This document provides an overview of organizational behavior concepts including:
- The definition of an organization and its key features.
- Different types of organizational goals and objectives.
- An introduction to organizational behavior including its key elements of people, structure, technology, and the external environment.
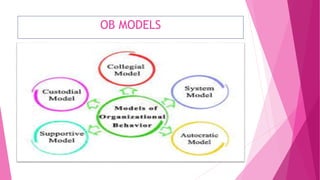
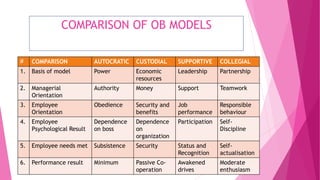
- Five models of organizational behavior: autocratic, custodial, supportive, collegial, and system. Each model is defined with an example.