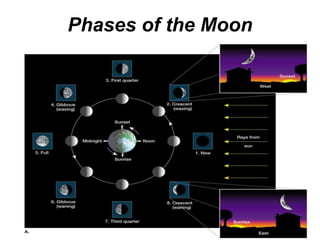
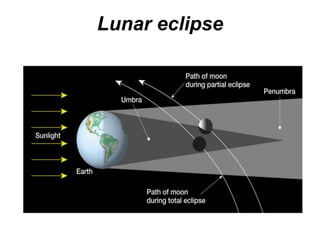
The document discusses the moon and its formation. The most accepted theory is that a large asteroid collided with Earth, sending debris into space that coalesced to form the moon. The moon has different terrain features like maria (smooth lowlands formed by lava) and craters created by meteoroid impacts. It rotates synchronously so the same side always faces Earth. The moon's phases are caused by our changing view of the illuminated half as it orbits, not Earth's shadow. Eclipses occur when the moon passes through Earth's shadow (lunar eclipse) or blocks the sun's light (solar eclipse).