-to-end and fail-over latency performance in empirical evaluations. The document outlines technical solutions, including resource reservation and a high-level API for configuration, showcasing the middleware's efficiency in meeting demanding system requirements during normal operations and fault scenarios.