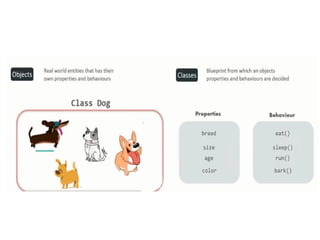
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) is a paradigm that structures software around objects, which combine data and behavior, making systems more modular and reusable. Its four foundational pillars are **Encapsulation** (bundling data and methods within classes, e.g., a `BankAccount` with private balance and deposit/withdraw methods), **Abstraction** (hiding complex details while exposing essential functionality, e.g., a `Car` class with a `drive()` method), **Inheritance** (allowing classes to derive properties and behaviors from parent classes, e.g., `Dog` inheriting from `Animal`), and **Polymorphism** (enabling methods to behave differently depending on the object, e.g., `draw()` implemented uniquely in `Circle`, `Square`, and `Triangle`). Together, these pillars make OOP a powerful approach for building flexible, scalable, and maintainable software systems.