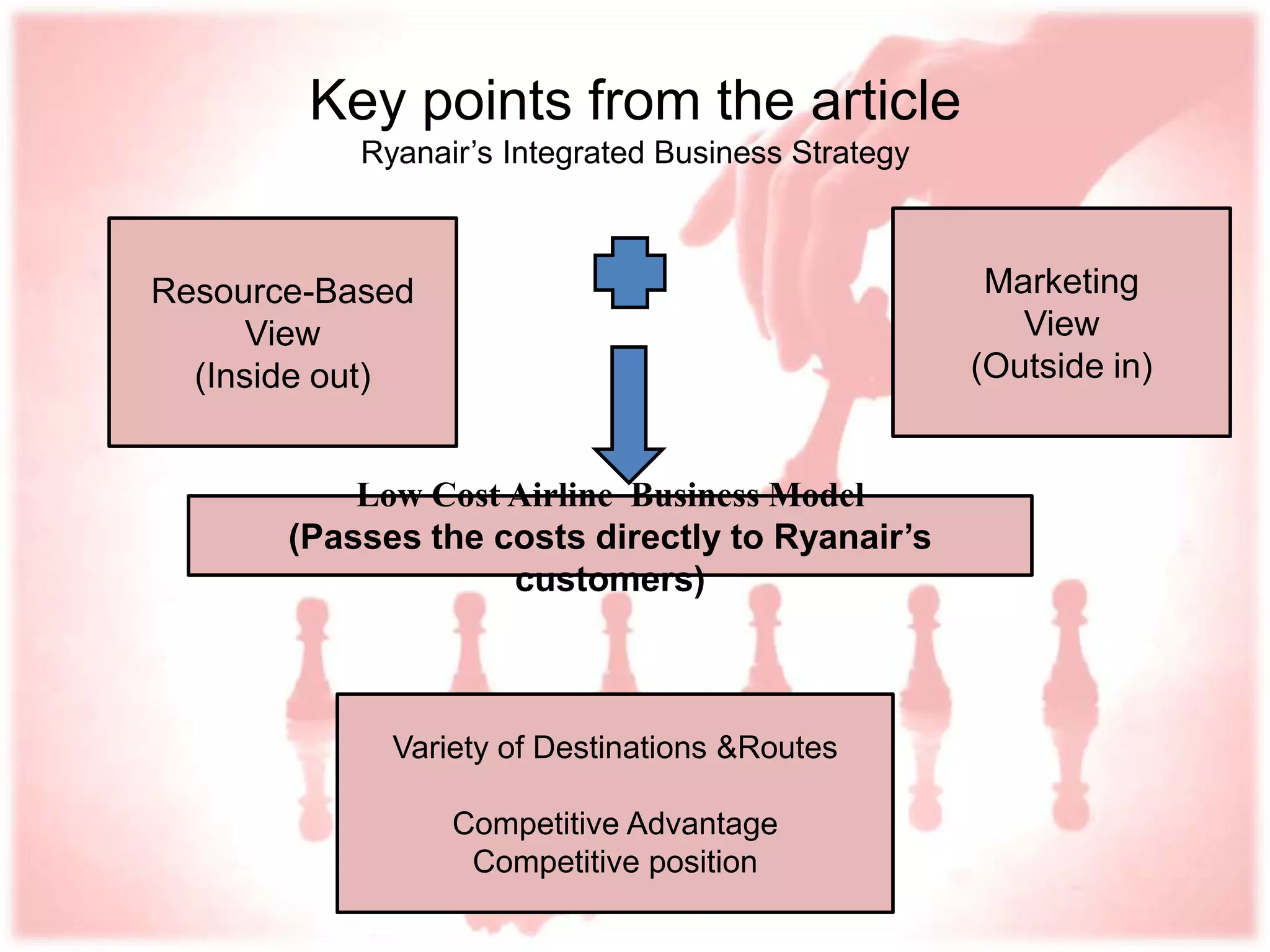
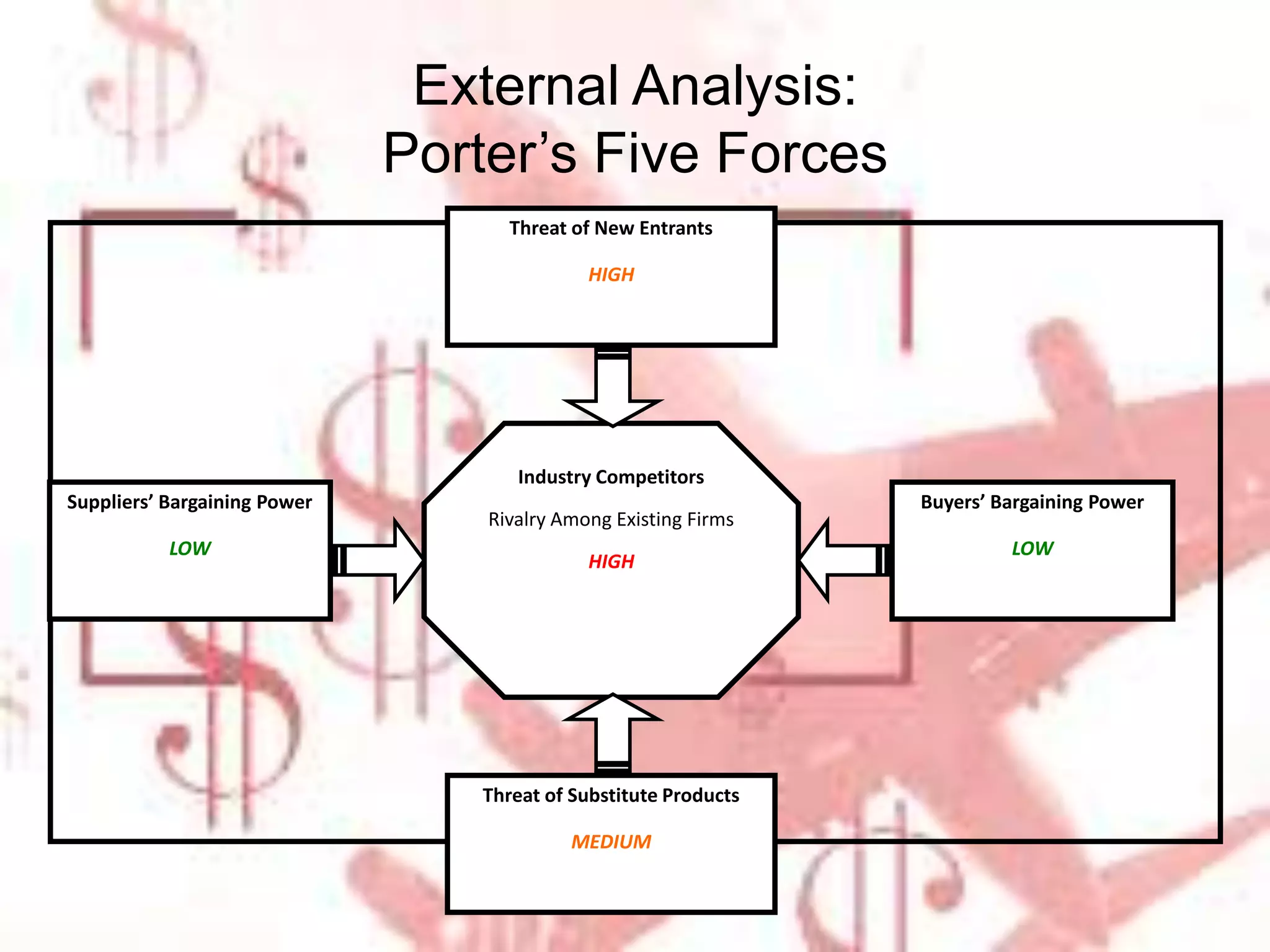
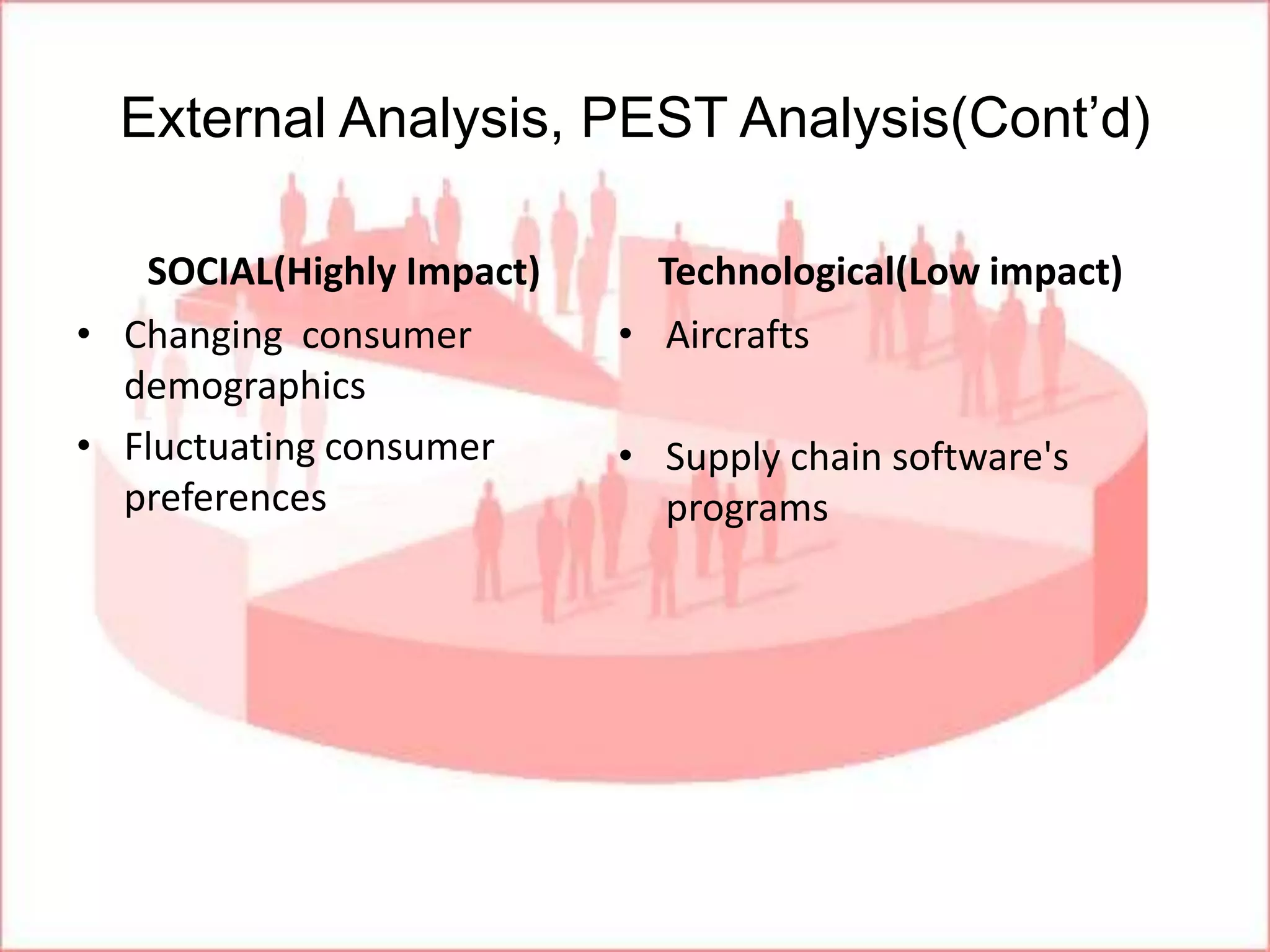
