Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


![Event loop illustration
// event loop
while (true) {
lock (queue) {
var tickEvents = copy(queue);
queue.empty();
}
for (var i = 0; i < tickEvents.length; i++) {
InvokeJSFunction(tickEvents[i]);
}
}
// thread-safe event pushing
lock (queue) {
queue.push(event);
}
// io call
fs.readFile(“pwd”, function(e, d){
console.log(“file data:”, d);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/node-140331045943-phpapp02/85/Node-js-quick-intro-5-320.jpg)

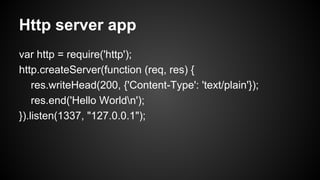

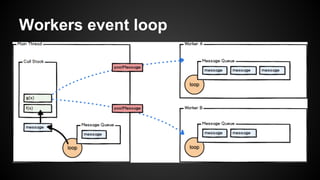


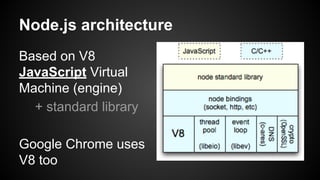
Node.js is an event-driven platform for building scalable network applications. It uses non-blocking I/O and asynchronous calls to handle many connections concurrently without blocking. At the core of Node.js is a single-threaded event loop that processes tasks in the order they are placed into the queue, executing callbacks asynchronously without blocking the main thread. The event loop handles all incoming requests and passes them to the JavaScript engine to execute callbacks and return responses. Node.js uses the V8 JavaScript engine and runs built-in modules and third-party modules for common tasks like HTTP servers and file system access.




![Event loop illustration
// event loop
while (true) {
lock (queue) {
var tickEvents = copy(queue);
queue.empty();
}
for (var i = 0; i < tickEvents.length; i++) {
InvokeJSFunction(tickEvents[i]);
}
}
// thread-safe event pushing
lock (queue) {
queue.push(event);
}
// io call
fs.readFile(“pwd”, function(e, d){
console.log(“file data:”, d);
});](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/node-140331045943-phpapp02/85/Node-js-quick-intro-5-320.jpg)




