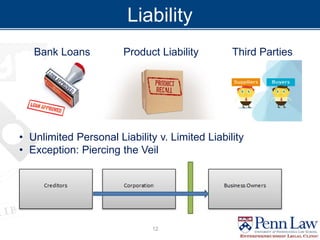
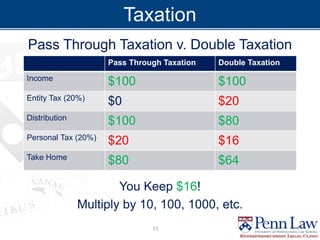
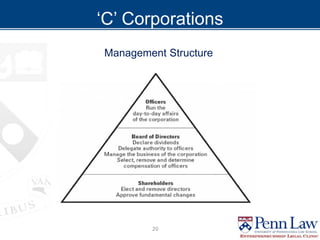
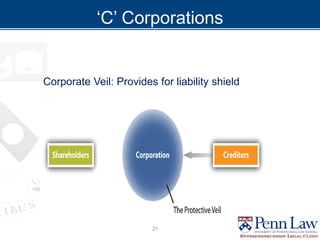
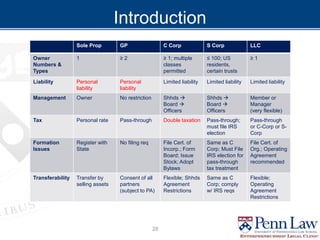
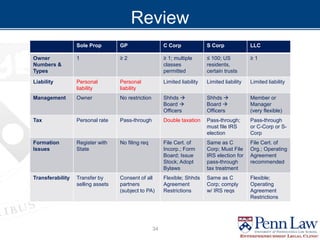
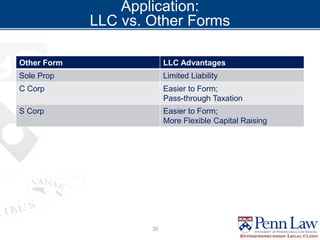
The document outlines critical considerations for business formation, including pre-formation issues, available entity types such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations, and their respective advantages and disadvantages. It discusses the implications of business size, ownership structure, liability, taxation, and administrative requirements. Additionally, real-world case studies are presented to illustrate the decision-making process in choosing the appropriate business entity.