This document provides a summary of observations from a site visit to Krrish Square, including:
- An overview of the site location, purpose, and details as well as acknowledgements.
- Descriptions of geotechnical investigations conducted including soil testing methods used.
- Explanations of various earthwork technologies and methods employed such as excavation, foundation installation, piling, and waterproofing.
- Discussions of machinery utilized like excavators, cranes, concrete pumps, and pile hammers.
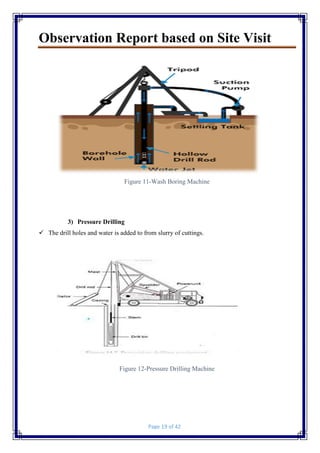
- Images documenting the site visit and construction processes.





































![Observation Report based on Site Visit
Page 41 of 42
References
Anon., 2019. Designing Buildings Wiki. [Online]
Available at: https://www.designingbuildings.co.uk/wiki/Building_foundations
[Accessed 02 05 2019].
Biswas, L., 2018. A CIVIL ENGINEER. [Online]
Available at: https://www.acivilengineer.com/soil-investigation-basic/
[Accessed 06 03 2018].
Irfan, D. M., 2018. SlideShare. [Online]
Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/1mirfan/geotechnical-engineeringi-lec-28-soil-
exploration?qid=20e795ba-e015-45a1-b8c5-9ddea7e39062&v=&b=&from_search=6
[Accessed 24 09 2018].
KM, S., 2014. SlideShare. [Online]
Available at: https://www.slideshare.net/shamjithkeyem/site-inveswtigation-vandana-
miss?qid=20e795ba-e015-45a1-b8c5-9ddea7e39062&v=&b=&from_search=15
[Accessed 06 08 2014].
Nieves, M., 2017. WorldBuild. [Online]
Available at: https://www.worldbuild365.com/blog/soil-investigation-what-is-it-and-why-is-it-
important-for-your-building-project-Bi1R4q
[Accessed 08 08 2017].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/observationsitereport-slideshare-190706185516/85/Observation-site-report-39-320.jpg)
