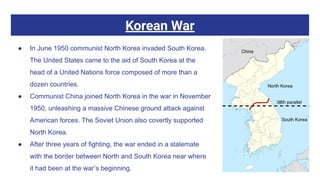
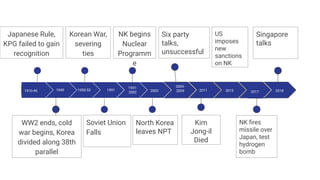
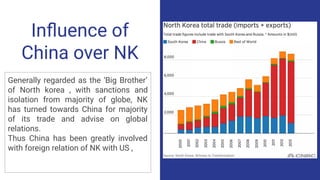
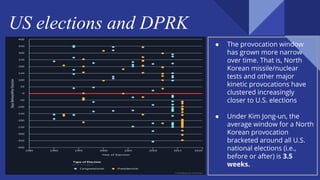
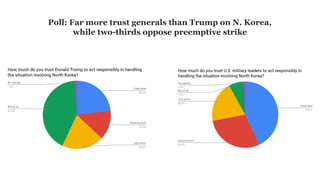
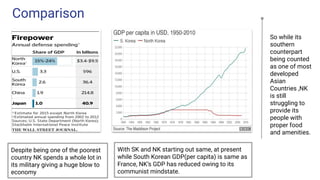
The US and North Korea have had strained relations since the Korean War divided the peninsula in the 1950s. While the US maintains troops in South Korea, North Korea has increasingly developed its nuclear weapons program in recent decades. Recent summits between US President Trump and North Korean leader Kim Jong Un have aimed to denuclearize the Korean Peninsula and formally end the Korean War. However, full denuclearization remains uncertain and longstanding tensions continue due to sanctions and military presence on both sides of the border.