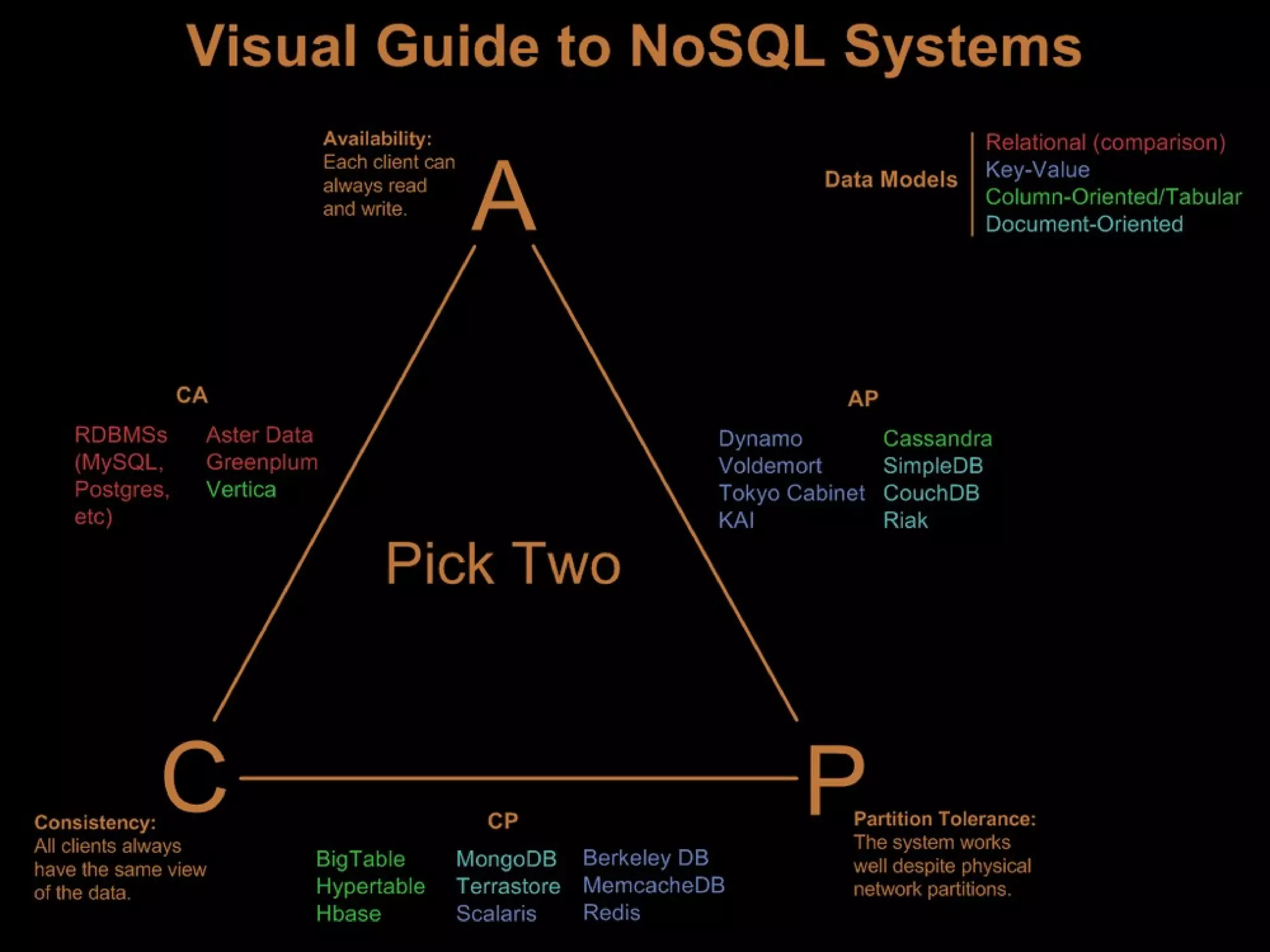
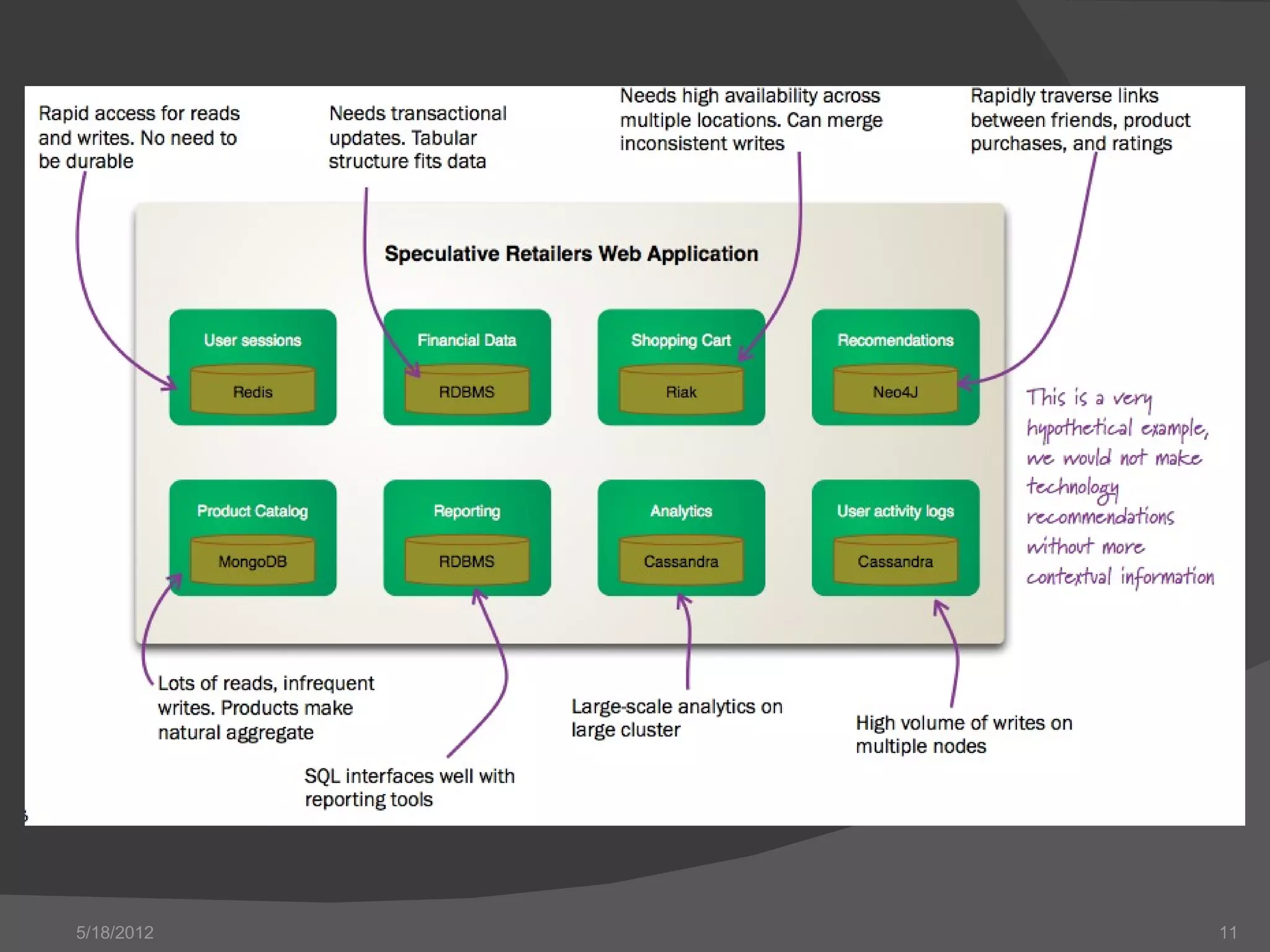