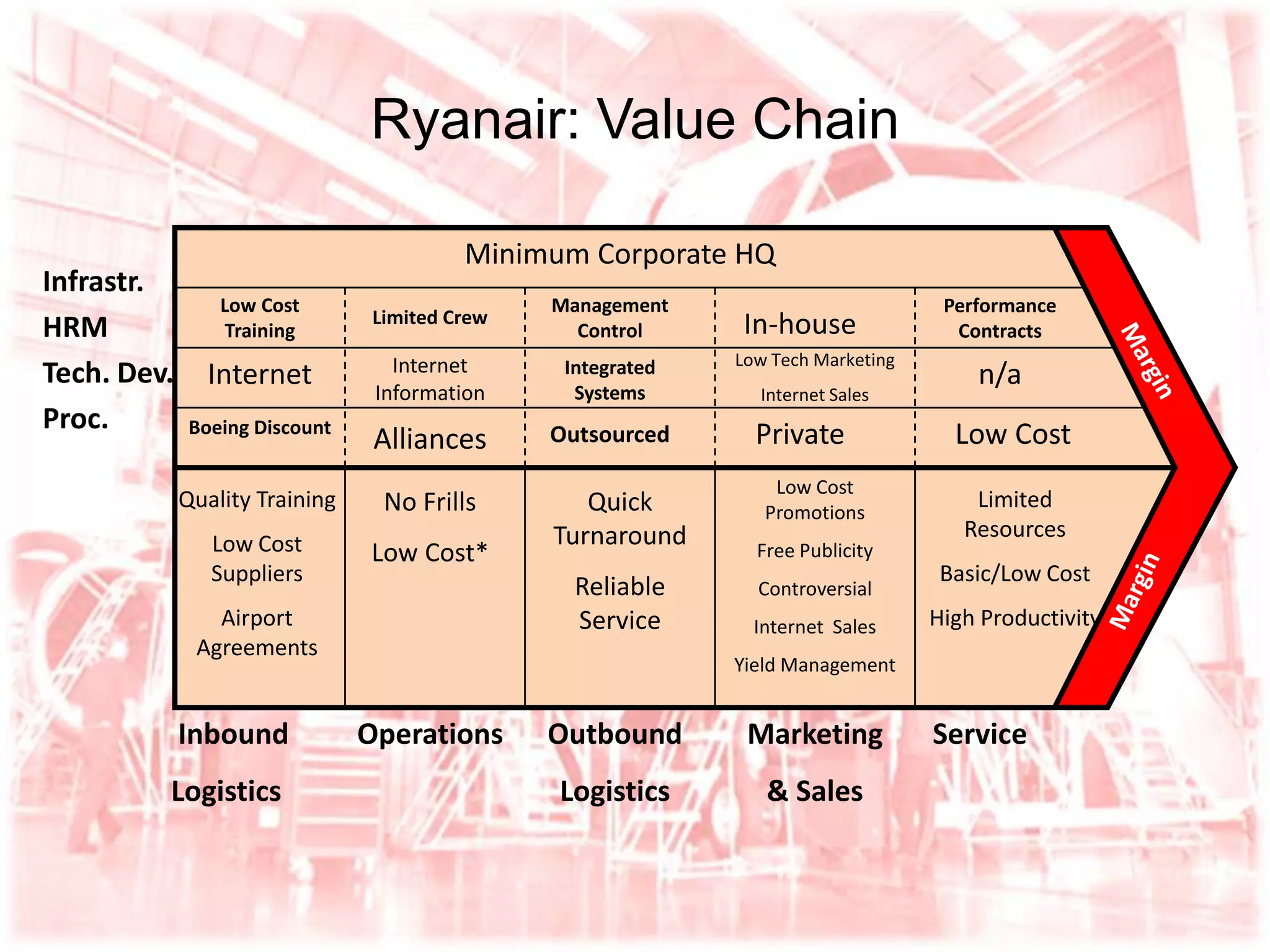
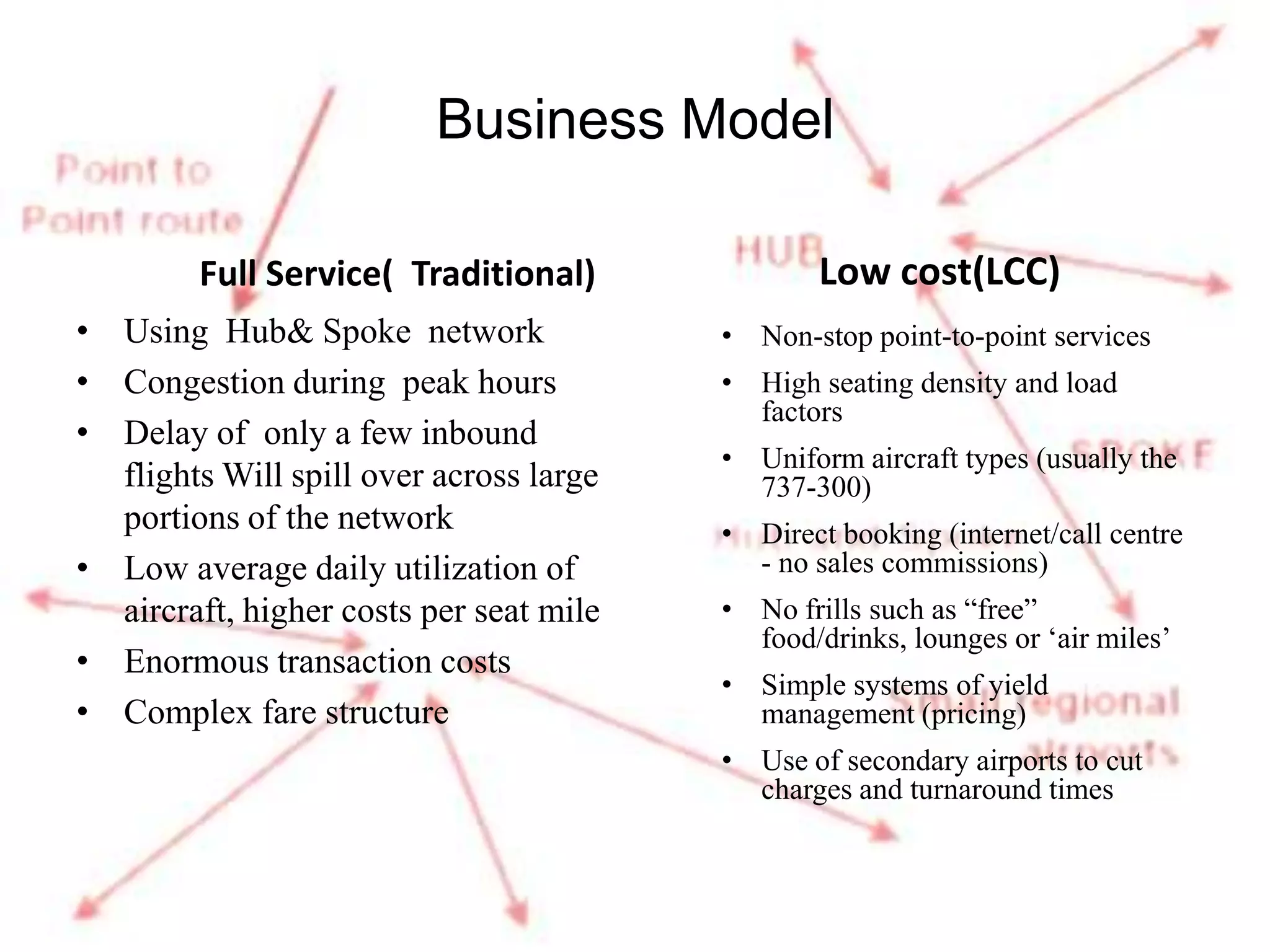
