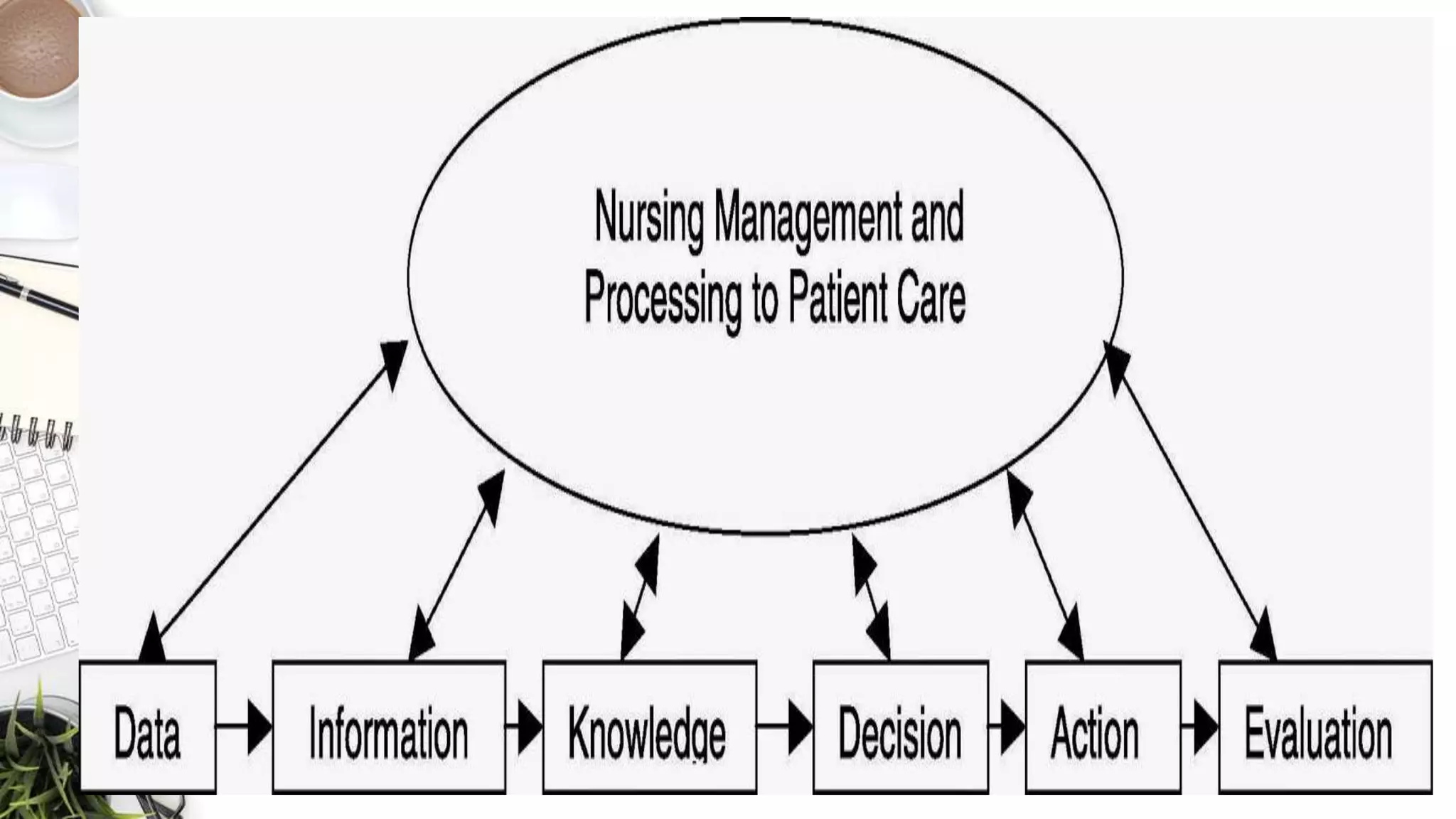
Nursing informatics is defined as integrating nursing science, computer science, and information science to manage and communicate patient information to support nurses and other providers in decision making. The American Nurses Association recognizes trends in information technology like electronic medical records and defines nursing informatics roles like collecting, recording, interpreting, and using clinical data to produce information and knowledge. Healthcare information systems include clinical information systems to support patient care, administrative systems to manage billing and scheduling, and nursing information systems that provide nurses the information they need to practice and document care.