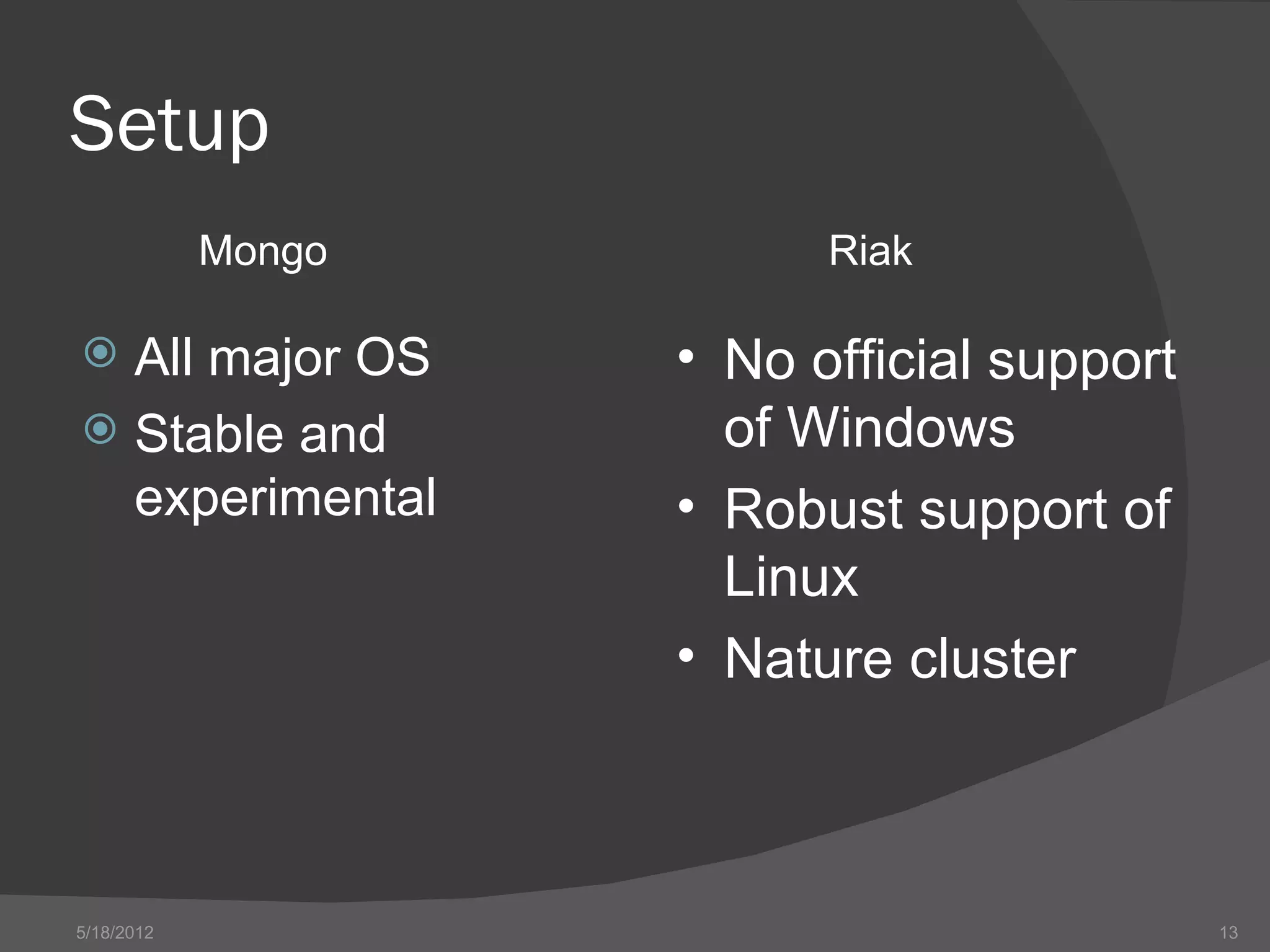
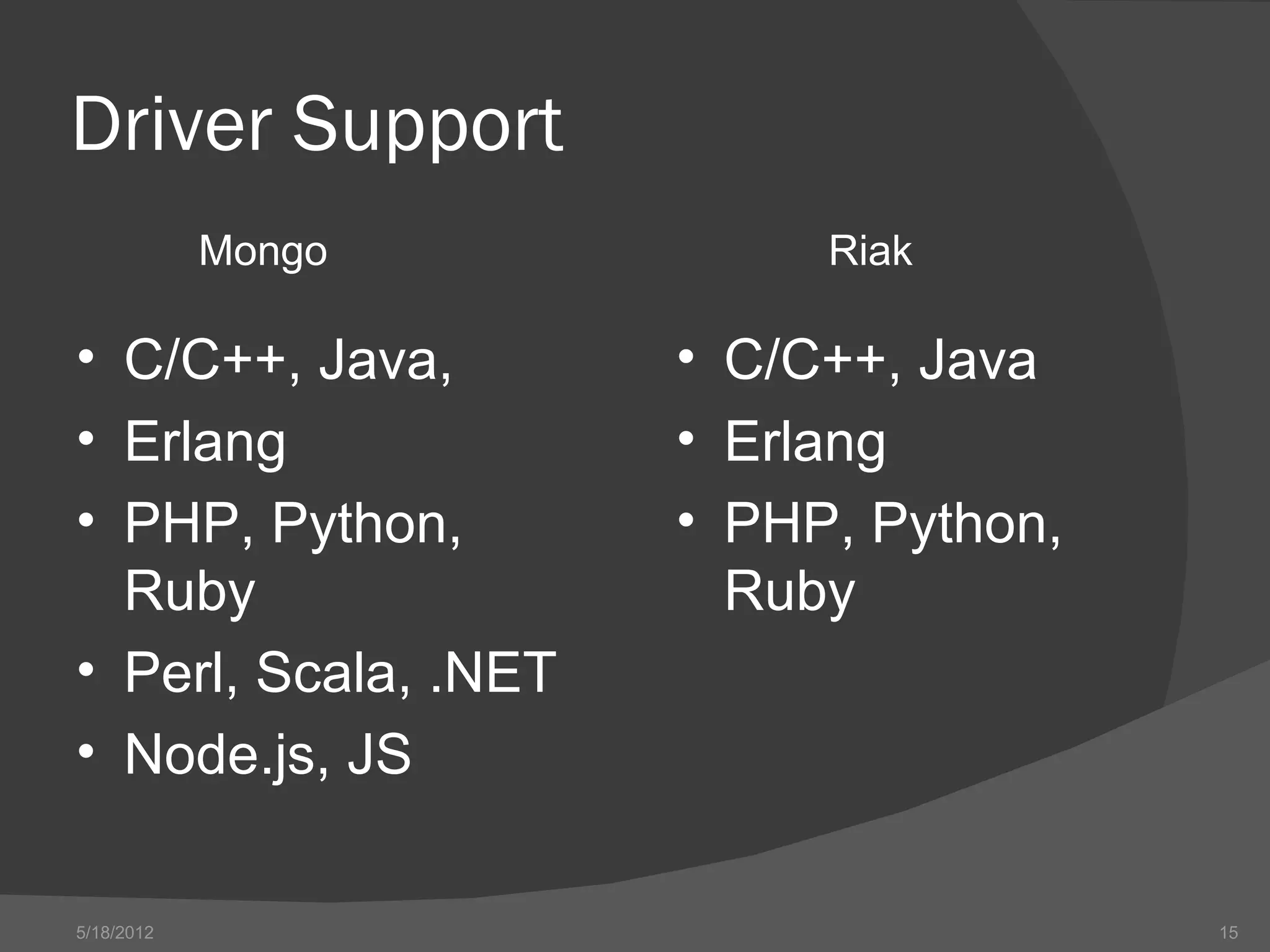
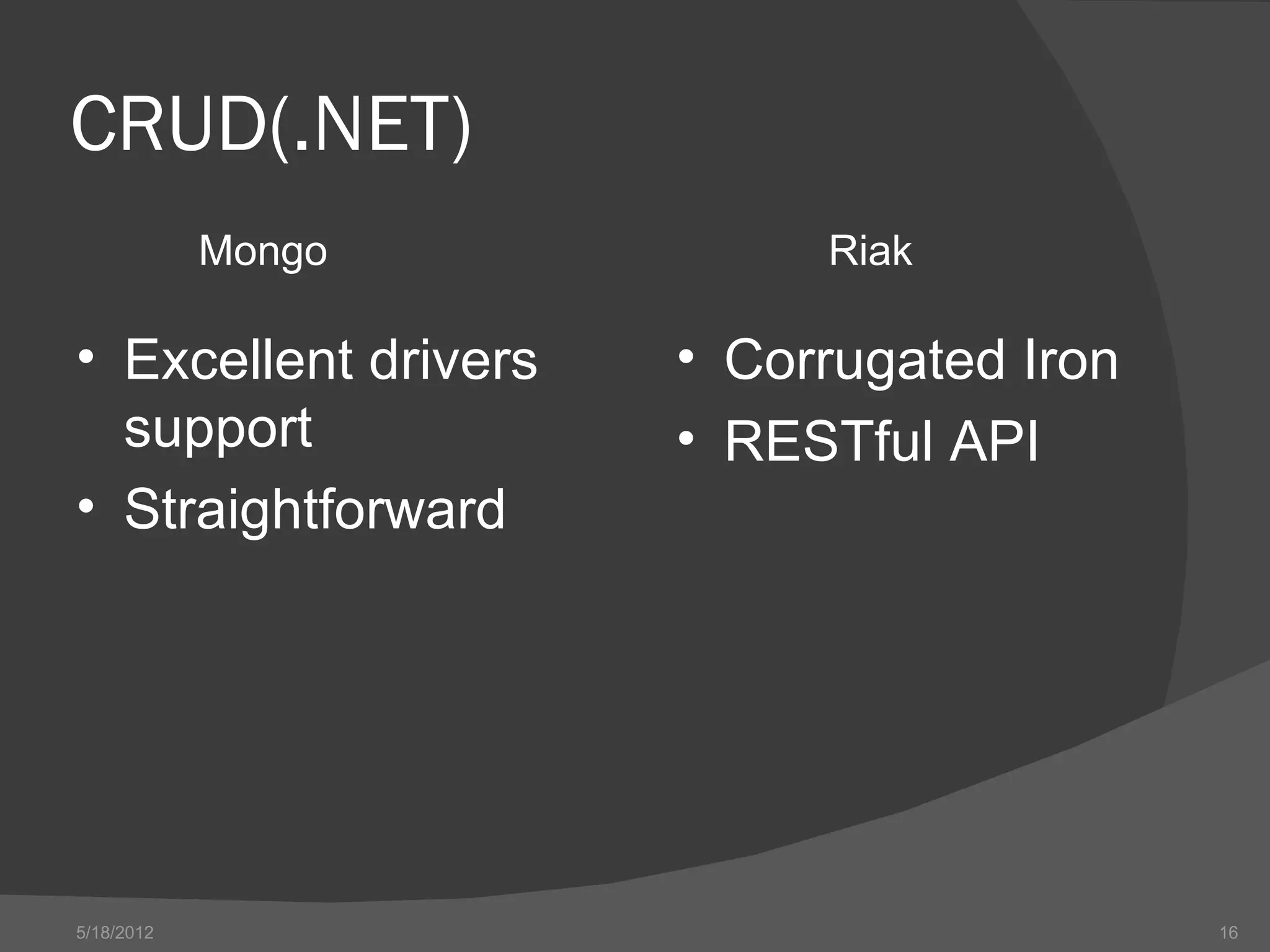