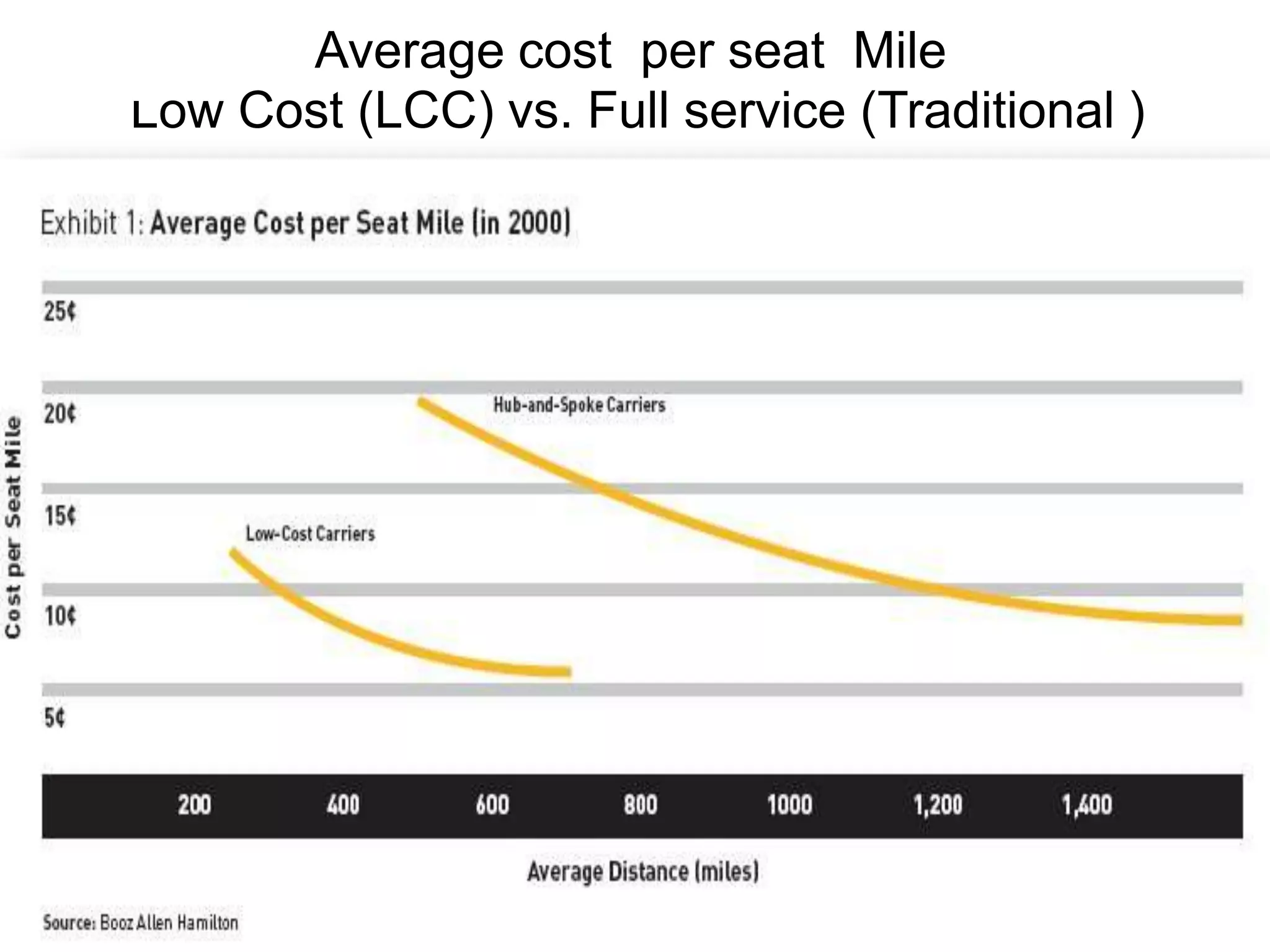
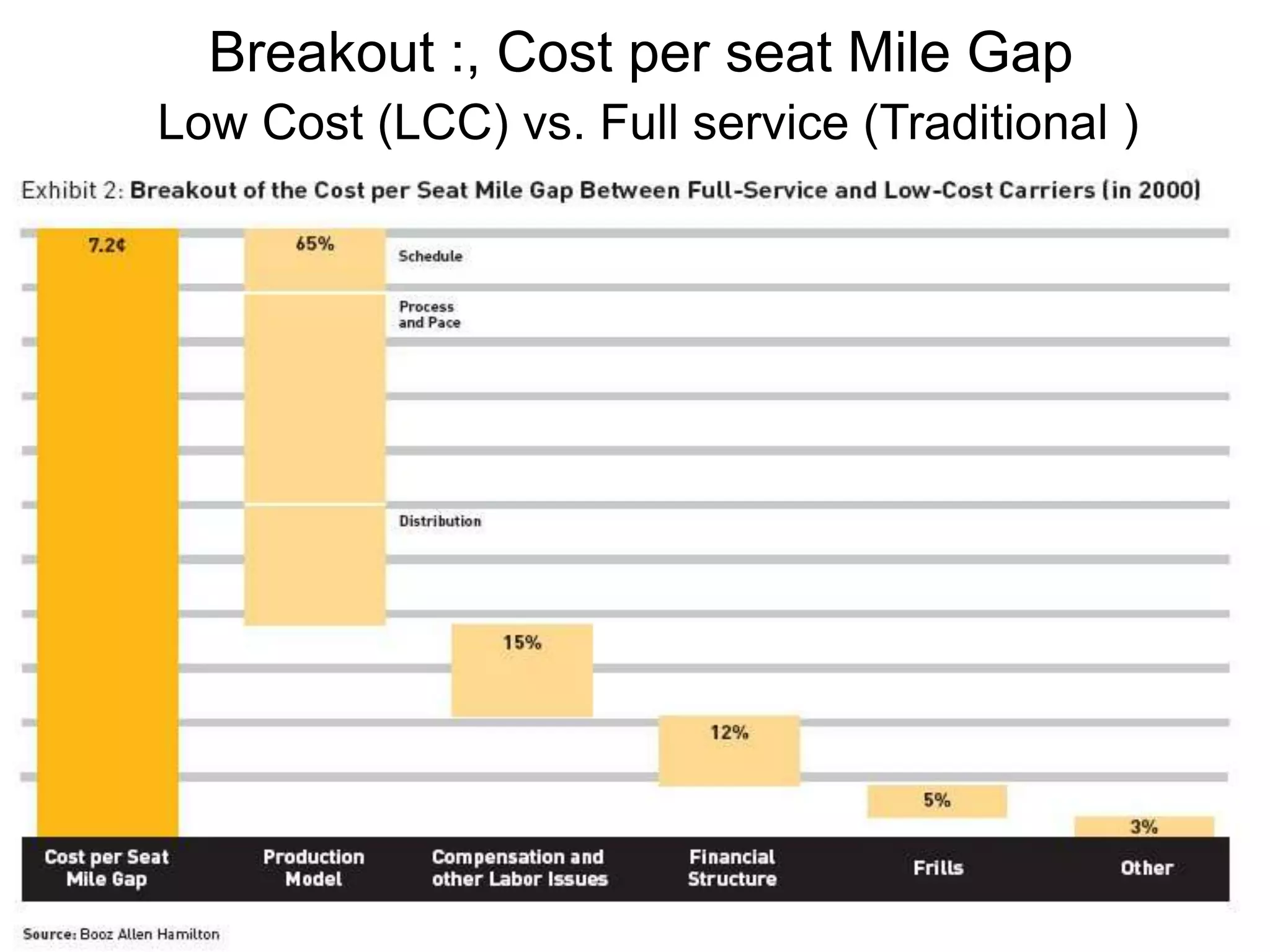
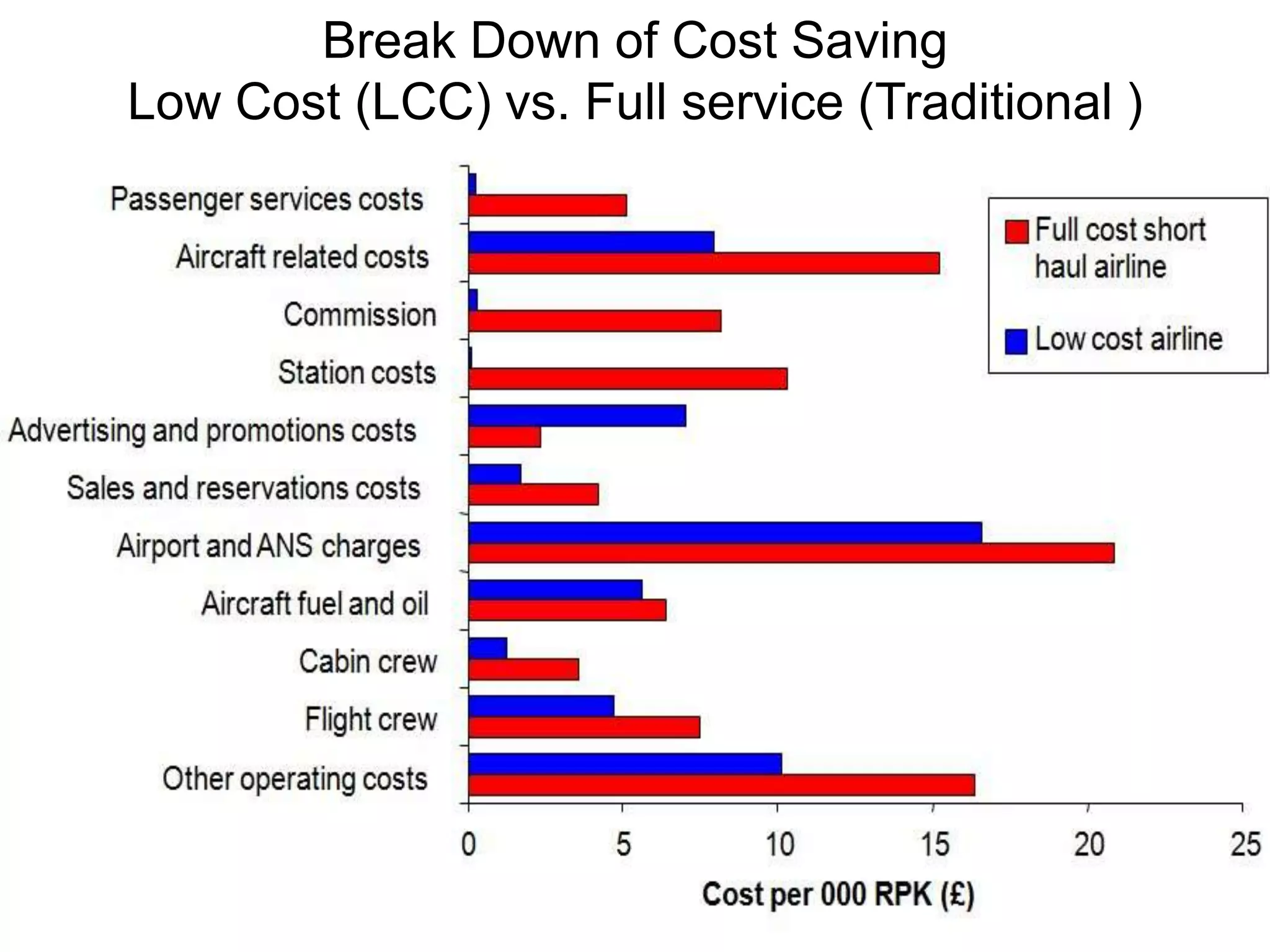
