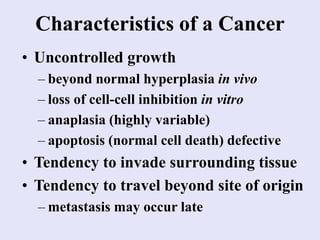
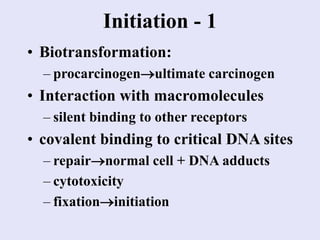
1. Carcinogenesis is a multistage process involving initiation, promotion, and progression. Initiation involves damage to DNA from carcinogens, radiation, or viruses.
2. Promotion stimulates cell division to fix the mutation and select for preneoplastic cells. Common promoters include hormones, phorbol esters, and foreign bodies.
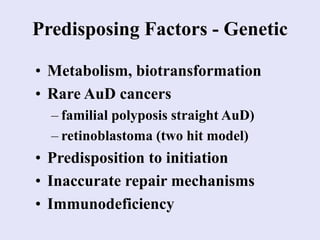
3. During progression the mutated clone proliferates into a detectable tumor through angiogenesis and evading the immune system. Genetic and dietary factors can predispose to cancer development.