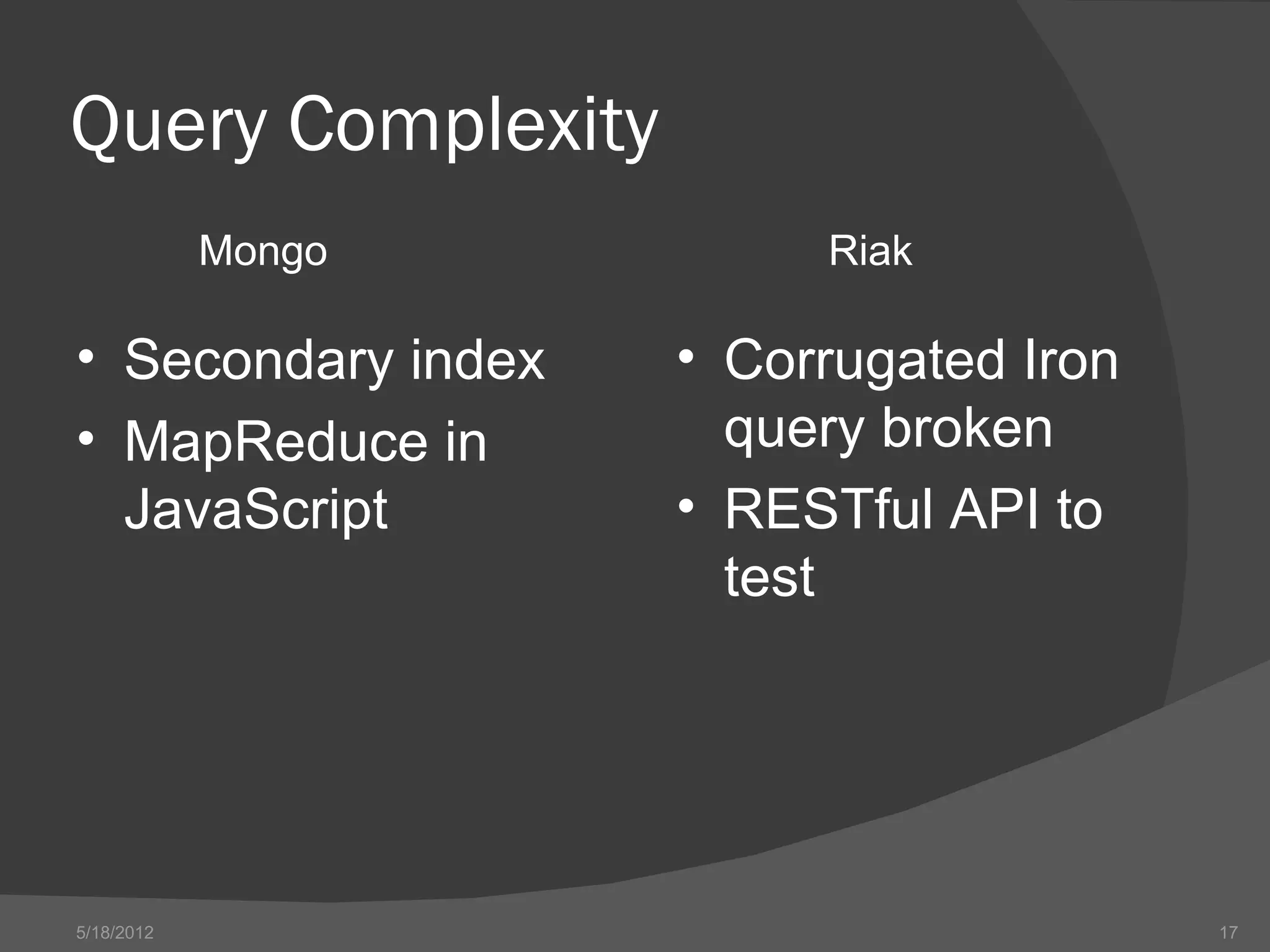
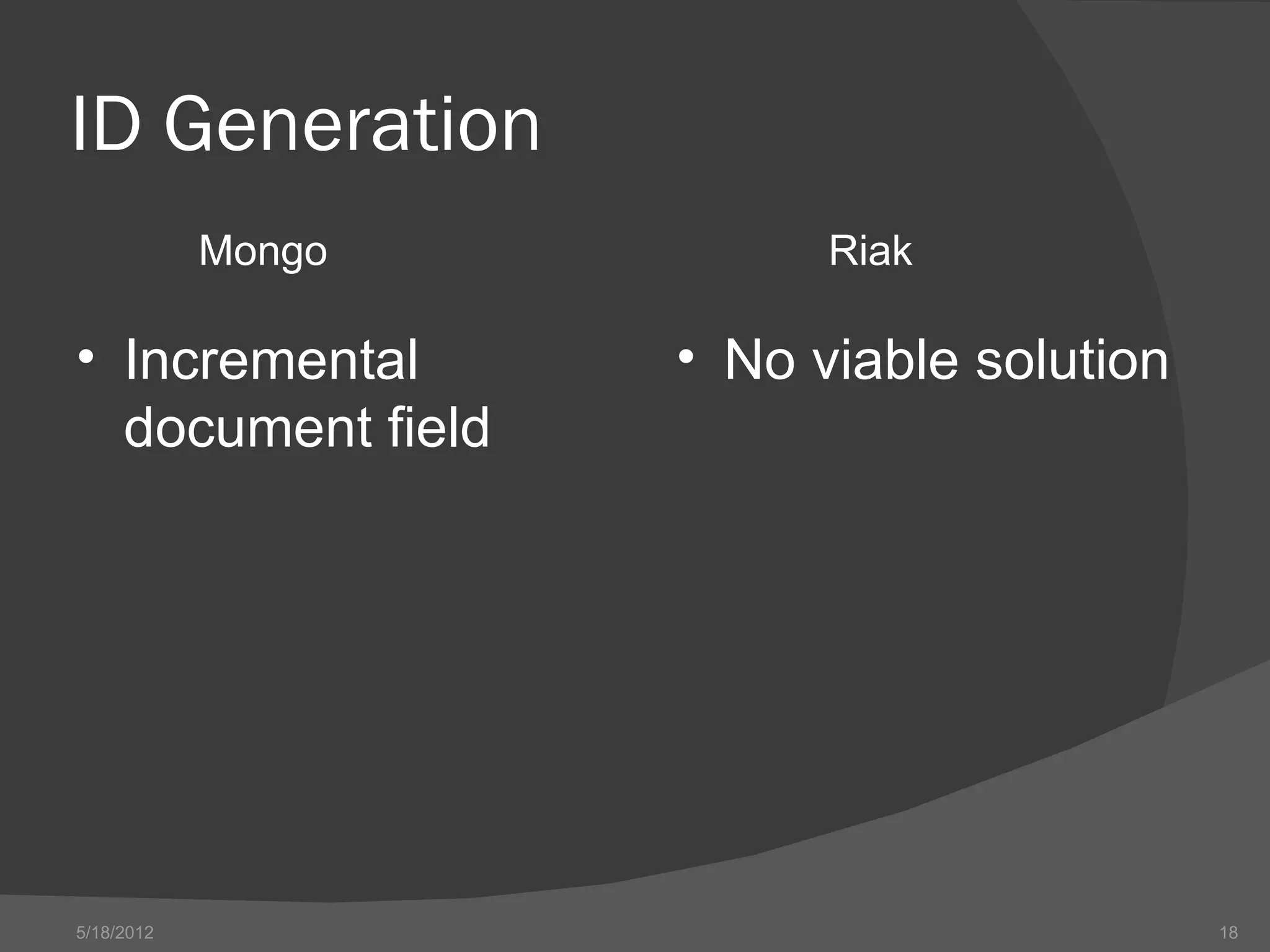
The document provides an overview of NoSQL databases, including their history and why they emerged. It discusses some key features of NoSQL databases like not requiring a fixed schema and not providing full ACID guarantees. The document then compares MongoDB and Riak on various aspects like their setup requirements, tooling support, driver support for CRUD operations, and their approaches to queries and ID generation.