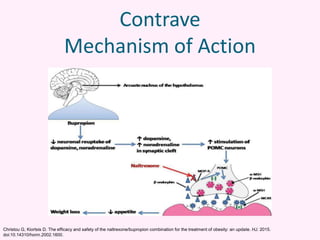
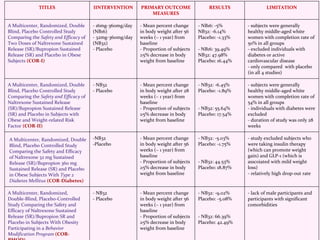
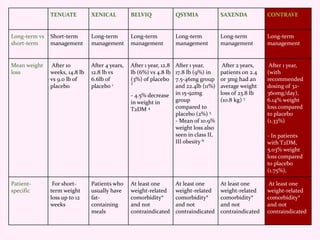
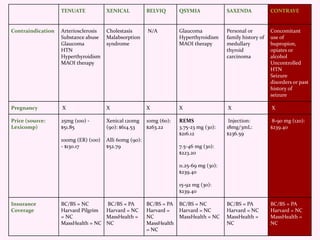
Contrave is an anti-obesity drug that combines naltrexone and bupropion. The document provides an overview of Contrave and compares it to other FDA-approved anti-obesity medications. It summarizes results from four clinical trials of Contrave, which showed average weight losses of 5-9% compared to 1-2% for placebo after 1 year of treatment. The document also reviews Contrave's mechanism of action, dosing, and side effect profile. It concludes that Contrave provides effective long-term weight management and compares its efficacy and safety profile to other anti-obesity medications.







![Pharmacological Weight Loss
Options
Tenuate® Xenical®
Alli®
(OTC)
Belviq® Qsymia® Saxenda® Contrave
®
Generic Diethyl-
propion
Orlistat Locaserin Phentermine
&
Topiramate
Liraglutide Naltrexone
&
Bupropion
Class Central
Nervous
Stimulant
Lipase
inhibitor
Serotonin
(5HT2c)
Receptor
Agonist
Sympatho-
mimetic &
Anti-
convulsant
Glucagon-
Like Peptide
(GPL-1)
Receptor
Agonist
Dopamine/
Norepi-
nephrine
Reuptake
Inhibitor &
Opioid
Antagonist
Lexi-drugs Online. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.;[updated 01/27/16; accessed 01/27/16]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/962b063e-4a3f-4166-bacb-0f93ec7e3e26-160518003454/85/Obesity-10-320.jpg)














![REFERENCES
Contrave. In: Lexi-drugs Online. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.;[updated 01/27/16; accessed 01/27/16].
http://online.lexi.com.ezproxymcp.flo.org/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/5338462
Tenuate. In: Lexi-drugs Online. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.;[updated 01/19/16; accessed 01/27/16].
http://online.lexi.com.ezproxymcp.flo.org/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/6740
Xenical. In: Lexi-drugs Online. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.;[updated 01/27/16; accessed 01/27/16].
http://online.lexi.com.ezproxymcp.flo.org/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/7402
Belviq. In: Lexi-drugs Online. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.;[updated 01/27/16; accessed 01/27/16].
http://online.lexi.com.ezproxymcp.flo.org/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/3808862
Qsymia. In: Lexi-drugs Online. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.;[updated 01/19/16; accessed 01/27/16].
http://online.lexi.com.ezproxymcp.flo.org/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/3832942
Saxenda. In: Lexi-drugs Online. Hudson (OH): Lexi-Comp, Inc.;[updated 01/27/16; accessed 01/27/16].
http://online.lexi.com.ezproxymcp.flo.org/lco/action/doc/retrieve/docid/patch_f/2144379
Torgerson JS, Hauptman J, Boldrin MN, Sjostrom L. XENical in the prevention of diabetes in obese subjects
(XENDOS) study: A randomized study of orlistat as an adjunct to lifestyle changes for the prevention of type 2
diabetes in obese patients. Diabetes Care 2004;27(1):155–161.
Fidler MC, Sanchez M, Raether B, Weissman NJ, et al. A one-year randomized trial of lorcaserin for weight loss in
obese and overweight adults: The BLOSSOM trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2011;96(10):3067–3077.
O’Neil PM, Smith SR, Weissman NJ, et al. Randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial of lorcaserin for weight loss
in type 2 diabetes mellitus: The BLOOM-DM study. Obesity 2012;20(7):1426–1436.
Gadde KM, Allison DB, Ryan DH, Peterson CA, et al. Effects of low-dose, controlled-release, phentermine plus
topiramate combination on weight and associated comorbidities in overweight and obese adults (CONQUER): A
randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011;377:1341–1352.
Allison DB, Gadde KM, Garvey WT, et al. Controlled-release phentermine/topiramate in severely obese adults: A
randomized controlled trial (EQUIP). Obesity 2012;20(2)330–342.
Clements, J. N., & Shealy, K. M. (2015). Liraglutide An Injectable Option for the Management of Obesity. Annals of
Pharmacotherapy, 1060028015586806.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/962b063e-4a3f-4166-bacb-0f93ec7e3e26-160518003454/85/Obesity-35-320.jpg)
