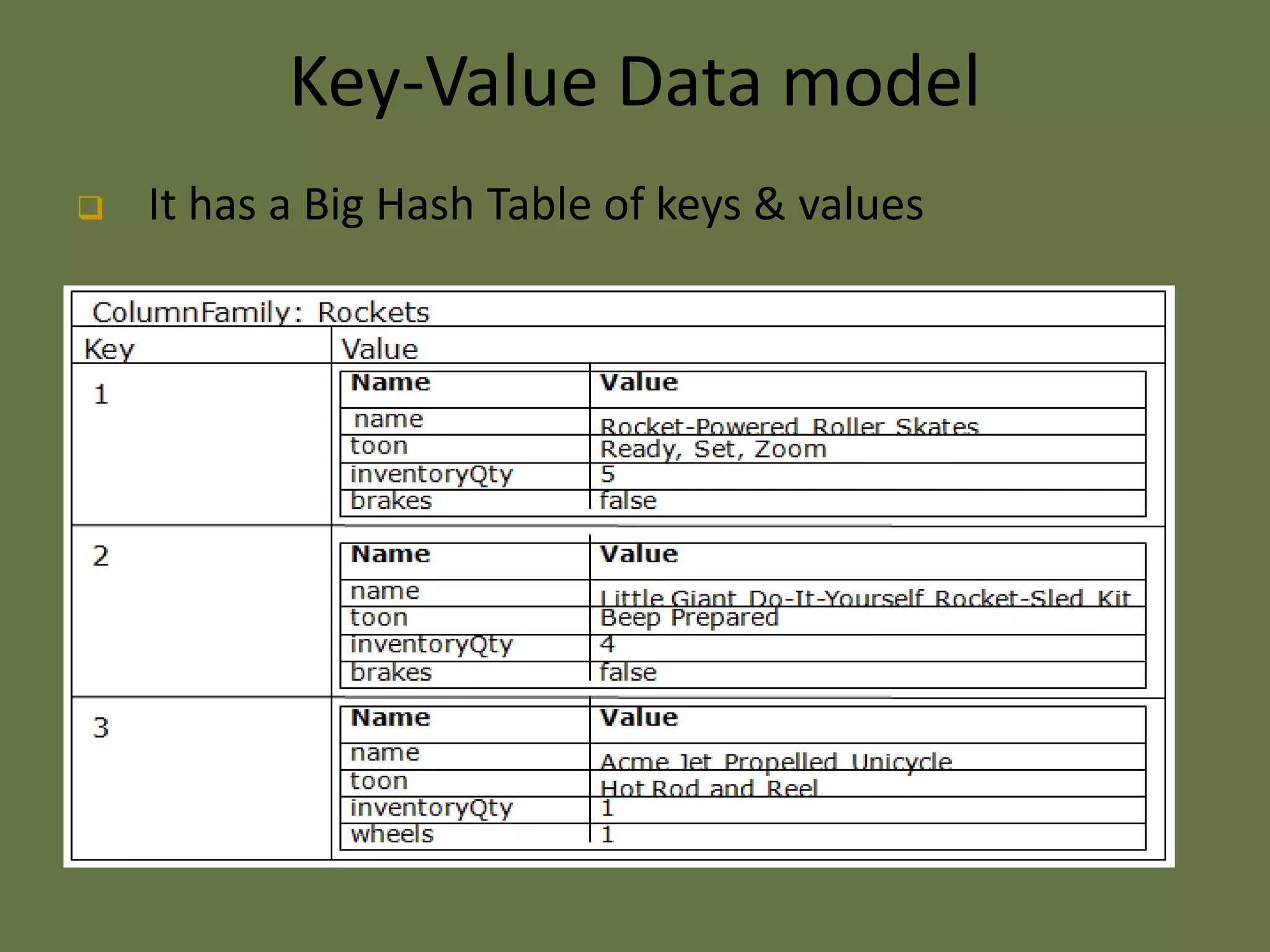
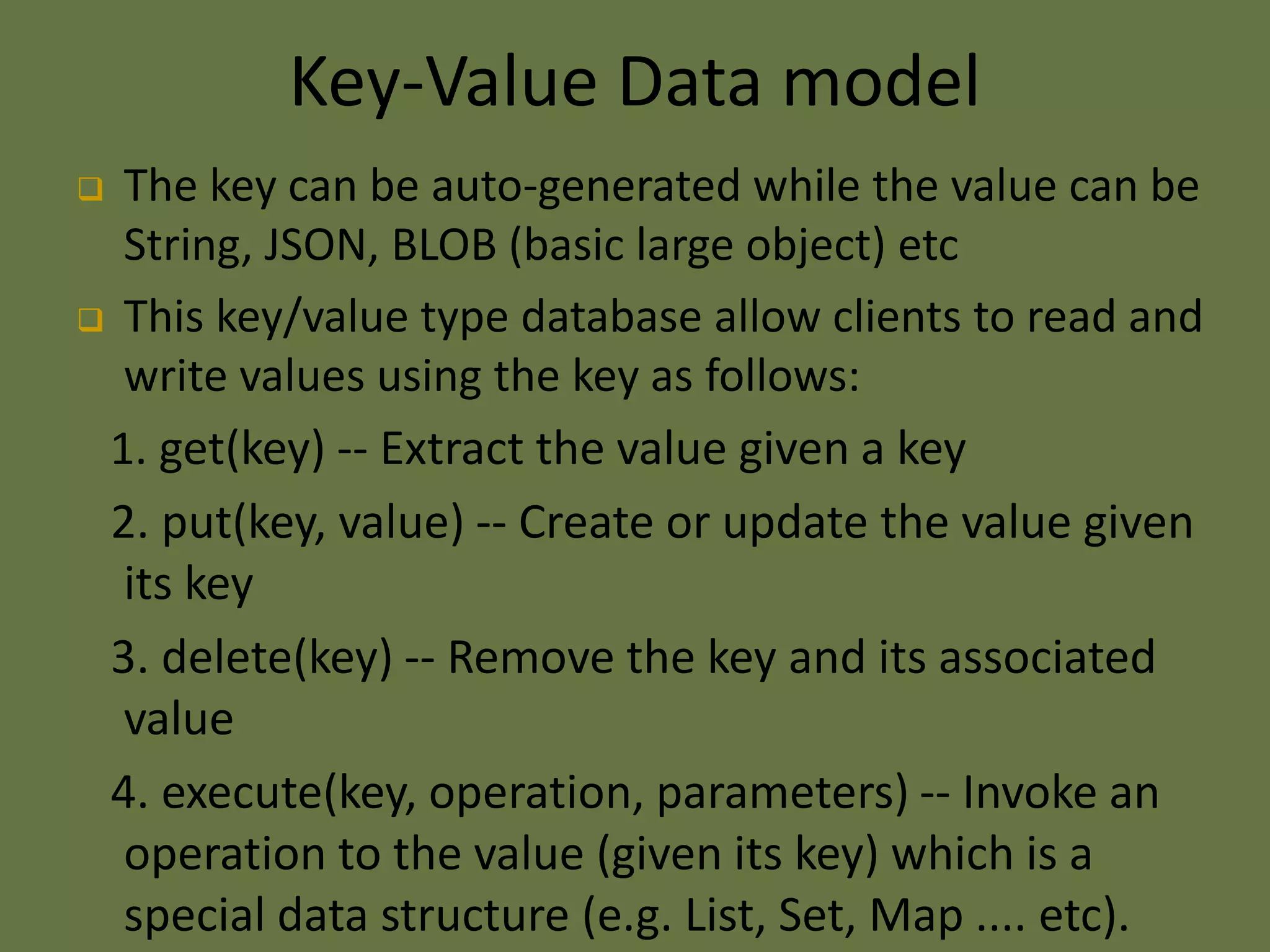
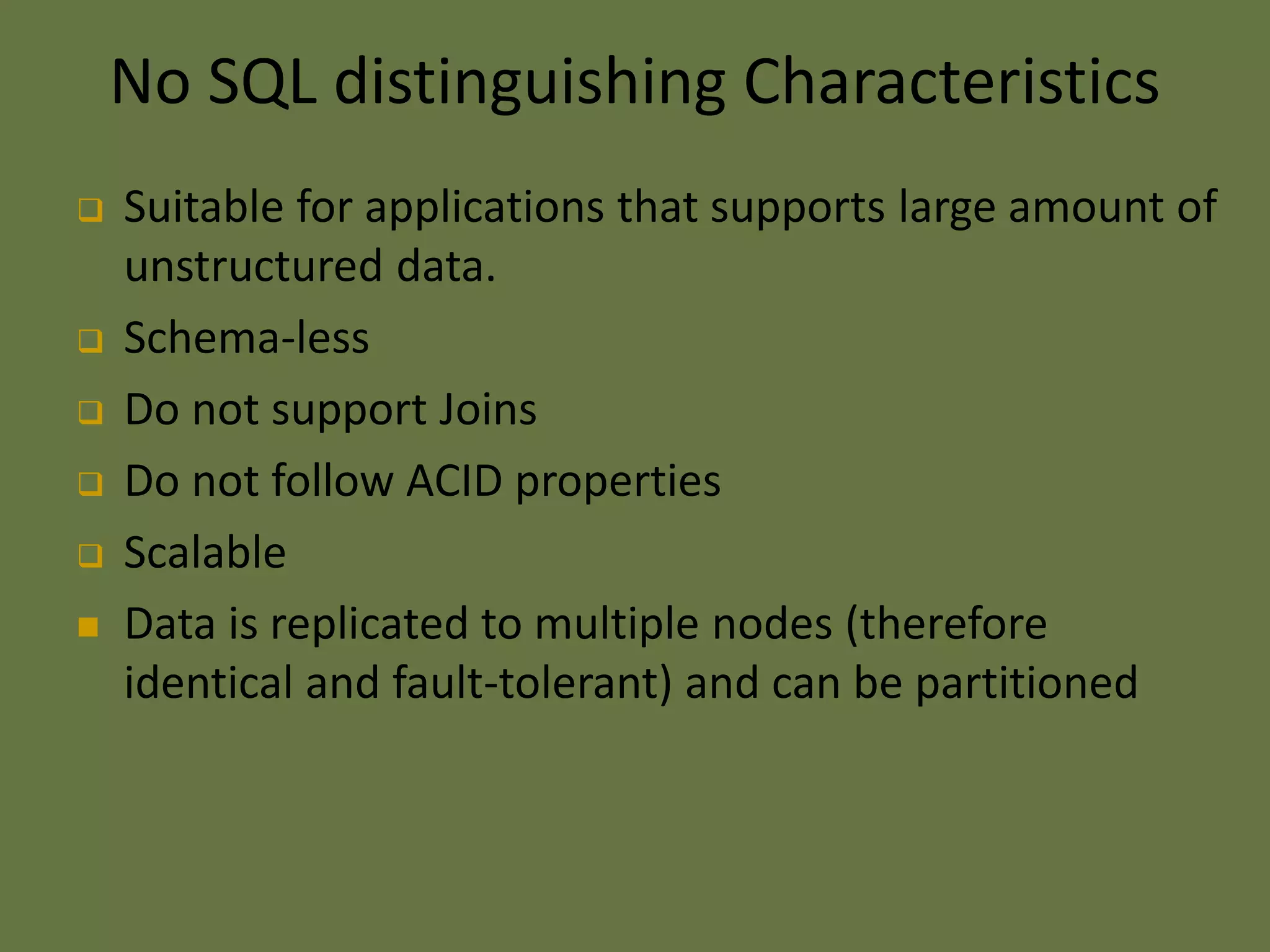
This document provides an overview of NoSQL databases. It discusses why cloud data stores became popular due to the rise of social media sites and need for large data storage. NoSQL databases provide a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is not modeled in tabular relations. NoSQL databases are scalable, do not require fixed schemas, and lack ACID properties. The document also discusses the CAP theorem, which states that a distributed system cannot achieve consistency, availability, and partition tolerance simultaneously.