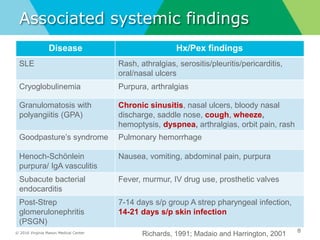
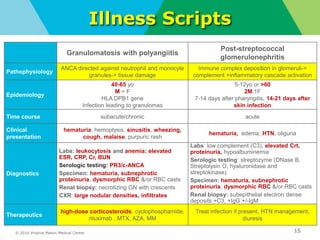
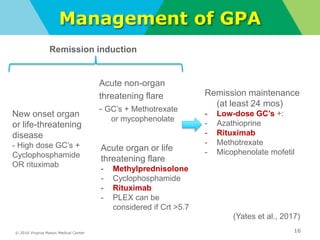
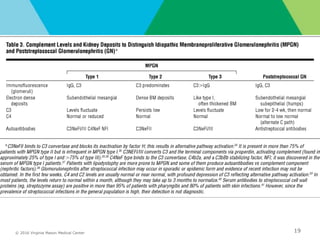
This document provides an overview of glomerular causes of hematuria including definitions, diagnostic workup, differential diagnoses, and treatment approaches. Key points discussed include:
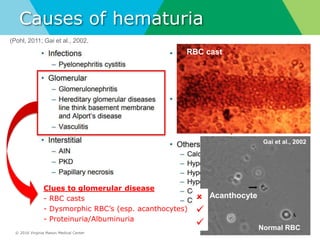
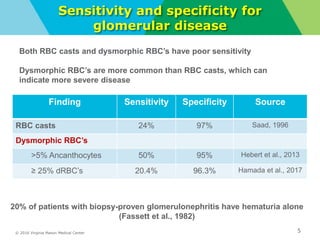
- Definitions of gross and microscopic hematuria and their clinical significance. Dysmorphic red blood cells and red blood cell casts can indicate glomerular disease but have low sensitivity.
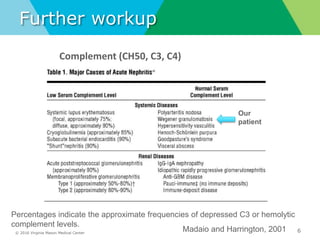
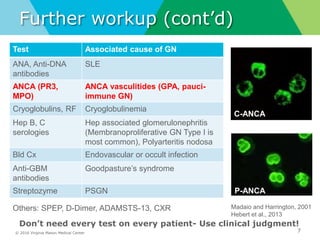
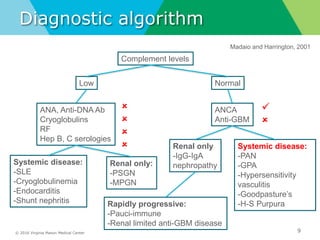
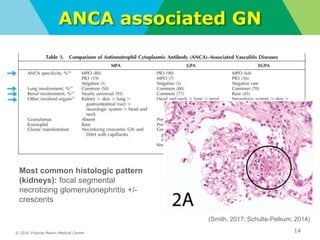
- Diagnostic workup may include complement levels, ANCA, ANA, hepatitis and cryoglobulin serologies to identify underlying causes like ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis, lupus, or hepatitis.
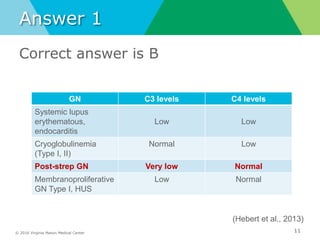
- Biopsy of the kidney has the highest diagnostic yield compared to other organs and should be considered for rapidly progressive or unexplained