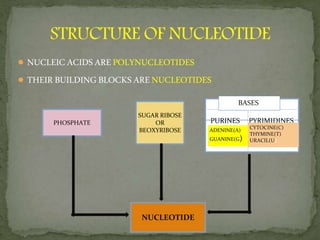
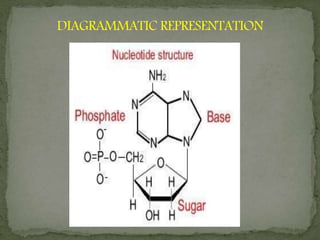
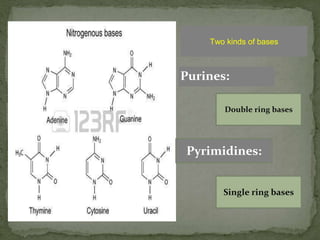
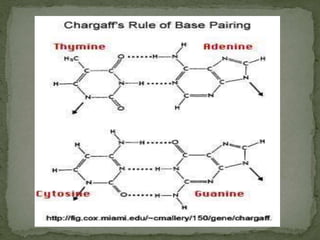
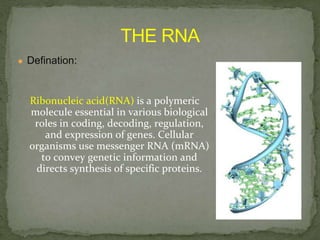
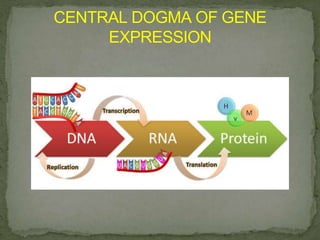
Johannes Friedrich Miescher was a Swiss physician and biologist who discovered nucleic acid in 1869. He isolated a substance that he called "nuclein" from nuclei of pus cells, which was later determined to have acidic properties and was named nucleic acid. Nucleic acids are essential biomolecules found in all living organisms that function to encode genetic information. They are composed of nucleotides which contain a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), which differ in their sugar component. DNA contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms.