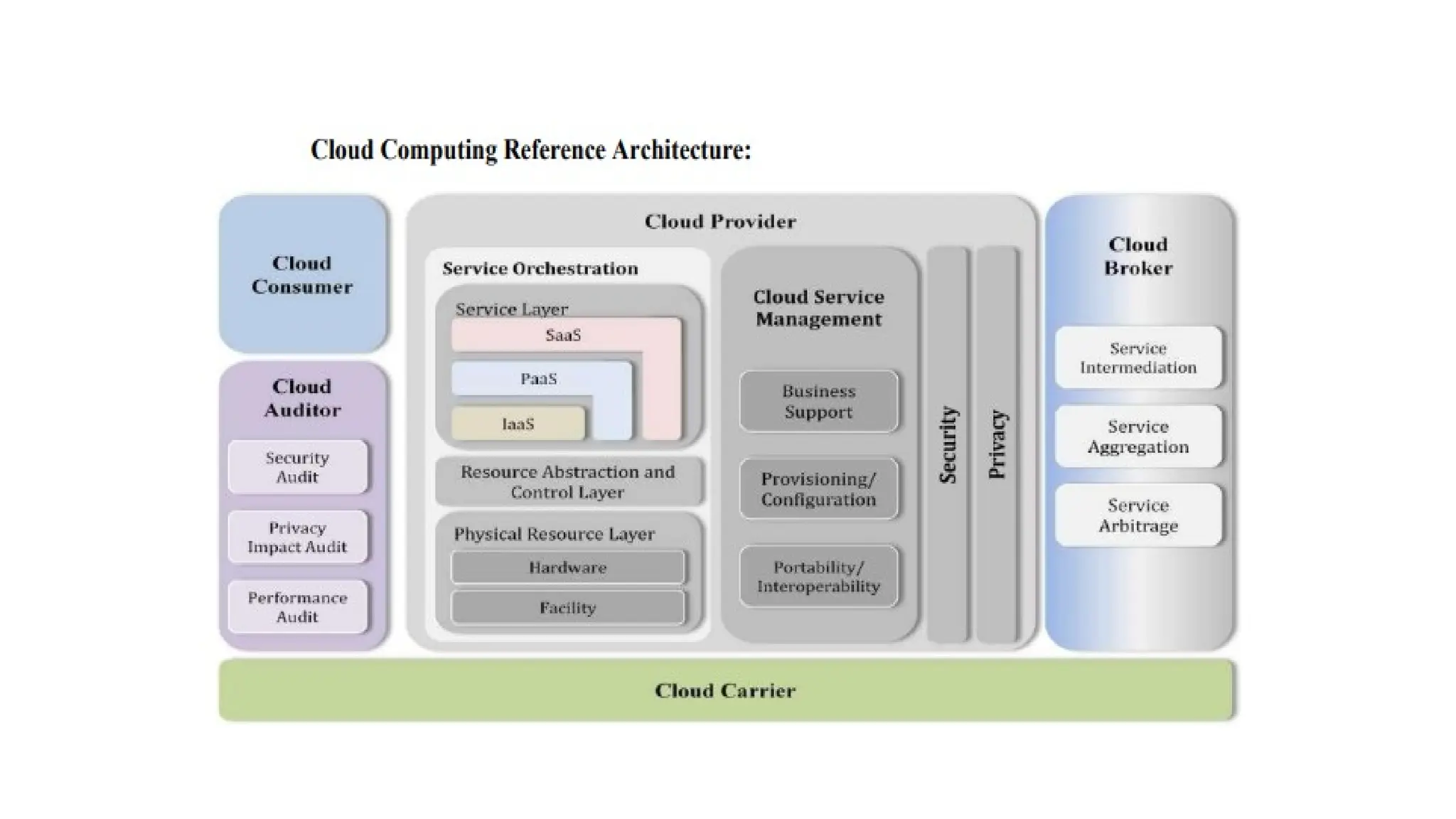
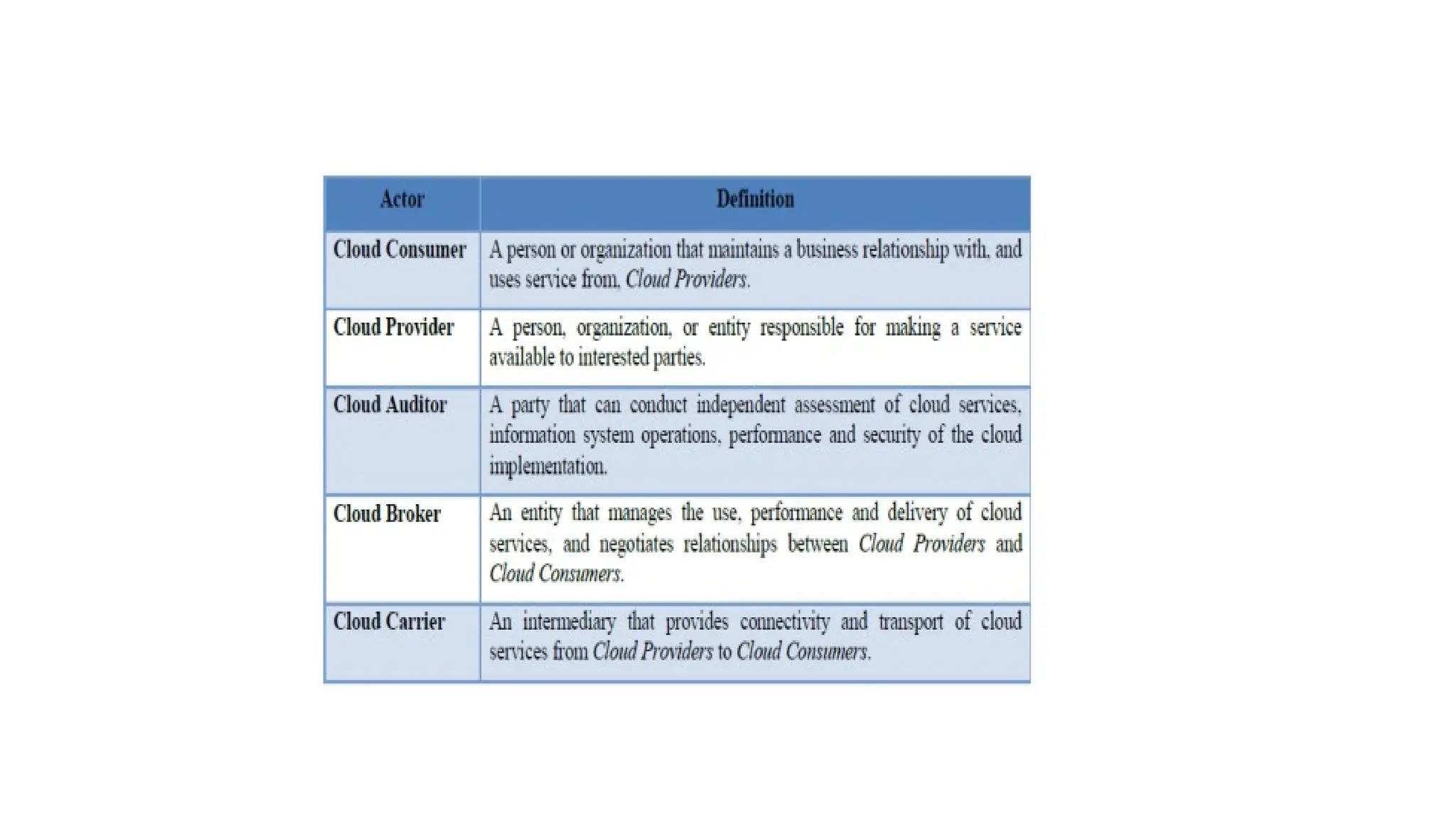
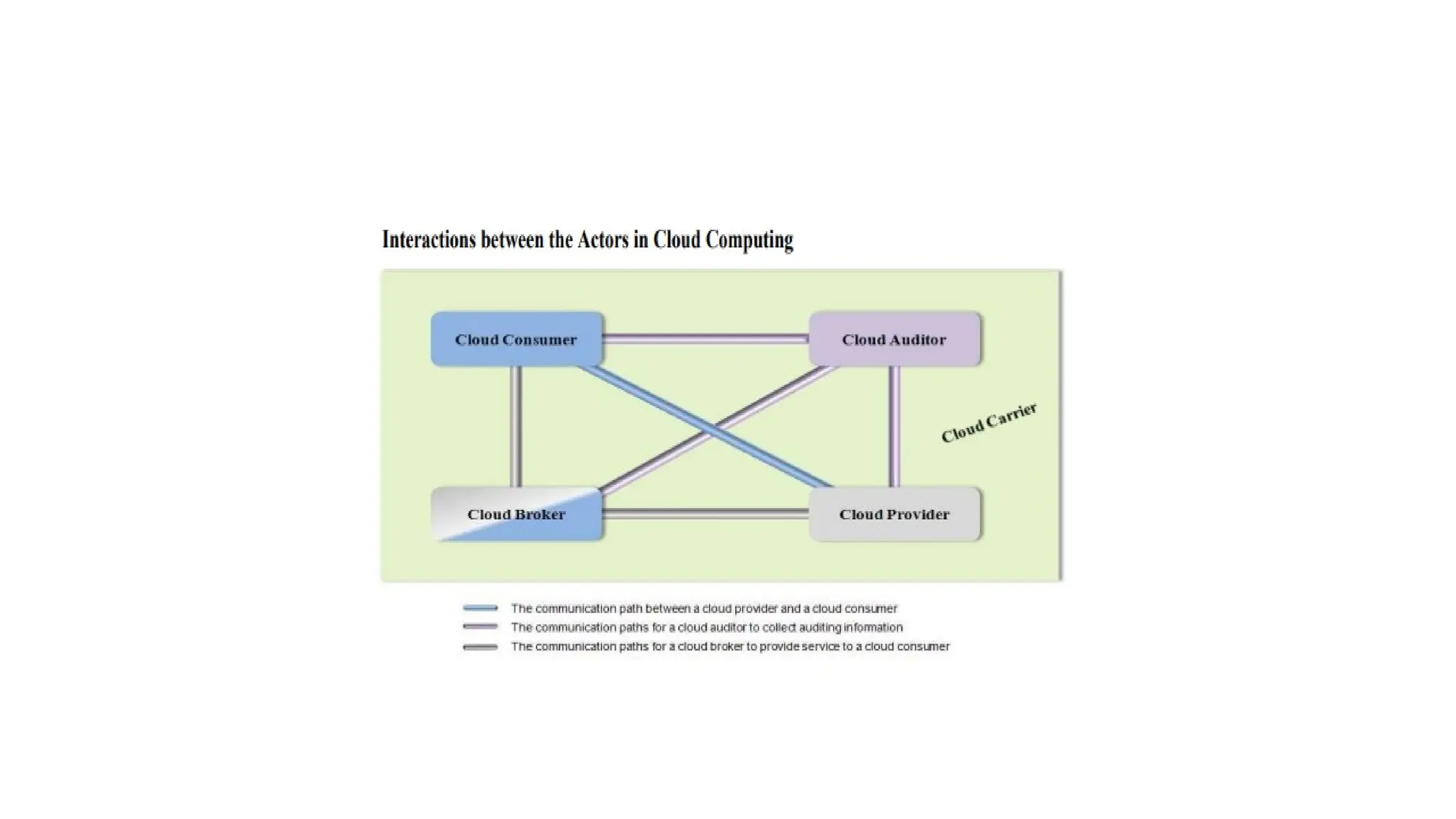
