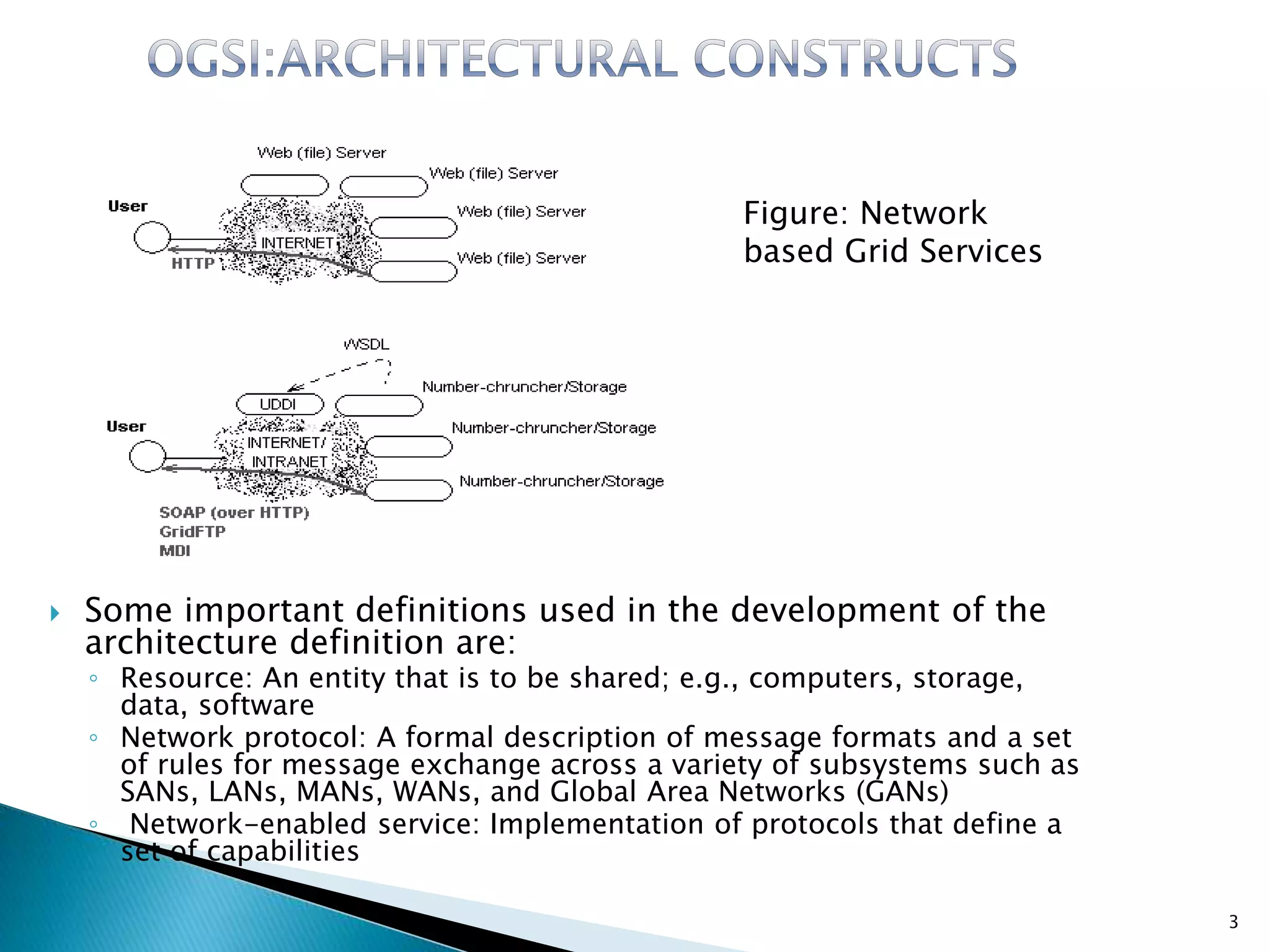
This document defines key terms used in developing a service-oriented grid architecture, including resource, network protocol, network-enabled service, API, SDK, and syntax. It describes an API as a specification for routines to facilitate application development, providing portability but not interoperability. A SDK is defined as an instantiation of an API that may include libraries and tools. Syntax is defined as rules for encoding information.


![ API: A specification for a set of routines to facilitate application development.
Examples include GSS API (Generic Security Service API) and MPI
(Message Passing Interface). A protocol can have multiple APIs (e.g., TCP/IP
APIs include BSD sockets, Winsock, and System V streams). The protocol
provides interoperability: programs using different APIs can exchange information
and one does not need to know the remote APIs. An API can have
multiple protocols. For example, MPI provides portability: any correct program
compiles and runs on a platform. MPI does not provide interoperability:
all processes must link to same SDK (e.g., MPICH and LAM versions of
MPI).
Software Development Kit (SDK): A particular instantiation of an API (it
may consists of libraries and tools). Examples of SDKs include MPICH and
Motif Widgets.
Syntax: Rules for encoding information. Examples include XML, Condor
ClassAds, Globus RSL, X.509 certificate format [Request For Comments
(RFC) 2459], Cryptographic Message Syntax (RFC 2630), and ASN.1. Syntaxes
are distinct from protocols in the sense that a syntax may be used by
many protocols (e.g., XML), and be useful for other purposes. Syntaxes may
be layered (e.g., Condor ClassAds uses XML, which uses ASCII.)
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ogsi-architecturalconstructs-190206160939/75/Ogsi-architectural-constructs-4-2048.jpg)
![ API: A specification for a set of routines to facilitate application
development. Examples include GSS API (Generic Security Service
API) and MPI (Message Passing Interface). A protocol can have
multiple APIs (e.g., TCP/IP APIs include BSD sockets, Winsock, and
System V streams). The protocol provides interoperability:
programs using different APIs can exchange information and one
does not need to know the remote APIs. An API can have multiple
protocols. For example, MPI provides portability: any correct
program compiles and runs on a platform. MPI does not provide
interoperability: all processes must link to same SDK (e.g., MPICH
and LAM versions of MPI).
Software Development Kit (SDK): A particular instantiation of an API
(it may consists of libraries and tools). Examples of SDKs include
MPICH and Motif Widgets.
Syntax: Rules for encoding information. Examples include XML,
Condor ClassAds, Globus RSL, X.509 certificate format [Request For
Comments (RFC) 2459], Cryptographic Message Syntax (RFC 2630),
and ASN.1. Syntaxes are distinct from protocols in the sense that a
syntax may be used by many protocols (e.g., XML), and be useful
for other purposes. Syntaxes may be layered (e.g., Condor ClassAds
uses XML, which uses ASCII.)
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ogsi-architecturalconstructs-190206160939/75/Ogsi-architectural-constructs-5-2048.jpg)