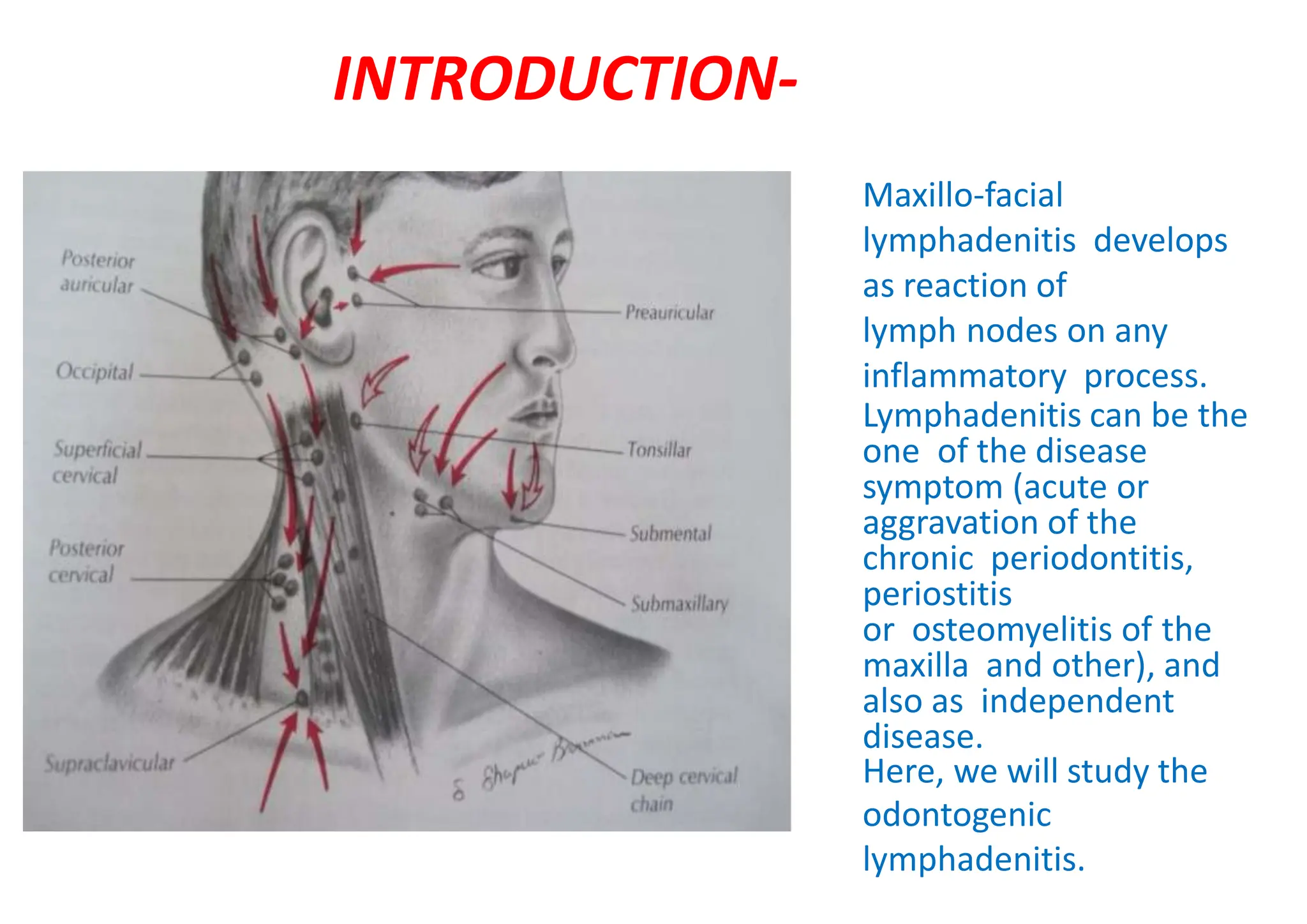
1. Odontogenic lymphadenitis develops as a reaction of lymph nodes to any inflammatory process, such as periodontitis, periostitis, or osteomyelitis of the maxilla.
