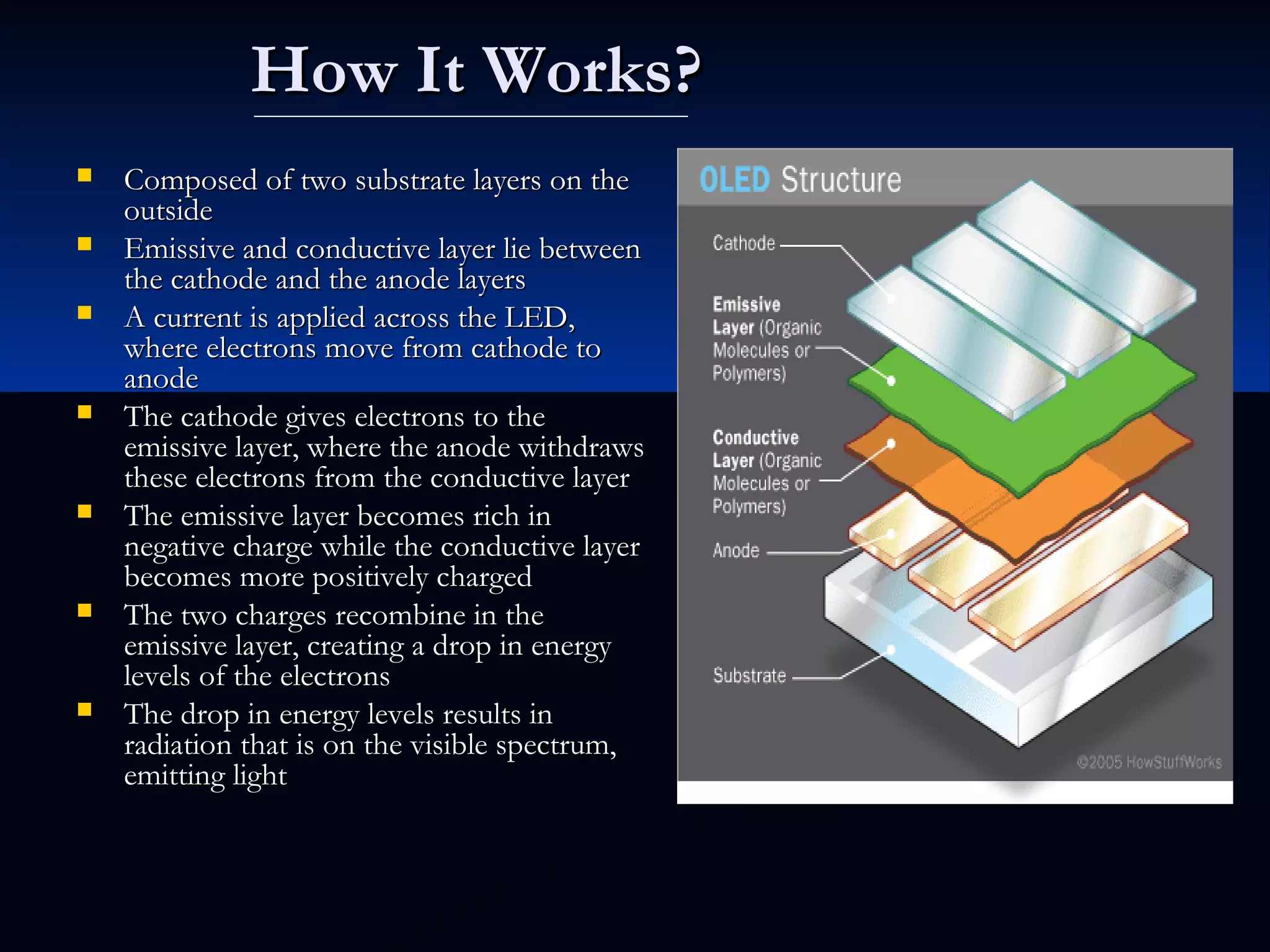
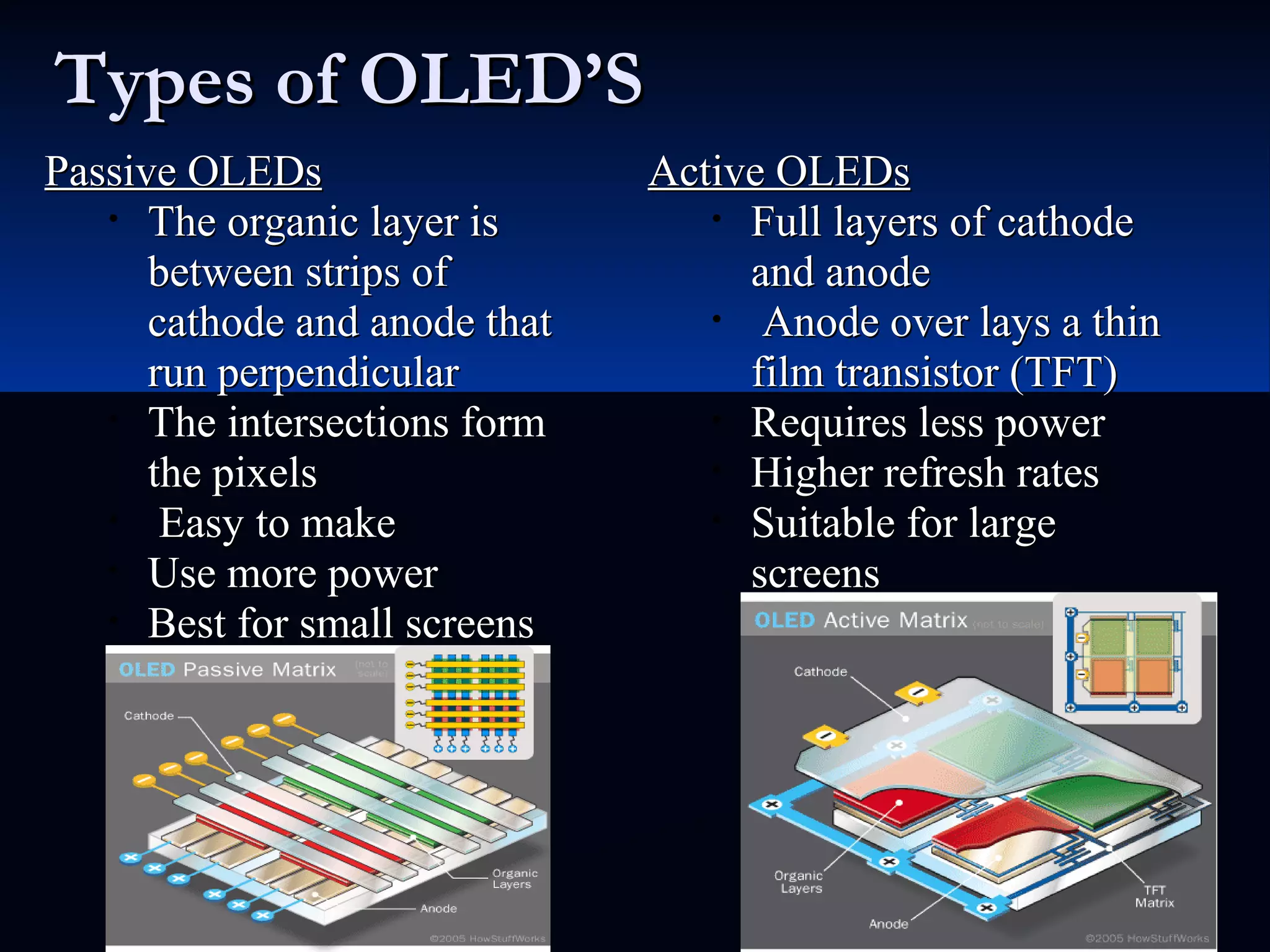
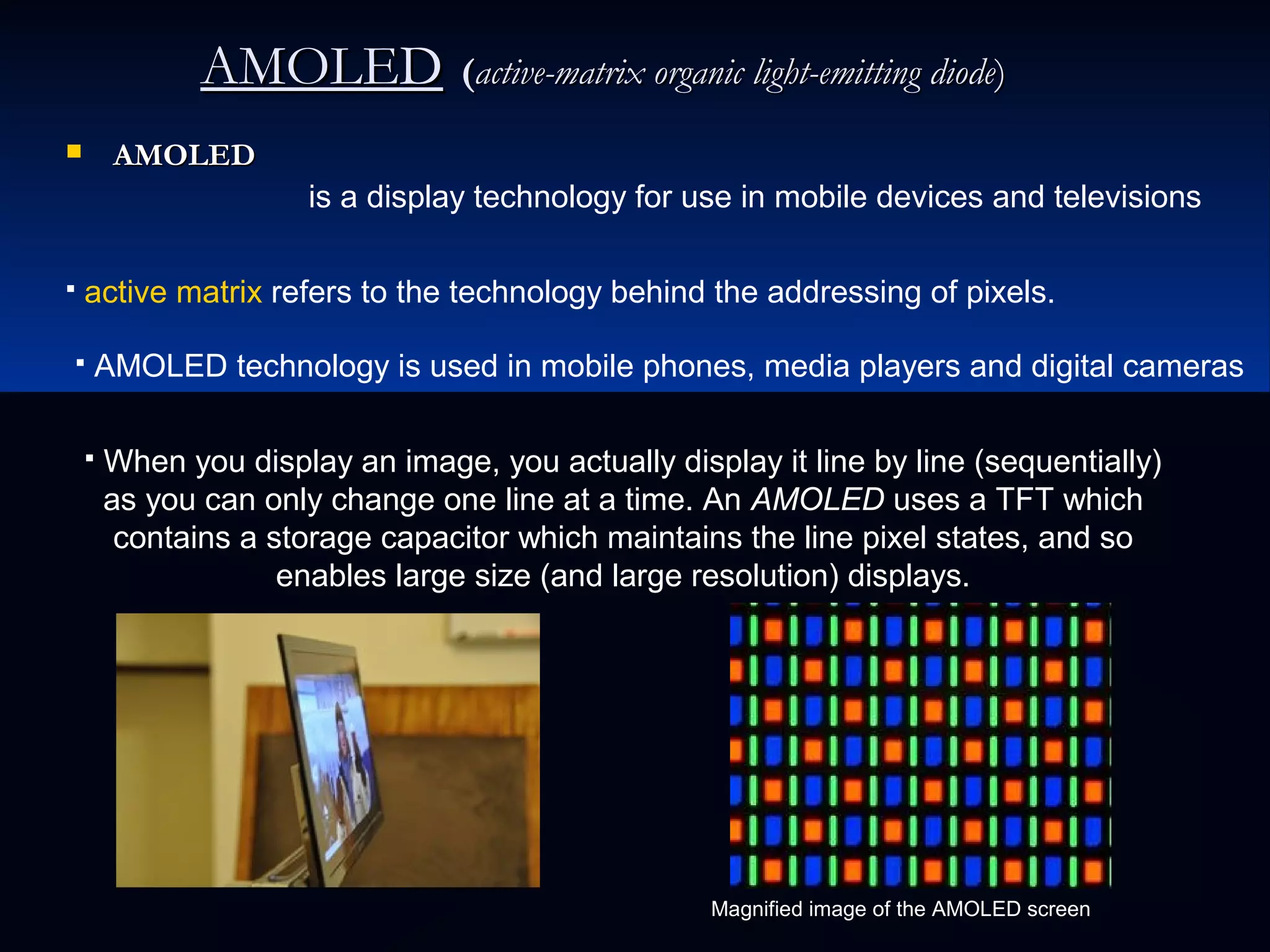
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) is a light emitting technology that uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current is applied. It has advantages over LCD/plasma like higher contrast, thinner displays, and wider viewing angles. There are different types like passive matrix OLED and active matrix OLED. AMOLED is an active matrix OLED used in phones. AMOLED has advantages like true black, faster response time, and can be made flexible/transparent. Popular applications include phones, TVs, and lighting panels.