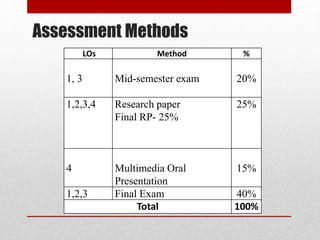
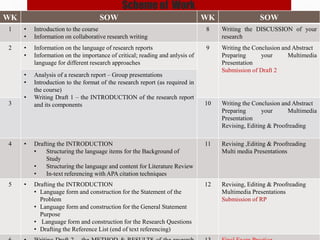
This document outlines the objectives and structure of an English for Academic Writing course, which emphasizes critical reading, writing techniques, and collaborative research. Students will engage with multimedia presentations and develop teamwork skills while focusing on humanistic research topics. Assessment includes a mid-semester exam, a final research paper, and presentations, with significant emphasis placed on the development of communication and problem-solving skills.