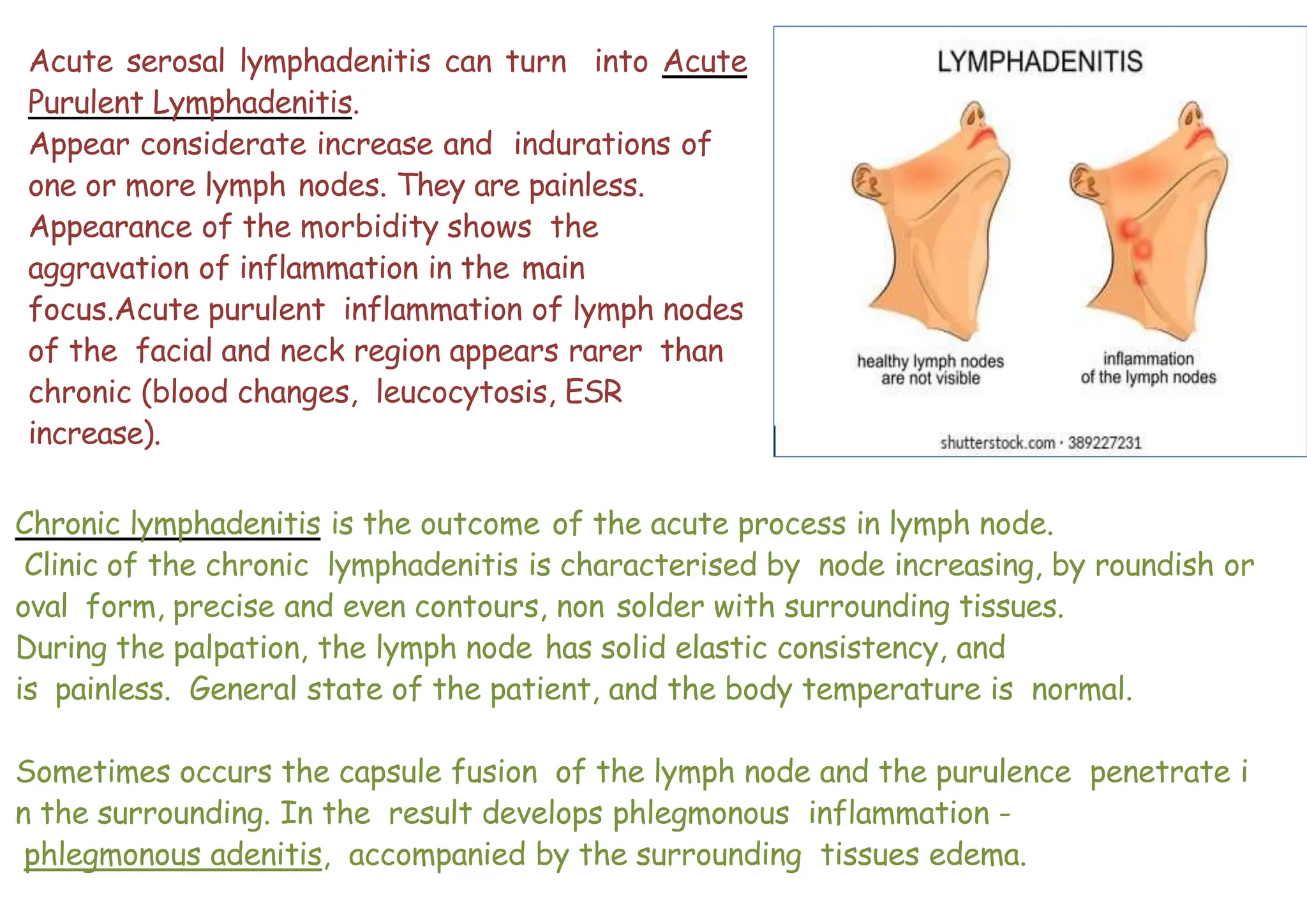
2. Examination of lymph nodes should note size, tenderness, mobility, and whether nodes are single or in groups. Enlarged, tender, and mobile nodes usually indicate acute infection while fixed nodes can be suspicious for malignancy.
3. Diagnosis of lymphadenitis involves sampling fluid from affected lymph nodes for culture to identify the infecting germs. Treatment involves incision and drainage of abscesses, extraction of infected teeth, physiotherapy, and antibiotic therapy.