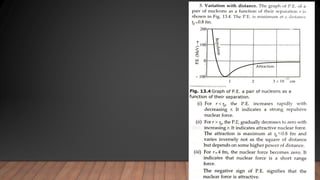
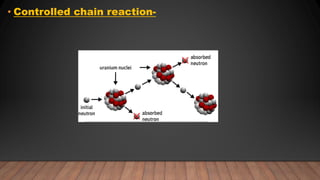
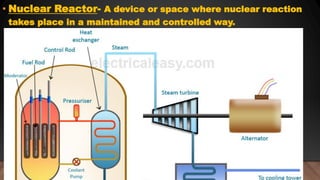
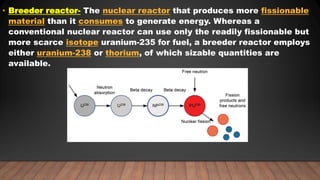
The document provides information on the structure of atomic nuclei and nuclear reactions. It discusses the proton-neutron hypothesis, which states that nuclei contain protons and neutrons. It defines key terms like nucleons, atomic number, mass number, and nuclide. It also describes the properties of protons and neutrons. The document discusses nuclear forces, mass-energy equivalence, nuclear size and density. It explains nuclear reactions like fission, chain reactions, and controlled nuclear reactors. It provides details on moderators, critical size and mass, and breeder reactors. In the end, it briefly discusses nuclear fusion.