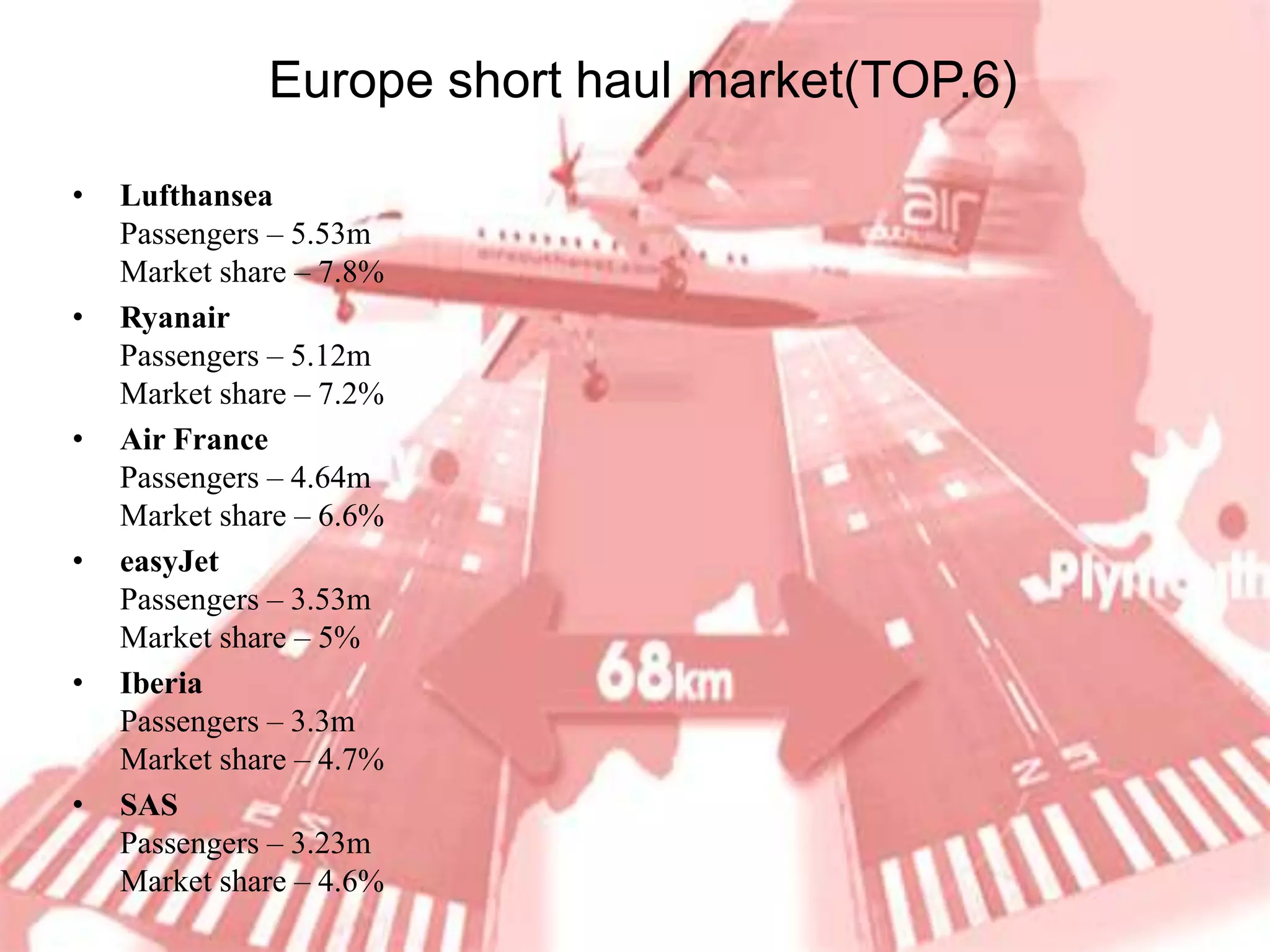
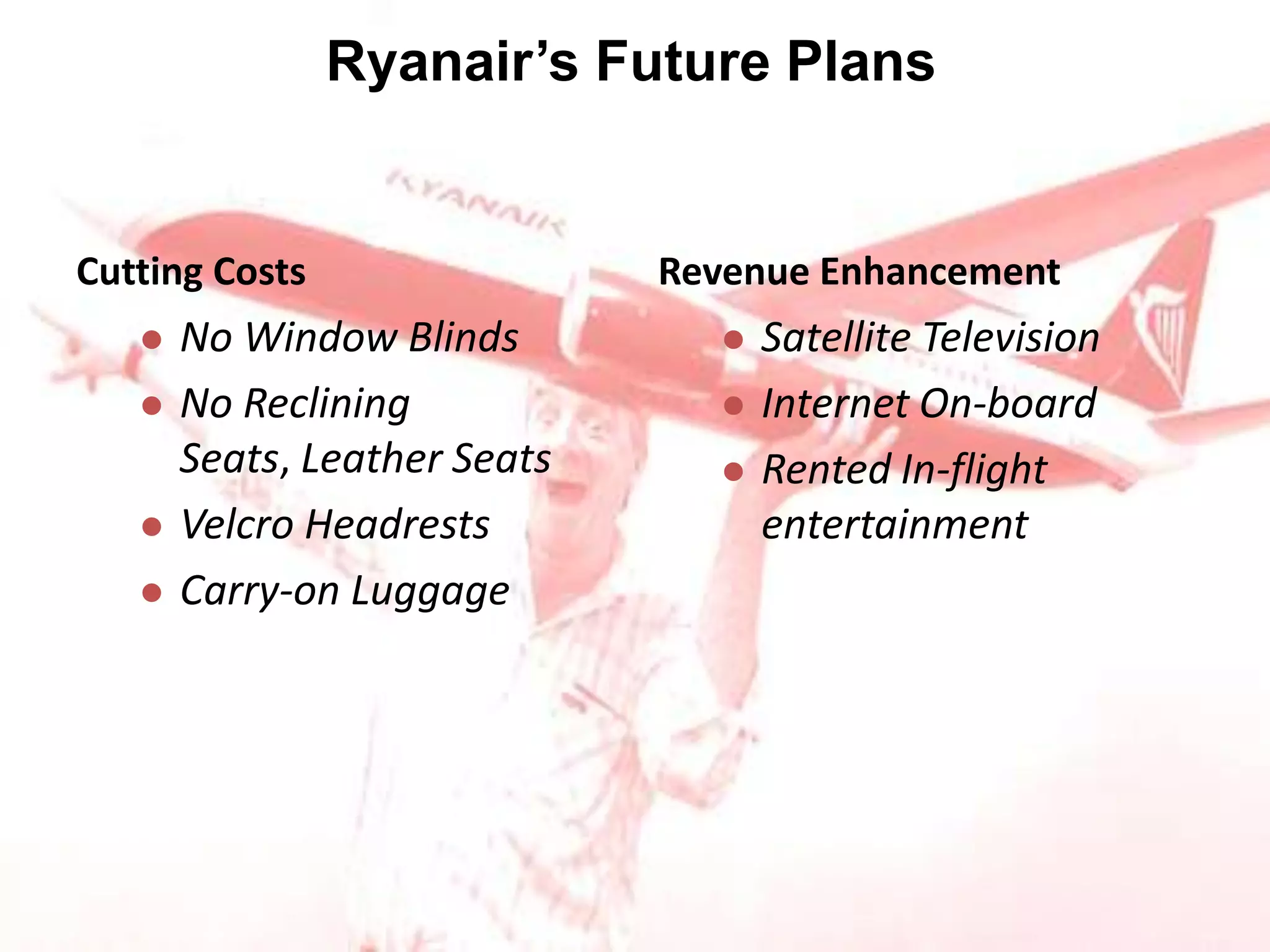
Ryanair has grown rapidly since the 1990s by pioneering the European low-cost carrier business model. It focuses on lowering costs through measures like direct online booking, point-to-point routes, secondary airports, and eliminating extras. This allows Ryanair to offer low fares that have driven huge passenger growth. Currently the largest European carrier, Ryanair aims to further cut costs and find new revenue streams like in-flight entertainment to maintain its low-cost advantage.