This document presents an overview of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) concepts such as inheritance, encapsulation, and polymorphism, focusing on their definitions and significance in software development. Inheritance allows classes to inherit properties and methods from parent classes, encapsulation involves bundling data and methods to protect data integrity, and polymorphism enables objects to be treated as instances of their parent class, allowing for multiple forms and behaviors. Examples in Java code illustrate these concepts, highlighting their roles in creating reusable and maintainable code.



![INHERITANCE
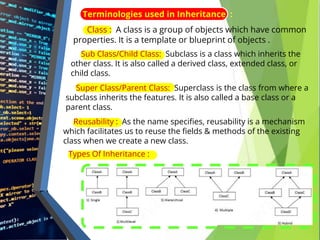
⮚ Inheritance in Java is a mechanism in which one object acquires all the
properties and behaviors of a parent object .
⮚ The idea behind inheritance in Java is that we can create new classes, -
which are built upon existing classes. When we inherit from an existing
class, we can re-use methods and fields of the parent class. So that due
to inheritance Code reusability increases .
⮚ Inheritance represents the IS-A relationship which is also known as a –
parent - child relationship .
⮚ Program as example :
class Bike{
int wheel = 2;
}
class SportsBike extends Bike {
int maxSpeed = 180;
public static void main(String args[]){
SportsBike ktm = new SportsBike();
System.out.println(“No.of Wheel in ktm is:"+ktm.wheel);
System.out.println(“Max Speed of
ktm is:"+ktm.maxSpeed+”Km/h”);
}
}
Code
No.of Wheel in ktm is : 2
Max Speed of ktm is : 180 Km/h
Output](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shuvrojitmajumder-230125101207-0b995cdf/85/Object-Oriented-Programming-pptx-4-320.jpg)
![ENCAPSULATION
class Name {
private int age; // Private is using to hide the data
public int getAge() { return age; } // getter
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
} // setter
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Name n1 = new Name();
n1.setAge(19);
System.out.println(“The age of the person is: ”+
n1.getAge());
}
}
Code
The age of the person is : 19
Output
⮚ Encapsulation in Java is a process of wrapping code and data together
into a single unit, for example, a capsule which is mixed of several
medicines.
⮚ We can create a fully encapsulated class in Java by making all the data
members of the class private. Now we can use setter and getter methods
to set and get the data in it.
⮚ The Java Bean class is the example of a fully encapsulated class.
⮚ Program as example :](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shuvrojitmajumder-230125101207-0b995cdf/85/Object-Oriented-Programming-pptx-6-320.jpg)



