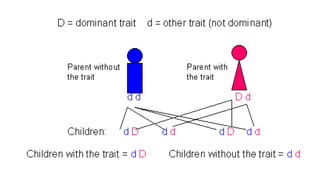
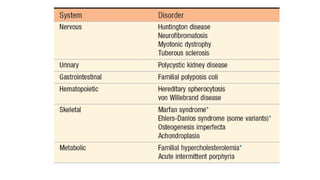
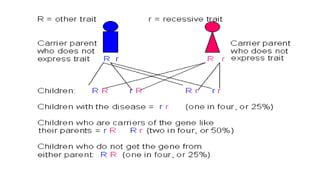
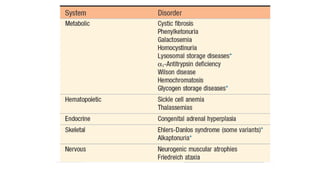
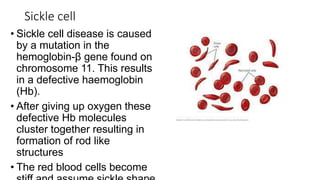
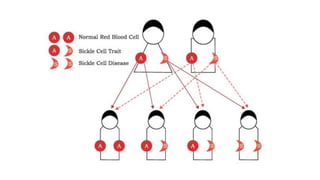
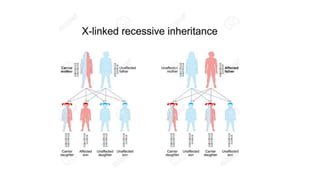
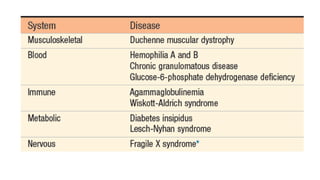
Genetic disorders can be caused by abnormalities in a single gene (single gene disorders), chromosomes (chromosomal disorders), or multiple factors (multifactorial disorders). Single gene disorders follow patterns of inheritance such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked. Autosomal dominant disorders affect both males and females and there is a 50% chance of passing the disorder to offspring. Autosomal recessive disorders occur when both alleles are mutated and siblings have a 25% chance of being affected. Examples of autosomal recessive disorders include sickle cell disease and cystic fibrosis. X-linked disorders mainly affect males and are more likely to be passed from mother to children than father to children.