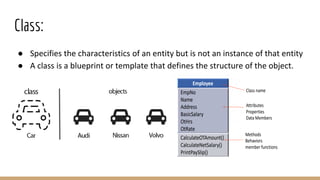
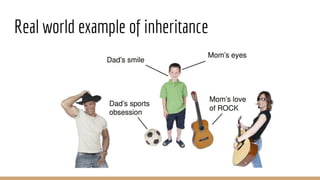
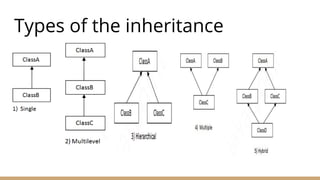
This document discusses object-oriented programming concepts. It aims to explain the fundamentals of OOP including classes, objects, and the four main OOP concepts: inheritance, abstraction, encapsulation, and polymorphism. The key OOP concepts are defined as inheritance allowing a class to inherit properties from another class, encapsulation hiding implementation details and only exposing a public interface, and abstraction and polymorphism allowing classes to take multiple forms. Examples are provided to illustrate classes, objects, and each of the OOP concepts.










![Activity: What is the value of X?
public class Calculator{
int x = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator myObj = new Calculator();
myObj.x = 25; // x is now 25
System.out.println(myObj.x);
}
}
Attributes
Method
Object](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorientedprogrammingdemo-230709150920-66d0796c/85/Object-Oriented-Programming-12-320.jpg)


![Example of inheritance
class Employee{
float salary=80000;
}
class Programmer extends Employee{
int bonus=30000;
public static void main(String args[]){
Programmer p=new Programmer();
System.out.println("Programmer salary is:"+p.salary);
System.out.println("Bonus of Programmer is:"+p.bonus);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorientedprogrammingdemo-230709150920-66d0796c/85/Object-Oriented-Programming-16-320.jpg)


![class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }
}
public class Display{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Person person = new Person();
person.setName("John");
person.setAge(30);
System.out.println("Name: " + person.getName());
System.out.println("Age: " + person.getAge());
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/objectorientedprogrammingdemo-230709150920-66d0796c/85/Object-Oriented-Programming-20-320.jpg)