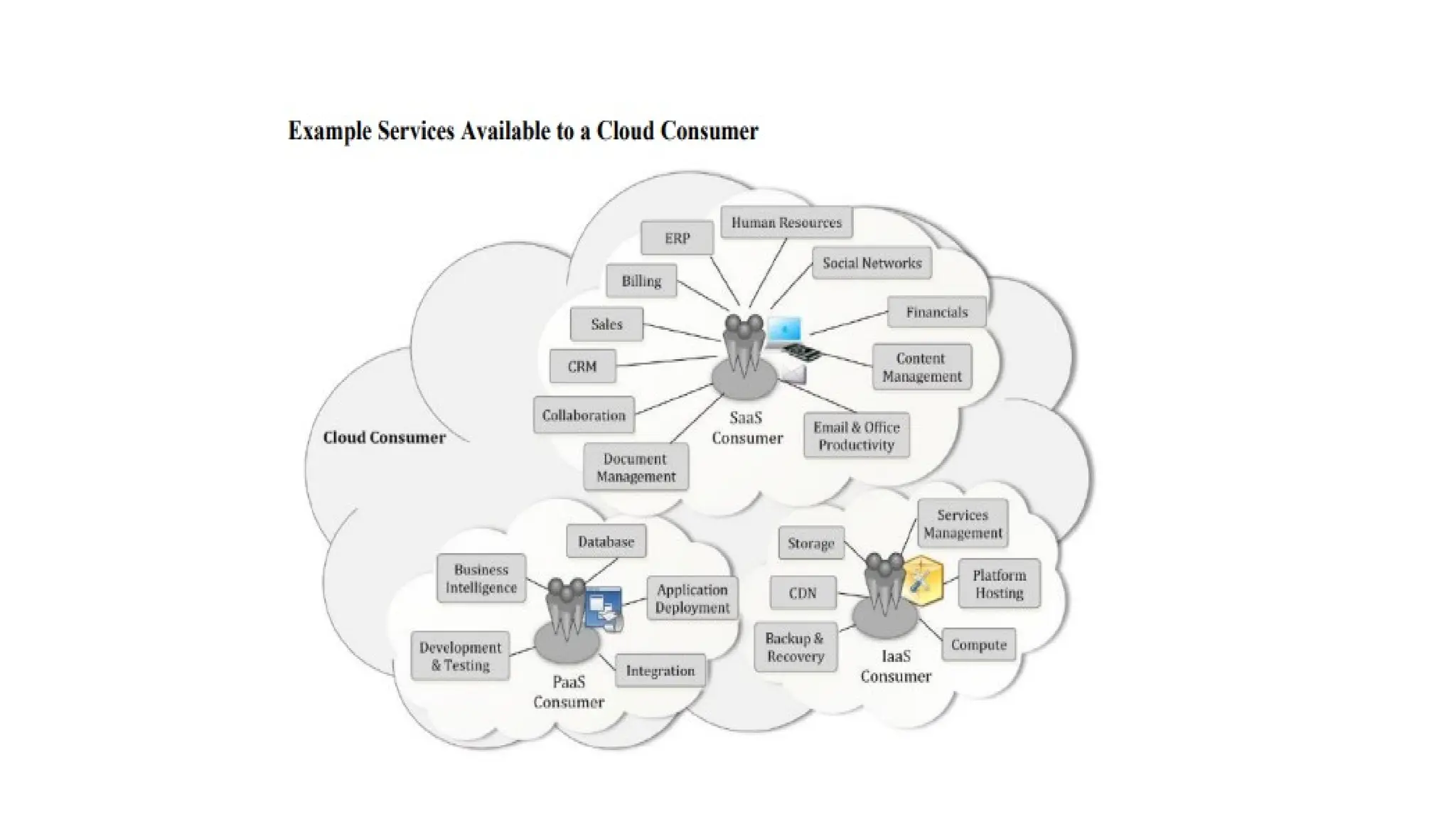
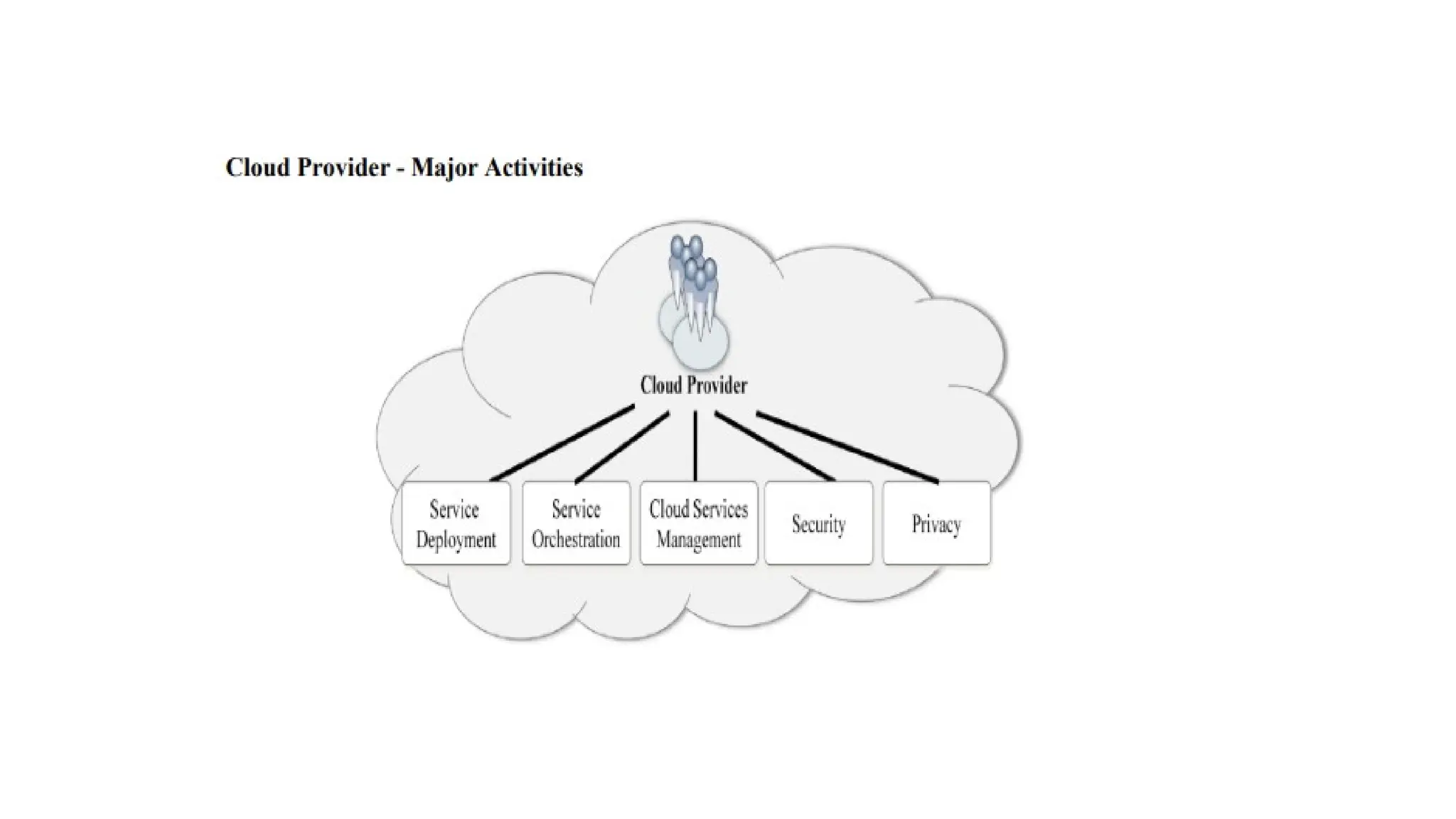
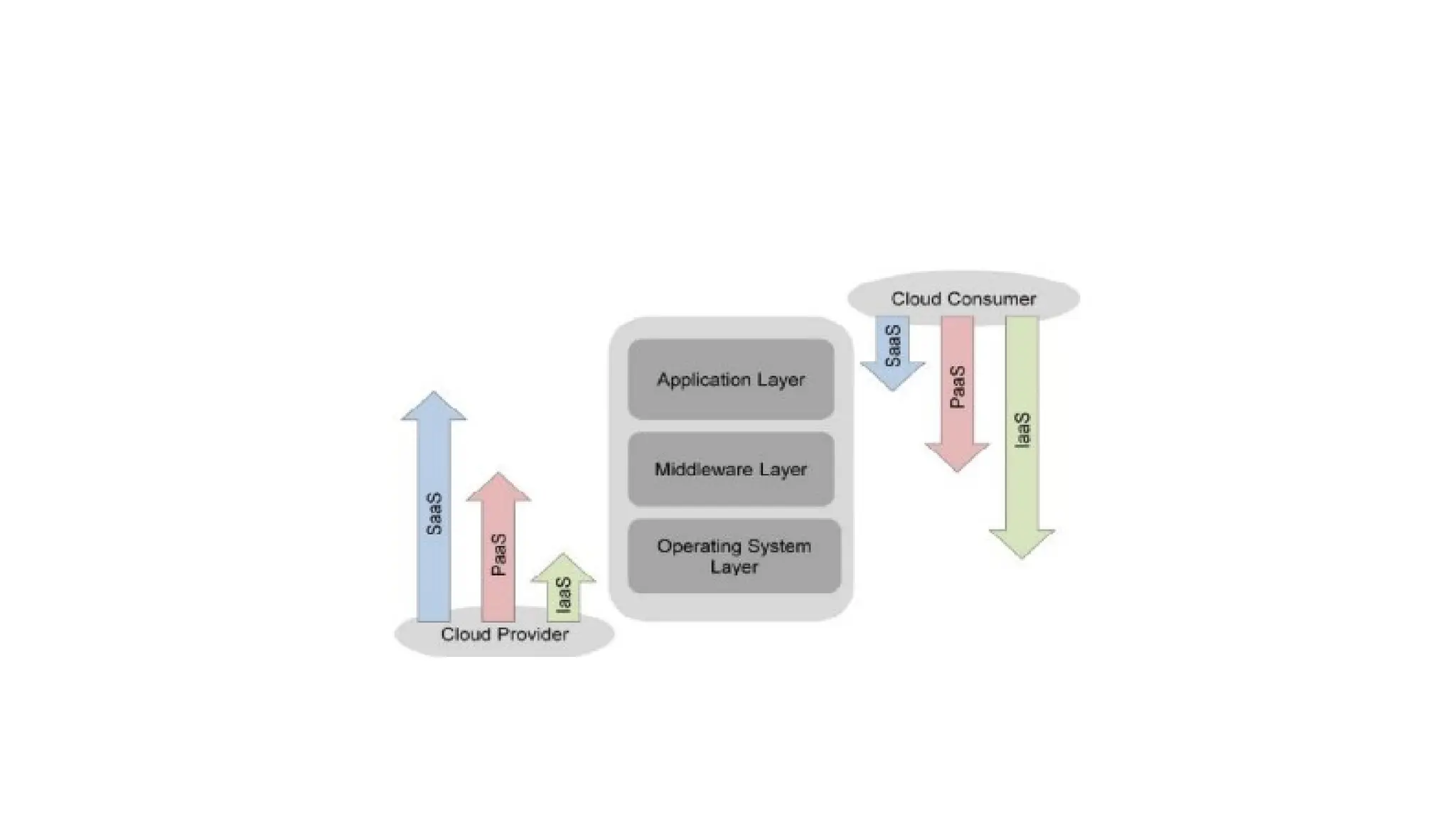
The NIST Cloud Computing Reference Architecture defines cloud computing as a pay-per-use model for on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources, aiming to enhance the federal government's adoption of secure cloud services. It outlines key roles such as cloud consumers, providers, brokers, carriers, and auditors, detailing how each interacts and operates within the cloud ecosystem. Examples illustrate scenarios involving service requests, agreements, and the intermediation of cloud services by brokers to optimize service delivery.